|
Track-via-missile
Track-via-missile or TVM refers to a missile guidance technique which combines features of semi-active radar homing (SARH) and radio command guidance. This avoids the problems with terminal accuracy normally seen by command guided missiles, especially at long range. It has been used on a number of long-range surface-to-air missiles (SAMs) including the MIM-104 Patriot. Explanation Command guidance has the advantage of isolating most of the equipment for the missile guidance at the launcher, where size and weight are significantly less important. In these systems, the radar that provides guidance is on the ground or ship and the missile lacks an independent guidance system. Typically two radars are used, one tracking the target and another the missile, so that they can fly independent and widely separated paths. A computer then calculates the position and velocity of the two and calculates an intercept point. The same computer then calculates the control inputs needed to fly the mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Command Guidance
Command guidance is a type of missile guidance in which a ground station or aircraft relay signals to a guided missile via radio control or through a wire connecting the missile to the launcher and tell the missile where to steer to intercept its target. This control may also command the missile to detonate, even if the missile has a fuze. Typically, the system giving the guidance commands is tracking both the target and the missile or missiles via radar. It determines the positions and velocities of a target and a missile, and calculates whether their paths will intersect. If not, the guidance system will relay commands to a missile, telling it to move the fins in a way that steers in the direction needed to maneuver to an intercept course with the target. If the target maneuvers, the guidance system can sense this and update the missiles' course continuously to counteract such maneuvering. If the missile passes close to the target, either its own proximity or contact fuze will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Missile Guidance
Missile guidance refers to a variety of methods of guiding a missile or a guided bomb to its intended target. The missile's target accuracy is a critical factor for its effectiveness. Guidance systems improve missile accuracy by improving its Probability of Guidance (Pg). These guidance technologies can generally be divided up into a number of categories, with the broadest categories being "active", "passive", and "preset" guidance. Missiles and guided bombs generally use similar types of guidance system, the difference between the two being that missiles are powered by an onboard engine, whereas guided bombs rely on the speed and height of the launch aircraft for propulsion. History The concept of unmanned guidance originated at least as early as World War I, with the idea of remotely guiding an airplane bomb onto a target, such as the systems developed for the first powered drones by Archibald Low (The Father of Radio Guidance). In World War II, guided missiles were first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RIM-50 Typhon
Typhon was a missile system developed by the United States Navy in the late 1950s, intended to serve as an integrated air-defense system for Navy fleets. Consisting of the SAM-N-8 Typhon LR, later designated RIM-50A, and the SAM-N-9 Typhon MR, later RIM-55A, paired with the AN/SPG-59 radar system, the cost and expense of the Typhon system led to it being cancelled in favor of the Standard Missile program. Design and development Development of Typhon was initiated in the late 1950s, as the existing Talos, Terrier, and Tartar ("3T") long-, medium-, and short-ranged missiles were considered to be approaching obsolescence; in the event of a mass attack by Soviet bomber forces, the requirement for each missile to have its own dedicated target illuminator would lead to rapid saturation of the defensive system. The Typhon system, developed under a contract awarded to the Bendix Corporation, would overcome this through the use of the AN/SPG-59 electronically scanned array radar syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-radiation Missiles
