|
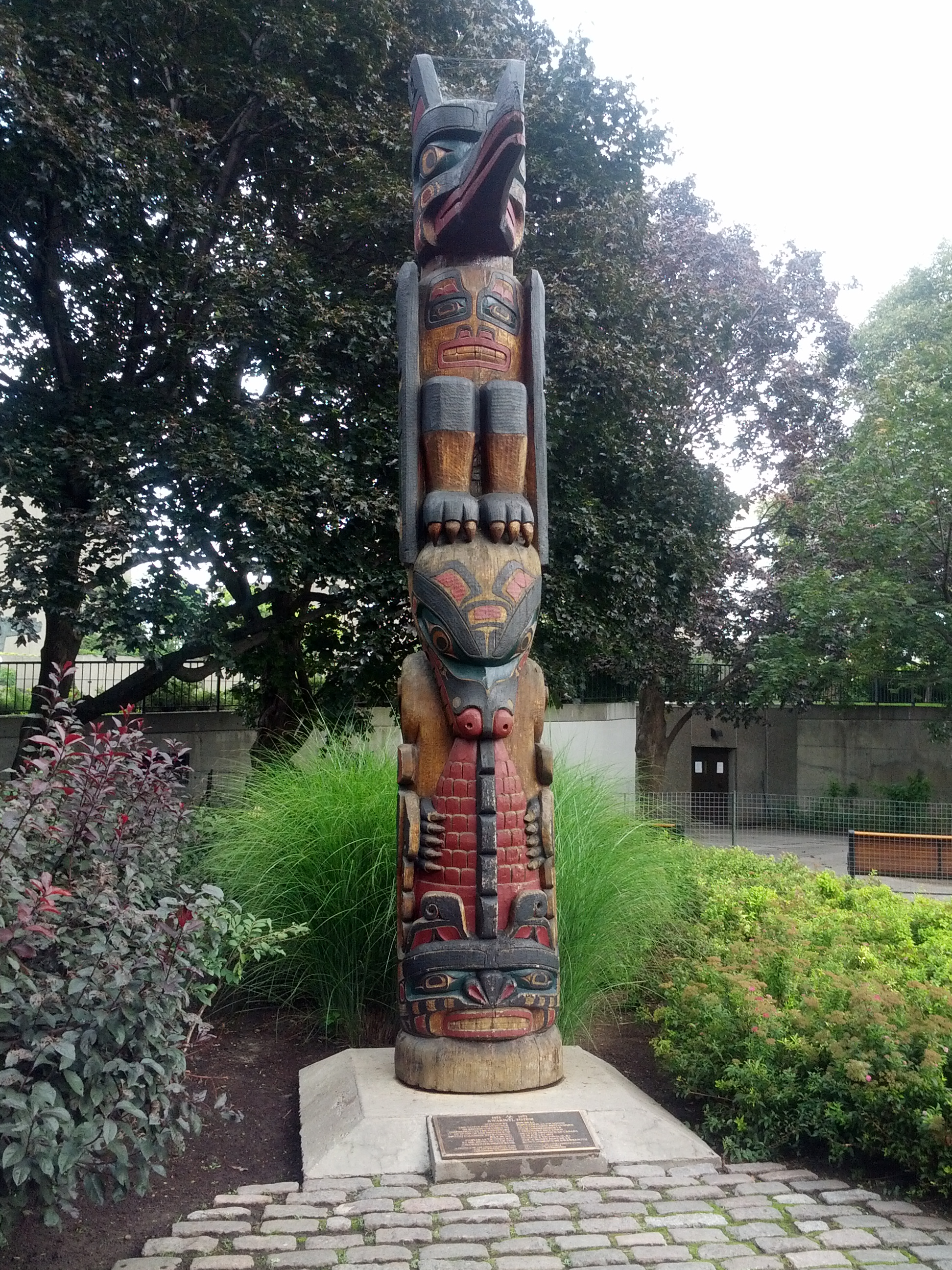
Traditional African Masks
Traditional African masks play an important role in ceremonies, rituals, and masquerades across West Africa, West, Central Africa, Central, and Southern Africa. Ceremonies in which masks are worn include Harvest festival, harvest celebrations, Funeral, funerals, Rite of passage, rites of passage, Wedding, weddings, and Coronations in Africa, coronations. In some societies, masks and masquerades are also used to settle disputes and communal conflicts. For example, members of the masquerade cult and Uma-Ada fraternity facilitate social justice and reconciliation processes among Igbo people, Igbo communities in Eastern Nigeria through masquerade performances. Mende people, Mende and Vai people, Vai women of the Sande society in Sierra Leone don the Sowei mask during rites of passage, specifically initiation ceremonies for young girls. The Plank Mask (Nwantantay) among the Bobo people, Bobo, Bwa people, Bwa, and Mossi people, Mossi people of Burkina Faso makes an appearance during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African Countries Where Masks Are Used
African or Africans may refer to: * Anything from or pertaining to the continent of Africa: ** People who are native to Africa, descendants of natives of Africa, or individuals who trace their ancestry to indigenous inhabitants of Africa *** Ethnic groups of Africa *** Demographics of Africa *** African diaspora ** African, an adjective referring to something of, from, or related to the African Union ** Citizenship of the African Union ** Demographics of the African Union ** Africanfuturism ** African art ** *** African jazz (other) ** African cuisine ** African culture ** African languages ** African music ** African Union ** African lion, a lion population in Africa Books and radio * ''The African'' (essay), a story by French author J. M. G. Le Clézio * ''The African'' (Conton novel), a novel by William Farquhar Conton * ''The African'' (Courlander novel), a novel by Harold Courlander * ''The Africans'' (radio program) Music * "African", a song by Peter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bobo People
The Bobo are a Mande ethnic group living primarily in Burkina Faso, with some living north in Mali. Bobo is also a shortened name of the second-largest city in Burkina Faso, Bobo-Dioulasso. Background In much of the literature on African art, the group that lives in the area of Bobo-Dioulasso is called Bobo-Fing, literally "black Bobo". These people call themselves Bobo and speak the Bobo language, a Mande language. The Bambara people also call another ethnic group "Bobo", the Bobo-Oule/Wule, more precisely called the Bwa. While the Bwa (Bobo-Oule) are a Gur people, speaking Gur languages (the Bwa languages), the true Bobo (Bobo Madare, Bobo Fing) are a Mande people. Demographics The Bobo number about 110,000 people, with the great majority in Burkina Faso. The major Bobo community in the south is Bobo-Dioulasso, the second-largest city of Burkina Faso and the old French colonial capital. Further north are large towns, including and Kouka, with Boura in the extreme north i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baoulé People
The Baule or Baoulé ( Baule: ''Baule'' a.u.le french: baoulé awle are an Akan people and one of the largest ethnicities in Côte d'Ivoire who historically migrated from what is today Ghana. The Baoulé are traditionally farmers who live in the centre of Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast), in a triangle shaped region (the Baoule “V”) between the rivers Bandama and N'Zi. This area broadly encompasses the regions around the cities of Bouaké and Yamoussoukro. The Baoulé have come to play a relatively important role in the recent history of Côte d'Ivoire: the State's first President, Félix Houphouët-Boigny, was a Baoulé; additionally, since the Ivorian cocoa boom of the 1960-1970s, the Baoulé have also become one of the most widespread ethnicity throughout the country, especially in the Southern forests (the "Low Coast") where they are amongst the most numerous planters of cocoa, rubber, and coffee and sometimes seem to outnumber the local native ethnic groups. Leisure O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lebe (Dogon)
