|
Tracheal Bifurcation
In anatomy, the carina or tracheal bifurcation is a ridge of cartilage in the trachea that occurs between the division of the two main bronchi. Structure The carina occurs at the lower end of the trachea (usually at the level of the 4th to 5th thoracic vertebra). This is in line with the sternal angle, but the carina may raise or descend up to two vertebrae higher or lower with breathing. The carina lies to the left of the midline, and runs antero-posteriorly (front to back). The bronchial arteries supply the carina and the rest of the lower trachea. The carina is around the area posterior to where the aortic arch crosses to the left of the trachea. The azygos vein crosses right to the trachea above the carina. Clinical significance Foreign bodies that fall down the trachea are more likely to enter the right bronchus. The mucous membrane of the carina is the most sensitive area of the trachea and larynx for triggering a cough reflex. Widening and distortion of the carina i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartilage
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints as articular cartilage, and is a structural component of many body parts including the rib cage, the neck and the bronchial tubes, and the intervertebral discs. In other taxa, such as chondrichthyans, but also in cyclostomes, it may constitute a much greater proportion of the skeleton. It is not as hard and rigid as bone, but it is much stiffer and much less flexible than muscle. The matrix of cartilage is made up of glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans, collagen fibers and, sometimes, elastin. Because of its rigidity, cartilage often serves the purpose of holding tubes open in the body. Examples include the rings of the trachea, such as the cricoid cartilage and carina. Cartilage is composed of specialized cells called chondrocytes that produce a large amount of collagenous extracellular matrix, abundant ground substance that is rich in pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breathing
Breathing (or ventilation) is the process of moving air into and from the lungs to facilitate gas exchange with the internal environment, mostly to flush out carbon dioxide and bring in oxygen. All aerobic creatures need oxygen for cellular respiration, which extracts energy from the reaction of oxygen with molecules derived from food and produces carbon dioxide as a waste product. Breathing, or "external respiration", brings air into the lungs where gas exchange takes place in the alveoli through diffusion. The body's circulatory system transports these gases to and from the cells, where "cellular respiration" takes place. The breathing of all vertebrates with lungs consists of repetitive cycles of inhalation and exhalation through a highly branched system of tubes or airways which lead from the nose to the alveoli. The number of respiratory cycles per minute is the breathing or respiratory rate, and is one of the four primary vital signs of life. Under normal conditions t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymph Node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that include B and T cells. Lymph nodes are important for the proper functioning of the immune system, acting as filters for foreign particles including cancer cells, but have no detoxification function. In the lymphatic system a lymph node is a secondary lymphoid organ. A lymph node is enclosed in a fibrous capsule and is made up of an outer cortex and an inner medulla. Lymph nodes become inflamed or enlarged in various diseases, which may range from trivial throat infections to life-threatening cancers. The condition of lymph nodes is very important in cancer staging, which decides the treatment to be used and determines the prognosis. Lymphadenopathy refers to glands that are enlarged or swollen. When inflamed or enlarged, lymph nodes can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carcinoma