An anti-radiation missile (ARM) is a missile designed to detect and home in on an enemy radio emission source. Typically, these are designed for use against an enemy radar, although jammers and even radios used for communications can also be targeted in this manner. The earliest known anti-radiation weapon is a variant of the Blohm & Voss BV 246 radar guided bomb. Air-to-surface Most ARM designs to date have been intended for use against ground-based radars. Commonly carried by specialist aircraft in the Suppression of Enemy Air Defenses (SEAD) role (known to United States Air Force as "Wild Weasels"), the primary purpose of this type of missile is to degrade enemy air defenses in the first period of a conflict in order to increase the chance of survival for the following waves of strike aircraft. They can also be used to quickly shut down unexpected surface-to-air missile (SAM) sites during an air raid. Often, SEAD escort aircraft also carry cluster bombs, which can be used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Countermeasures
An electronic countermeasure (ECM) is an electrical or electronic device designed to trick or deceive radar, sonar, or other detection systems, like infrared (IR) or lasers. It may be used both offensively and defensively to deny targeting information to an enemy. The system may make many separate targets appear to the enemy, or make the real target appear to disappear or move about randomly. It is used effectively to protect aircraft from guided missiles. Most air forces use ECM to protect their aircraft from attack. It has also been deployed by military ships and recently on some advanced tanks to fool laser/IR guided missiles. It is frequently coupled with stealth advances so that the ECM systems have an easier job. Offensive ECM often takes the form of jamming. Self-protecting (defensive) ECM includes using blip enhancement and jamming of missile terminal homers. History The first example of electronic countermeasures being applied in a combat situation took place du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spoofing Attack
In the context of information security, and especially network security, a spoofing attack is a situation in which a person or program successfully identifies as another by falsifying data, to gain an illegitimate advantage. Internet Spoofing and TCP/IP Many of the protocols in the TCP/IP suite do not provide mechanisms for authenticating the source or destination of a message, leaving them vulnerable to spoofing attacks when extra precautions are not taken by applications to verify the identity of the sending or receiving host. IP spoofing and ARP spoofing in particular may be used to leverage man-in-the-middle attacks against hosts on a computer network. Spoofing attacks which take advantage of TCP/IP suite protocols may be mitigated with the use of firewalls capable of deep packet inspection or by taking measures to verify the identity of the sender or recipient of a message. Domain name spoofing The term 'Domain name spoofing' (or simply though less accurately, 'Domain spo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar Jamming And Deception
Radar jamming and deception is a form of electronic countermeasures that intentionally sends out radio frequency signals to interfere with the operation of radar by saturating its receiver with noise or false information. Concepts that blanket the radar with signals so its display cannot be read are normally known as jamming, while systems that produce confusing or contradictory signals are known as deception, but it is also common for all such systems to be referred to as jamming. There are two general classes of radar jamming, mechanical and electronic. Mechanical jamming entails reflecting enemy radio signals in various ways to provide false or misleading target signals to the radar operator. Electronic jamming works by transmitting additional radio signals towards enemy receivers, making it difficult to detect real target signals, or take advantage of known behaviors of automated systems like radar lock-on to confuse the system. Various counter-countermeasures can sometimes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sidelobe