The Lebe or Lewe ( fr. Lébé) is a Dogon religious, secret institution and primordial ancestor, who arose from a serpent. According to Dogon cosmogony, Lebe is the reincarnation of the first Dogon ancestor who, resurrected in the form of a snake, guided the Dogons from the Mandé to the cliff of Bandiagara where they are found today. This Lebe sect is one of the important facets of Dogon religion, based on ancestor veneration as well as the worship of the creator god Amma. This practice of traditional African religion takes four forms: #the veneration of Lebe, #the veneration of Binou, #the veneration of souls, and #the "Society of the Masks" (the Awa society) Dogon religion posits that it was through Amma's powers which brought forth the creation of the universe, matter, and the biological processes of reproduction. Asante, Molefi Kete; Mazama, Ama; ''Encyclopedia of African Religion, Volume 1'', SAGE (2009), pp. 40–41, (retrieved March 16, 2020/ref> With a complex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binou (Dogon Religion)
The Binou (or Binou cult) is a Dogon totemic, religious order and secret ceremonial practice which venerates the immortal ancestors. It can also mean a water serpent or protector of a family or clan in Dogon.Bouju, Jacky, ''Graine de l'homme, enfant du mil'', Société d'éthnologie (1984), pp. 33–4, 218,/ref> It is one of the four tenets of Dogon religion—an African spirituality among the Dogon people of Mali. Although the Dogons' "Society of the Masks" (the Awa Society) is more well known, due in part to Dogon mask–dance culture which attracts huge tourism, it is only one aspect of Dogon religion, which apart from the worship of the Creator God Amma, a rather distant and abstract deity in the Dogon world-view, is above all made up of ancestor veneration (the four aspects of that practice). The Binou serves as one of the four aspects of Dogon religion's ancestor veneration. Other than the Binou and the worship of Amma, the other three aspects of the religion includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Awa Society
Awa (in Dogon), also known as the Awa Society, the Society of Masks, is an African mask and initiatory society of the Dogon people of Mali which is made up of circumcised men, and whose role is both ritual and political within Dogon society. The Awa Society takes an important role in Dogon religious affairs, and regularly preside over funereally rites and the ''dama'' ceremony—a ritual ceremony that marks the end of bereavement in Dogon country ( fr ).Ezra, Kate, ''Art of the Dogon: Selections from the Lester Wunderman Collection'', Metropolitan Museum of Art (1988), pp. 23–25, (retrieved March 3, 2020/ref> This Society is one of the important aspect of Dogon religious life—which is primarily based on the worship of the single Omnipotence, omnipotent, omniscient and omnipresent Creator God Amma and the veneration of the ancestors. Although it is only one aspect of Dogon's religious sects, it is perhaps more well known than the others partly due to Dogon mask–dance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mali
Mali (; ), officially the Republic of Mali,, , ff, 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞥆𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 𞤃𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭, Renndaandi Maali, italics=no, ar, جمهورية مالي, Jumhūriyyāt Mālī is a landlocked country in West Africa. Mali is the eighth-largest country in Africa, with an area of over . The population of Mali is million. 67% of its population was estimated to be under the age of 25 in 2017. Its capital and largest city is Bamako. The sovereign state of Mali consists of eight regions and its borders on the north reach deep into the middle of the Sahara Desert. The country's southern part is in the Sudanian savanna, where the majority of inhabitants live, and both the Niger and Senegal rivers pass through. The country's economy centres on agriculture and mining. One of Mali's most prominent natural resources is gold, and the country is the third largest producer of gold on the African continent. It also exports salt. Present-day Mali was once part of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dogon People
