|
Tragulina
Tragulina (also known as Traguliformes) is an infraorder of even-toed ungulates. Only the chevrotains survive to the present, including the genera ''Tragulus'' (the mouse deer) and ''Hyemoschus'', all within the family Tragulidae. Taxonomy and Classification Tragulina is an infraorder within the larger suborder Ruminantia, and is the sister clade to the infraorder Pecora. Tragulina contains one extant (living) family, Tragulidae, as well as several extinct families, although the extinct members currently classified as within Tragulina causes it to be considered paraphyletic. Tragulina's placement within Artiodactyla can be represented in the following cladogram:(see e.g. Fig S10) The following is the taxonomy of the group Tragulina. *Infrarorder TRAGULINA **† Praetragulidae ***'' Praetragulus'' ***'' Parvitragulus'' ***'' Simimeryx'' **† Archaeomerycidae ***'' Archaeomeryx'' ***'' Miomeryx'' ***'' Paukkaungmeryx'' **†Gelocidae ***'' Phaneromeryx'' ***'' Paragelocus' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pecora
Pecora is an infraorder of even-toed hoofed mammals with ruminant digestion. Most members of Pecora have cranial appendages projecting from their frontal bones; only two extant genera lack them, ''Hydropotes'' and ''Moschus''. The name “Pecora” comes from the Latin word ''pecus'', which means “horned livestock”.Bubenik, A. Epigenetical, Morphological, Physiological, and Behavioral Aspects of Evolution of Horns, Pronghorns, and Antlers. in ''Horns, Pronghorns, and Antlers''. G. Bubenik and A. Bubenik eds. Springer-Verlag. New York. 1990 Although most pecorans have cranial appendages, only some of these are properly called “horns”, and many scientists agree that these appendages did not arise from a common ancestor, but instead evolved independently on at least two occasions.Janis, C., K. Scott. The Interrelationships of Higher Ruminant Families with Special Emphasis on the Members of the Cervoidea. ''American Museum Novitates''. 2893: 1-85. 1987. http://digitallibrary. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruminantia
Ruminants ( suborder Ruminantia) are hoofed herbivorous grazing or browsing mammals that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principally through microbial actions. The process, which takes place in the front part of the digestive system and therefore is called foregut fermentation, typically requires the fermented ingesta (known as cud) to be regurgitated and chewed again. The process of rechewing the cud to further break down plant matter and stimulate digestion is called rumination. The word "ruminant" comes from the Latin ''ruminare'', which means "to chew over again". The roughly 200 species of ruminants include both domestic and wild species. Ruminating mammals include cattle, all domesticated and wild bovines, goats, sheep, giraffes, deer, gazelles, and antelopes.Fowler, M.E. (2010).Medicine and Surgery of Camelids, Ames, Iowa: Wiley-Blackwell. Chapter 1 General Biology and Evolution addresses the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Even-toed Ungulate
The even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla , ) are ungulates—hoofed animals—which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes: the third and fourth. The other three toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or pointing posteriorly. By contrast, odd-toed ungulates bear weight on an odd number of the five toes. Another difference between the two is that many other even-toed ungulates (with the exception of Suina) digest plant cellulose in one or more stomach chambers rather than in their intestine as the odd-toed ungulates do. Cetaceans (whales, dolphins, and porpoises) evolved from even-toed ungulates, and are therefore often classified under the same taxonomic branch because a species cannot outgrow its evolutionary ancestry; some modern taxonomists combine the two under the name Cetartiodactyla , while others opt to include cetaceans in the already-existing Artiodactyla. The roughly 270 land-based even-toed ungulate species include pigs, peccaries, hippo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chevrotain
Chevrotains, or mouse-deer, are small even-toed ungulates that make up the family Tragulidae, the only extant members of the infraorder Tragulina. The 10 extant species are placed in three genera, but several species also are known only from fossils. The extant species are found in forests in South and Southeast Asia, with a single species, the water chevrotain, in the rainforests of Central and West Africa. They are solitary or live in pairs, and feed almost exclusively on plant material. Chevrotains are the smallest hoofed mammals in the world. The Asian species weigh between , while the African chevrotain is considerably larger at . With an average length of and an average height of , the Java mouse-deer is the smallest extant (living) ungulate or hoofed mammal, as well as the smallest extant even-toed ungulate. In November 2019, conservation scientists announced that they had photographed silver-backed chevrotains (''Tragulus versicolor'') in a Vietnamese for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chevrotain
Chevrotains, or mouse-deer, are small even-toed ungulates that make up the family Tragulidae, the only extant members of the infraorder Tragulina. The 10 extant species are placed in three genera, but several species also are known only from fossils. The extant species are found in forests in South and Southeast Asia, with a single species, the water chevrotain, in the rainforests of Central and West Africa. They are solitary or live in pairs, and feed almost exclusively on plant material. Chevrotains are the smallest hoofed mammals in the world. The Asian species weigh between , while the African chevrotain is considerably larger at . With an average length of and an average height of , the Java mouse-deer is the smallest extant (living) ungulate or hoofed mammal, as well as the smallest extant even-toed ungulate. In November 2019, conservation scientists announced that they had photographed silver-backed chevrotains (''Tragulus versicolor'') in a Vietnamese for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artiodactyla