Carcinoma is a malignancy that develops from epithelial cells. Specifically, a carcinoma is a cancer that begins in a tissue that lines the inner or outer surfaces of the body, and that arises from cells originating in the endodermal, mesodermal or ectodermal germ layer during embryogenesis. Carcinomas occur when the DNA of a cell is damaged or altered and the cell begins to grow uncontrollably and become malignant. It is from the el, καρκίνωμα, translit=karkinoma, lit=sore, ulcer, cancer (itself derived from meaning ''crab''). Classification As of 2004, no simple and comprehensive classification system has been devised and accepted within the scientific community. Traditionally, however, malignancies have generally been classified into various types using a combination of criteria, including: The cell type from which they start; specifically: * Epithelial cells ⇨ carcinoma * Non-hematopoietic mesenchymal cells ⇨ sarcoma * Hematopoietic cells **Bone marrow-de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foreign Body
A foreign body (FB) is any object originating outside the body of an organism. In machinery, it can mean any unwanted intruding object. Most references to foreign bodies involve propulsion through natural orifices into hollow organs. Foreign bodies can be inert or irritating. If they irritate they will cause inflammation and scarring. They can bring infection into the body or acquire infectious agents and protect them from the body's immune defenses. They can obstruct passageways either by their size or by the scarring they cause. Some can be toxic or generate toxic chemicals from reactions with chemicals produced by the body, as is the case with many examples of ingested metal objects. With sufficient force (as in firing of bullets), a foreign body can become lodged into nearly any tissue. Gastrointestinal tract One of the most common locations for a foreign body is the alimentary tract. It is possible for foreign bodies to enter the tract from the mouth or rectum. Both ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azygos Vein
The azygos vein is a vein running up the right side of the thoracic vertebral column draining itself towards the superior vena cava. It connects the systems of superior vena cava and inferior vena cava and can provide an alternative path for blood to the right atrium when either of the venae cavae is blocked. Structure The azygos vein transports deoxygenated blood from the posterior walls of the thorax and abdomen into the superior vena cava. It is formed by the union of the ascending lumbar veins with the right subcostal veins at the level of the 12th thoracic vertebra, ascending to the right of the descending aorta and thoracic duct, passing behind the right crus of diaphragm, anterior to the vertebral bodies of T12 to T5 and right posterior intercostal arteries. At the level of T4 vertebrae, it arches over the root of the right lung from behind to the front to join the superior vena cava. The trachea and oesophagus is located medially to the arch of the azygous vein. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
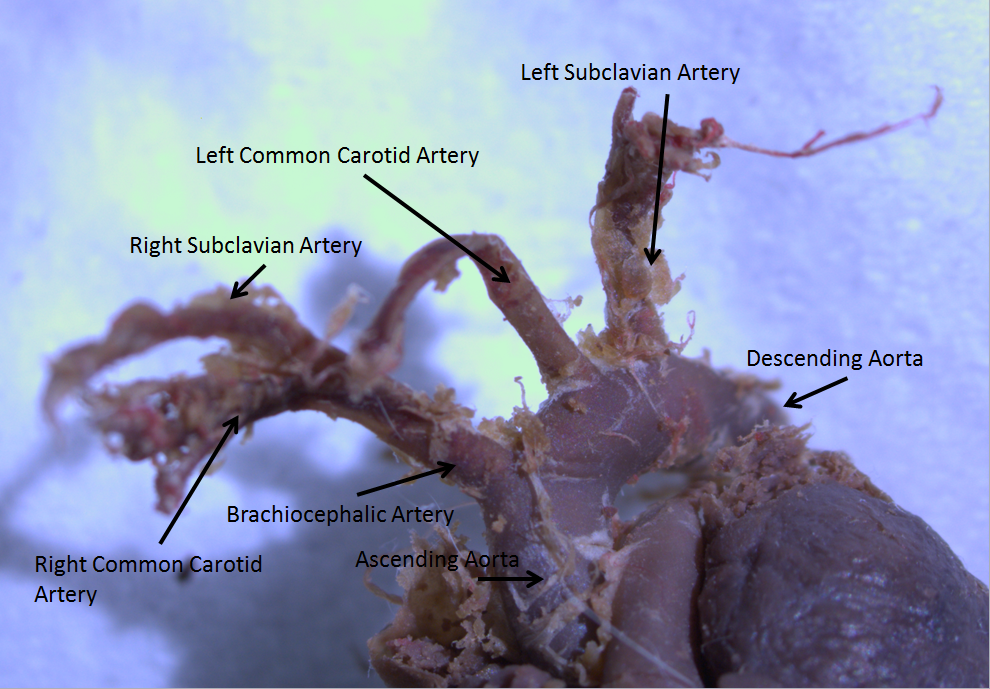
Aortic Arch
The aortic arch, arch of the aorta, or transverse aortic arch () is the part of the aorta between the ascending and descending aorta. The arch travels backward, so that it ultimately runs to the left of the trachea. Structure The aorta begins at the level of the upper border of the second/third sternocostal articulation of the right side, behind the ventricular outflow tract and pulmonary trunk. The right atrial appendage overlaps it. The first few centimeters of the ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk lies in the same pericardial sheath. and runs at first upward, arches over the pulmonary trunk, right pulmonary artery, and right main bronchus to lie behind the right second coastal cartilage. The right lung and sternum lies anterior to the aorta at this point. The aorta then passes posteriorly and to the left, anterior to the trachea, and arches over left main bronchus and left pulmonary artery, and reaches to the left side of the T4 vertebral body. Apart from T4 vertebral body ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronchial Artery
In human anatomy, the bronchial arteries supply the lungs with nutrition and oxygenated blood. Although there is much variation, there are usually two bronchial arteries that run to the left lung, and one to the right lung and are a vital part of the respiratory system. Structure There are typically two left and one right bronchial arteries. The ''left bronchial arteries'' (superior and inferior) usually arise directly from the thoracic aorta. The single ''right bronchial artery'' usually arises from one of the following: * 1) the thoracic aorta at a common trunk with the right 3rd posterior intercostal artery * 2) the superior bronchial artery on the left side * 3) any number of the right intercostal arteries mostly the third right posterior. Function The bronchial arteries supply blood to the bronchi and connective tissue of the lungs. They travel with and branch with the bronchi, ending about at the level of the respiratory bronchioles. They anastomose with the branche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sternal Angle