In antenna engineering, sidelobes are the lobes (local maxima) of the far field radiation pattern of an antenna or other radiation source, that are not the ''main lobe''. The radiation pattern of most antennas shows a pattern of "''lobes''" at various angles, directions where the radiated signal strength reaches a maximum, separated by "'' nulls''", angles at which the radiated signal strength falls to zero. This can be viewed as the diffraction pattern of the antenna. In a directional antenna in which the objective is to emit the radio waves in one direction, the lobe in that direction is designed to have a larger field strength than the others; this is the "''main lobe''". The other lobes are called "''sidelobes''", and usually represent unwanted radiation in undesired directions. The sidelobe directly behind the main lobe is called the back lobe. The longer the antenna relative to the radio wavelength, the more lobes its radiation pattern has. In transmitting antenn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
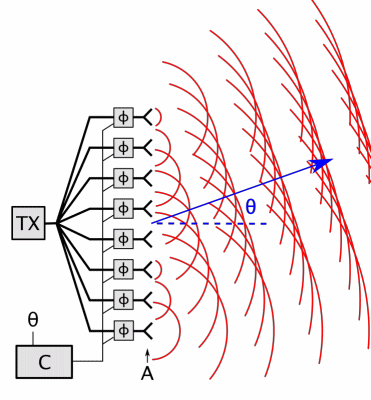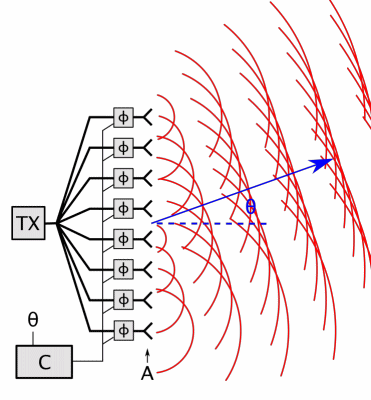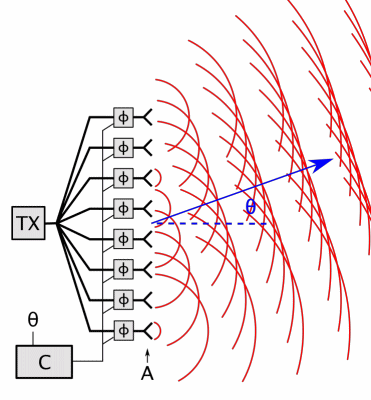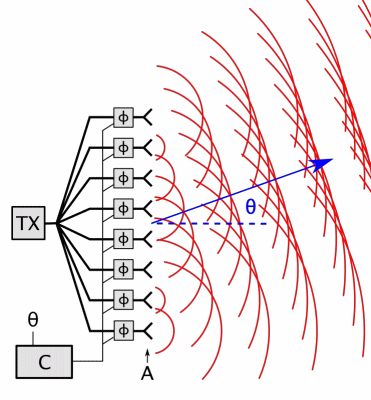
Phased Array
In antenna theory, a phased array usually means an electronically scanned array, a computer-controlled array of antennas which creates a beam of radio waves that can be electronically steered to point in different directions without moving the antennas. In a simple array antenna, the radio frequency current from the transmitter is fed to multiple individual antenna elements with the proper phase relationship so that the radio waves from the separate elements combine ( superpose) to form beams, to increase power radiated in desired directions and suppress radiation in undesired directions. In a phased array, the power from the transmitter is fed to the radiating elements through devices called '' phase shifters'', controlled by a computer system, which can alter the phase or signal delay electronically, thus steering the beam of radio waves to a different direction. Since the size of an antenna array must extend many wavelengths to achieve the high gain needed for narrow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface-to-air Missile
A surface-to-air missile (SAM), also known as a ground-to-air missile (GTAM) or surface-to-air guided weapon (SAGW), is a missile designed to be launched from the ground to destroy aircraft or other missiles. It is one type of anti-aircraft system; in modern armed forces, missiles have replaced most other forms of dedicated anti-aircraft weapons, with anti-aircraft guns pushed into specialized roles. The first attempt at SAM development took place during World War II, but no operational systems were introduced. Further development in the 1940s and 1950s led to operational systems being introduced by most major forces during the second half of the 1950s. Smaller systems, suitable for close-range work, evolved through the 1960s and 1970s, to modern systems that are man-portable. Shipborne systems followed the evolution of land-based models, starting with long-range weapons and steadily evolving toward smaller designs to provide a layered defence. This evolution of design increasin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar Warning Receiver
Radar warning receiver (RWR) systems detect the radio emissions of radar systems. Their primary purpose is to issue a warning when a radar signal that might be a threat is detected, like a fighter aircraft's fire control radar. The warning can then be used, manually or automatically, to evade the detected threat. RWR systems can be installed in all kind of airborne, sea-based, and ground-based assets such as aircraft, ships, automobiles, military bases. This article is focused mainly on airborne military RWR systems; for commercial police speed detection radar RWR systems, see radar detector. Depending on the market the RWR system is designed for, it can be as simple as detecting the presence of energy in a specific radar band, such as the frequencies of known surface-to-air missile systems. Modern RWR systems are often capable of classifying the source of the radar by the signal's strength, phase and signal details. The information about the signal's strength and waveform can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


.jpg)