The even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla , ) are ungulates—hoofed animals—which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes: the third and fourth. The other three toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or pointing posteriorly. By contrast, odd-toed ungulates bear weight on an odd number of the five toes. Another difference between the two is that many other even-toed ungulates (with the exception of Suina) digest plant cellulose in one or more stomach chambers rather than in their intestine as the odd-toed ungulates do. Cetaceans (whales, dolphins, and porpoises) evolved from even-toed ungulates, and are therefore often classified under the same taxonomic branch because a species cannot outgrow its evolutionary ancestry; some modern taxonomists combine the two under the name Cetartiodactyla , while others opt to include cetaceans in the already-existing Artiodactyla. The roughly 270 land-based even-toed ungulate species include pigs, peccaries, hippopo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artiofabula
Artiofabula is a clade made up of the Suina and the Cetruminantia. The clade was found in molecular phylogenetic analyses and contradicted traditional relationships based on morphological analyses. Etymology The name Artiofabula was derived from Greek "artios" (meaning complete or perfect of its kind or, with respect to numbers, even), and Latin "fabula" (meaning fable). The latter referred to the clade breaking up traditional views on artiodactyl taxonomy based on morphological analyses, where camels grouped with ruminants, hippos with pigs, and whales were unrelated. Phylogeny Phylogenetic analyses of artiodactyls revealed the following relationships:(see e.g. Fig S10) Classification *Order Artiodactyla (even-toed ungulates) **Suborder Tylopoda (camelids) **Artiofabula (ruminants, pigs, peccaries, whales, and dolphins) ***Suborder Suina (pigs and peccaries) **** Family Suidae 19 species (pigs) **** Family Tayassuidae 4 species (peccaries) *** Cetruminantia (ruminants, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tylopoda
Tylopoda (meaning "calloused foot") is a suborder of terrestrial herbivorous even-toed ungulates belonging to the order Artiodactyla. They are found in the wild in their native ranges of South America and Asia, while Australian feral camels are introduced. The group has a long fossil history in North America and Eurasia. Tylopoda appeared during the Eocene around 50 million years ago. Tylopoda has only one extant family, Camelidae, which includes camels, llamas, guanacos, alpacas and vicuñas. This group was much more diverse in the past, containing a number of extinct families in addition to the ancestors of living camelids (see below). Tylopods are not ruminants. Taxonomy and systematics Tylopoda was named by Illiger (1811) and considered monophyletic by Matthew (1908). It was treated as an unranked clade by Matthew (1908) and as a suborder by Carroll (1988), Ursing et al. (2000) and Whistler and Webb (2005). It was assigned to Ruminantia by Matthew (1908); to Artiodactyla b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladogram Of Cetacea Within Artiodactyla (Camelus Bactrianus)
A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to descendants, nor does it show how much they have changed, so many differing evolutionary trees can be consistent with the same cladogram. A cladogram uses lines that branch off in different directions ending at a clade, a group of organisms with a last common ancestor. There are many shapes of cladograms but they all have lines that branch off from other lines. The lines can be traced back to where they branch off. These branching off points represent a hypothetical ancestor (not an actual entity) which can be inferred to exhibit the traits shared among the terminal taxa above it. This hypothetical ancestor might then provide clues about the order of evolution of various features, adaptation, and other evolutionary narratives about ances ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cetruminantia
The Cetruminantia are a clade made up of the Cetancodontamorpha (or Whippomorpha) and their closest living relatives, the Ruminantia. Cetruminantia's placement within Artiodactyla can be represented in the following cladogram: (see fig S10) Classification *Order Artiodactyla (even-toed ungulates) **Tylopoda (camelids) **Artiofabula (ruminants, pigs, peccaries, whales, and dolphins) ***Suina (pigs and peccaries) ***Cetruminantia (ruminants, whales, and dolphins) ****Suborder Ruminantia (antelope, buffalo, cattle, goats, sheep, deer, giraffes, and chevrotains) *****Family Antilocapridae (pronghorn) *****Family Bovidae, 135 species (antelope, bison, buffalo, cattle, goats, and sheep) *****Family Cervidae, 55~94 species (deer, elk, and moose) *****Family Giraffidae, 2 species (giraffes, okapis) *****Family Moschidae, 4~7 species (musk deer) *****Family Tragulidae, 6~10 species (chevrotains, or mouse deer) ****Suborder Whippomorpha (aquatic or semi-a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
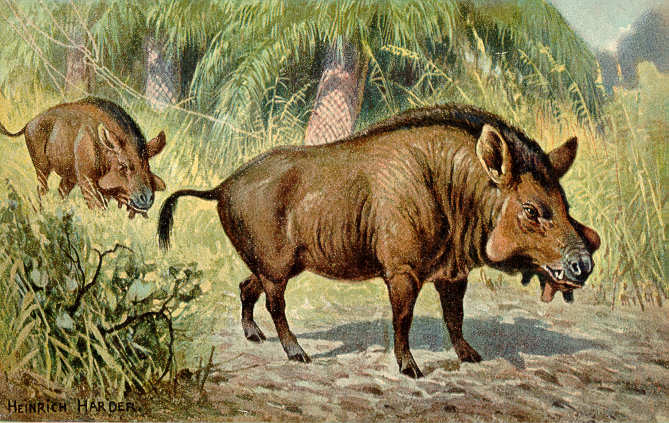
Suina
Suina (also known as Suiformes) is a suborder of omnivorous, non-ruminant artiodactyl mammals that includes the domestic pig and peccaries. A member of this clade is known as a suine. Suina includes the family Suidae, termed suids, known in English as pigs or swine, as well as the family Tayassuidae, termed tayassuids or peccaries. Suines are largely native to Africa, South America, and Southeast Asia, with the exception of the wild boar, which is additionally native to Europe and Asia and introduced to North America and Australasia, including widespread use in farming of the domestic pig subspecies. Suines range in size from the 55 cm (22 in) long pygmy hog to the 210 cm (83 in) long giant forest hog, and are primarily found in forest, shrubland, and grassland biomes, though some can be found in deserts, wetlands, or coastal regions. Most species do not have population estimates, though approximately two billion domestic pigs are used in farming, while sever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)