The sternal angle (also known as the angle of Louis, angle of Ludovic or manubriosternal junction) is the synarthrotic joint formed by the articulation of the manubrium and the body of the sternum. The sternal angle is a palpable clinical landmark in surface anatomy. Anatomy The sternal angle, which varies around 162 degrees in males, marks the approximate level of the 2nd pair of costal cartilages, which attach to the second ribs, and the level of the intervertebral disc between T4 and T5. In clinical applications, the sternal angle can be palpated at the T4 vertebral level. The sternal angle is used in the definition of the thoracic plane. This marks the level of a number of other anatomical structures: The angle also marks a number of other features: :* Carina of the trachea is deep to the sternal angle :* :*Passage of the thoracic duct from right to left behind esophagus :* :* Ligamentum arteriosum :* :* Loop of left recurrent laryngeal nerve around aortic arch The ang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal inlet is about 4–5 centimeters in diameter. The larynx houses the vocal cords, and manipulates pitch and volume, which is essential for phonation. It is situated just below where the tract of the pharynx splits into the trachea and the esophagus. The word ʻlarynxʼ (plural ʻlaryngesʼ) comes from the Ancient Greek word ''lárunx'' ʻlarynx, gullet, throat.ʼ Structure The triangle-shaped larynx consists largely of cartilages that are attached to one another, and to surrounding structures, by muscles or by fibrous and elastic tissue components. The larynx is lined by a ciliated columnar epithelium except for the vocal folds. The cavity of the larynx extends from its triangle-shaped inlet, to the epiglottis, and to the circular outlet at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thoracic Vertebrae
In vertebrates, thoracic vertebrae compose the middle segment of the vertebral column, between the cervical vertebrae and the lumbar vertebrae. In humans, there are twelve thoracic vertebra (anatomy), vertebrae and they are intermediate in size between the cervical and lumbar vertebrae; they increase in size going towards the lumbar vertebrae, with the lower ones being much larger than the upper. They are distinguished by the presence of Zygapophysial joint, facets on the sides of the bodies for Articulation (anatomy), articulation with the head of rib, heads of the ribs, as well as facets on the transverse processes of all, except the eleventh and twelfth, for articulation with the tubercle (rib), tubercles of the ribs. By convention, the human thoracic vertebrae are numbered T1–T12, with the first one (T1) located closest to the skull and the others going down the spine toward the lumbar region. General characteristics These are the general characteristics of the second throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronchus
A bronchus is a passage or airway in the lower respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. The first or primary bronchi pronounced (BRAN-KAI) to branch from the trachea at the carina are the right main bronchus and the left main bronchus. These are the widest bronchi, and enter the right lung, and the left lung at each hilum. The main bronchi branch into narrower secondary bronchi or lobar bronchi, and these branch into narrower tertiary bronchi or segmental bronchi. Further divisions of the segmental bronchi are known as 4th order, 5th order, and 6th order segmental bronchi, or grouped together as subsegmental bronchi. The bronchi, when too narrow to be supported by cartilage, are known as bronchioles. No gas exchange takes place in the bronchi. Structure The trachea (windpipe) divides at the carina into two main or primary bronchi, the left bronchus and the right bronchus. The carina of the trachea is located at the level of the sternal angle and the fifth thoracic vert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)