The Dogon are an ethnic group indigenous to the central plateau region of Mali, in West Africa, south of the Niger River, Niger bend, near the city of Bandiagara, and in Burkina Faso. The population numbers between 400,000 and 800,000. They speak the Dogon languages, which are considered to constitute an independent branch of the Niger–Congo language family, meaning that they are not closely related to any other languages. The Dogon are best known for Dogon religion, their religious traditions, their mask dances, wooden sculpture, and their architecture. Since the twentieth century, there have been significant changes in the social organisation, material culture and beliefs of the Dogon, in part because Dogon country is one of Mali's major tourist attractions. Geography and history The principal Dogon area is bisected by the Bandiagara Escarpment, a sandstone cliff of up to high, stretching about 150 km (90 miles). To the southeast of the cliff, the sandy Séno-Gond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Totem
A totem (from oj, ᑑᑌᒼ, italics=no or ''doodem'') is a spirit being, sacred object, or symbol that serves as an emblem of a group of people, such as a family, clan, lineage, or tribe, such as in the Anishinaabe clan system. While ''the word'' totem itself is an anglicisation of the Ojibwe term (and both the word and beliefs associated with it are part of the Ojibwe language and culture), belief in tutelary spirits and deities is not limited to the Ojibwe people. Similar concepts, under differing names and with variations in beliefs and practices, may be found in a number of cultures worldwide. The term has also been adopted, and at times redefined, by anthropologists and philosophers of different cultures. Contemporary neoshamanic, New Age, and mythopoetic men's movements not otherwise involved in the practice of a traditional, tribal religion have been known to use "totem" terminology for the personal identification with a tutelary spirit or spirit guide. However, this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Witchcraft
Witchcraft traditionally means the use of magic or supernatural powers to harm others. A practitioner is a witch. In medieval and early modern Europe, where the term originated, accused witches were usually women who were believed to have used malevolent magic against their own community, and often to have communed with evil beings. It was thought witchcraft could be thwarted by protective magic or counter-magic, which could be provided by cunning folk or folk healers. Suspected witches were also intimidated, banished, attacked or killed. Often they would be formally prosecuted and punished, if found guilty or simply believed to be guilty. European witch-hunts and witch trials in the early modern period led to tens of thousands of executions. In some regions, many of those accused of witchcraft were folk healers or midwives. European belief in witchcraft gradually dwindled during and after the Age of Enlightenment. Contemporary cultures that believe in magic and the superna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bantu Peoples
The Bantu peoples, or Bantu, are an ethnolinguistic grouping of approximately 400 distinct ethnic groups who speak Bantu languages. They are native to 24 countries spread over a vast area from Central Africa to Southeast Africa and into Southern Africa. There are several hundred Bantu languages. Depending on the definition of "language" or "dialect", it is estimated that there are between 440 and 680 distinct languages. The total number of speakers is in the hundreds of millions, ranging at roughly 350 million in the mid-2010s (roughly 30% of the population of Africa, or roughly 5% of the total world population). About 60 million speakers (2015), divided into some 200 ethnic or tribal groups, are found in the Democratic Republic of the Congo alone. The larger of the individual Bantu groups have populations of several million, e.g. the people of Rwanda and Burundi (25 million), the Bagandapeople of Uganda (10 million as of 2019), the Shona of Zimbabwe (15 million ), the Zulu of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |