|
Trade Barrier
Trade barriers are government-induced restrictions on international trade. According to the theory of comparative advantage, trade barriers are detrimental to the world economy and decrease overall economic efficiency. Most trade barriers work on the same principle: the imposition of some sort of cost (money, time, bureaucracy, quota) on trade that raises the price or availability of the traded products. If two or more nations repeatedly use trade barriers against each other, then a trade war results. Barriers take the form of tariffs (which impose a financial burden on imports) and non-tariff barriers to trade (which uses other overt and covert means to restrict imports and occasionally exports). In theory, free trade involves the removal of all such barriers, except perhaps those considered necessary for health or national security. In practice, however, even those countries promoting free trade heavily subsidize certain industries, such as agriculture and steel. Overview ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Trade
International trade is the exchange of capital, goods, and services across international borders or territories because there is a need or want of goods or services. (see: World economy) In most countries, such trade represents a significant share of gross domestic product (GDP). While international trade has existed throughout history (for example Uttarapatha, Silk Road, Amber Road, scramble for Africa, Atlantic slave trade, salt roads), its economic, social, and political importance has been on the rise in recent centuries. Carrying out trade at an international level is a complex process when compared to domestic trade. When trade takes place between two or more states factors like currency, government policies, economy, judicial system, laws, and markets influence trade. To ease and justify the process of trade between countries of different economic standing in the modern era, some international economic organizations were formed, such as the World Trade Organizati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Export Control
Export control is legislation that regulates the export of goods, software and technology. Some items could potentially be useful for purposes that are contrary to the interest of the exporting country. These items are considered to be ''controlled''. The export of controlled item is regulated to restrict the harmful use of those items. Many governments implement export controls. Typically, legislation lists and classifies the controlled items, classifies the destinations, and requires exporters to apply for a licence to a local government department. A wide range of goods have been subject to export control in different jurisdictions, including arms, goods with a military potential, cryptography, currency, and precious stones or metals. Some countries prohibit the export of uranium, endangered animals, national artefacts, and goods in short supply in the country, such as medicines. History The United States has had export controls since the American Revolution, although the mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
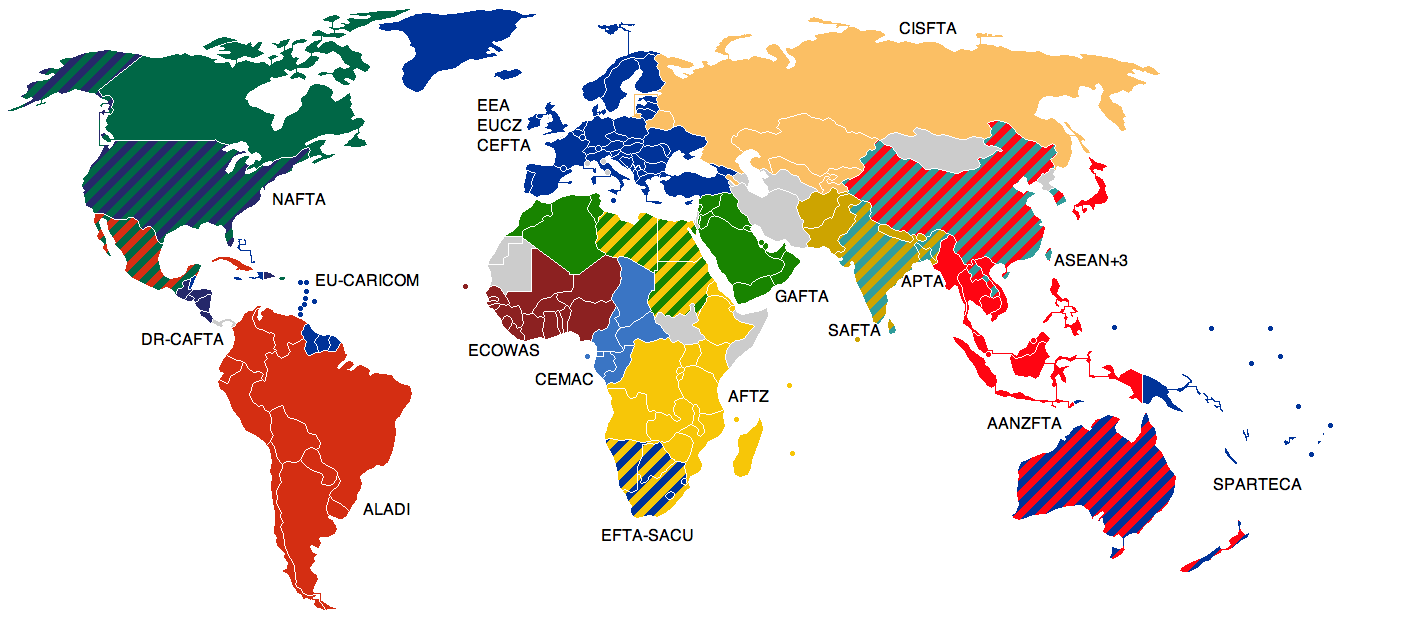
North American Free Trade Agreement
The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA ; es, Tratado de Libre Comercio de América del Norte, TLCAN; french: Accord de libre-échange nord-américain, ALÉNA) was an agreement signed by Canada, Mexico, and the United States that created a trilateral trade bloc in North America. The agreement came into force on January 1, 1994, and superseded the 1988 Canada–United States Free Trade Agreement between the United States and Canada. The NAFTA trade bloc formed one of the largest trade blocs in the world by gross domestic product. The impetus for a North American free trade zone began with U.S. president Ronald Reagan, who made the idea part of his 1980 presidential campaign. After the signing of the Canada–United States Free Trade Agreement in 1988, the administrations of U.S. president George H. W. Bush, Mexican President Carlos Salinas de Gortari, and Canadian prime minister Brian Mulroney agreed to negotiate what became NAFTA. Each submitted the agreement for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Trade Agreement
A free-trade agreement (FTA) or treaty is an agreement according to international law to form a free-trade area between the cooperating states. There are two types of trade agreements: bilateral and multilateral. Bilateral trade agreements occur when two countries agree to loosen trade restrictions between the two of them, generally to expand business opportunities. Multilateral trade agreements are agreements among three or more countries, and are the most difficult to negotiate and agree. FTAs, a form of trade pacts, determine the tariffs and duties that countries impose on imports and exports with the goal of reducing or eliminating trade barriers, thus encouraging international trade. Such agreements usually "center on a chapter providing for preferential tariff treatment", but they also often "include clauses on trade facilitation and rule-making in areas such as investment, intellectual property, government procurement, technical standards and sanitary and phytosanitary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trade Bloc
A trade bloc is a type of intergovernmental agreement, often part of a regional intergovernmental organization, where barriers to trade (tariffs and others) are reduced or eliminated among the participating states. Trade blocs can be stand-alone agreements between several states (such as the North American Free Trade Agreement) or part of a regional organization (such as the European Union). Depending on the level of economic integration, trade blocs can be classified as preferential trading areas, free-trade areas, customs unions, common markets, or economic and monetary unions. Use Historic trading blocs include the Hanseatic League, a Northern European economic alliance between the 12th and 17th centuries, and the German Customs Union, formed on the basis of the German Confederation and subsequently the German Empire from 1871. Surges of trade bloc formation occurred in the 1960s and 1970s, as well as in the 1990s after the collapse of Communism. By 1997, more than 5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free-trade Area
A free-trade area is the region encompassing a trade bloc whose member countries have signed a free trade agreement (FTA). Such agreements involve cooperation between at least two countries to reduce trade barriers, import quotas and tariffs, and to increase trade of goods and services with each other. If natural persons are also free to move between the countries, in addition to a free-trade agreement, it would also be considered an open border. It can be considered the second stage of economic integration. Customs unions are a special type of free-trade area. All such areas have internal arrangements which parties conclude in order to liberalize and facilitate trade among themselves. The crucial difference between customs unions and free-trade areas is their approach to third parties. While a customs union requires all parties to establish and maintain identical external tariffs with regard to trade with non-parties, parties to a free-trade area are not subject to this requirem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Economic Zone
Free economic zones (FEZ), free economic territories (FETs) or free zones (FZ) are a class of special economic zone (SEZ) designated by the trade and commerce administrations of various countries. The term is used to designate areas in which companies are taxed very lightly or not at all to encourage economic activity. The taxation rules and duties are determined by each country. The World Trade Organization (WTO) Agreement on Subsidies and Countervailing Measures (SCM) has content on the conditions and benefits of free zones. Some special economic zones are called free ports. Sometimes they have historically been endowed with favorable customs regulations, such as the free port of Trieste. As the United Kingdom was proposing the creation of ten free ports after leaving the European Union in early 2020, the EU was clamping down on 82 free zones after finding that their special status had aided the financing of terrorism, money laundering and organised crime. Definition Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commitment To Development Index
The Commitment to Development Index (CDI), published annually by the Center for Global Development, ranks the world's richest countries on their dedication to policies that benefit the five billion people living in poorer nations. Rich and poor countries are linked in many ways; thus the Index looks beyond standard comparisons of foreign aid flows. It measures "development-friendliness" of 40 of the world's richest countries, all member nations of the OECD's Development Assistance Committee. The CDI assesses national effort in seven policy areas: aid, trade, investment, migration, environment, security, and technology. It is considered to be a numerical targeting indicator for Goal 8 of the Millennium Development Goals. It shows that aid is about more than quantity – quality also matters – and that development policy is about more than aid. The Index penalizes countries that give with one hand, for instance through aid or investment, but take away with the other, through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overproduction
In economics, overproduction, oversupply, excess of supply or glut refers to excess of supply over demand of products being offered to the market. This leads to lower prices and/or unsold goods along with the possibility of unemployment. The demand side equivalent is underconsumption; some consider supply and demand two sides to the same coin – excess supply is only relative to a given demand, and insufficient demand is only relative to a given supply – and thus consider overproduction and underconsumption equivalent. Overproduction is often attributed as due to previous overinvestment – creation of excess productive capacity, which must then either lie idle (or under capacity), which is unprofitable, or produce an excess supply. Explanation Overproduction is the accumulation of unsalable inventories in the hands of businesses. Overproduction is a relative measure, referring to the excess of production over consumption. The tendency for an overproduction of commodities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trade Restriction
A trade restriction is an artificial restriction on the trade of goods and/or services between two or more countries. It is the byproduct of protectionism. However, the term is controversial because what one part may see as a trade restriction another may see as a way to protect consumers from inferior, harmful or dangerous products. Examples German purity laws: Beer Germany required the production of beer to adhere to its purity law. The law, originally implemented in Bavaria in 1516 and eventually becoming law for newly unified Germany in 1871, made many foreign beers unable to be sold in Germany as "beer". This law was struck down in 1987 by the European Court of Justice, but is still voluntarily followed by many German breweries. US motor vehicle headlamps Rectangular headlamps were promoted in the United States where round lamps were required until 1975. By 1979, the majority of new cars now had the rectangular headlamps. Again, the US permitted only two standardized si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devaluation
In macroeconomics and modern monetary policy, a devaluation is an official lowering of the value of a country's currency within a fixed exchange-rate system, in which a monetary authority formally sets a lower exchange rate of the national currency in relation to a foreign reference currency or currency basket. The opposite of devaluation, a change in the exchange rate making the domestic currency more expensive, is called a '' revaluation''. A monetary authority (e.g., a central bank) maintains a fixed value of its currency by being ready to buy or sell foreign currency with the domestic currency at a stated rate; a devaluation is an indication that the monetary authority will buy and sell foreign currency at a lower rate. However, under a floating exchange rate system (in which exchange rates are determined by market forces acting on the foreign exchange market, and not by government or central bank policy actions), a decrease in a currency's value relative to other major cur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embargo
Economic sanctions are commercial and financial penalties applied by one or more countries against a targeted self-governing state, group, or individual. Economic sanctions are not necessarily imposed because of economic circumstances—they may also be imposed for a variety of political, military, and social issues. Economic sanctions can be used for achieving domestic and international purposes. The efficacy of sanctions is debatable—there are many failures—and sanctions can have unintended consequences. Economic sanctions may include various forms of trade barriers, tariffs, and restrictions on financial transactions. Since the mid-1990s, United Nations Security Council (UNSC) sanctions have tended to target individuals and entities, in contrast to the comprehensive embargoes of earlier decades. An embargo is similar, but usually implies a more severe sanction. An embargo (from the Spanish ''embargo'', meaning hindrance, obstruction, etc. in a general sense, a tradi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |