|
Tracheal Cytotoxin
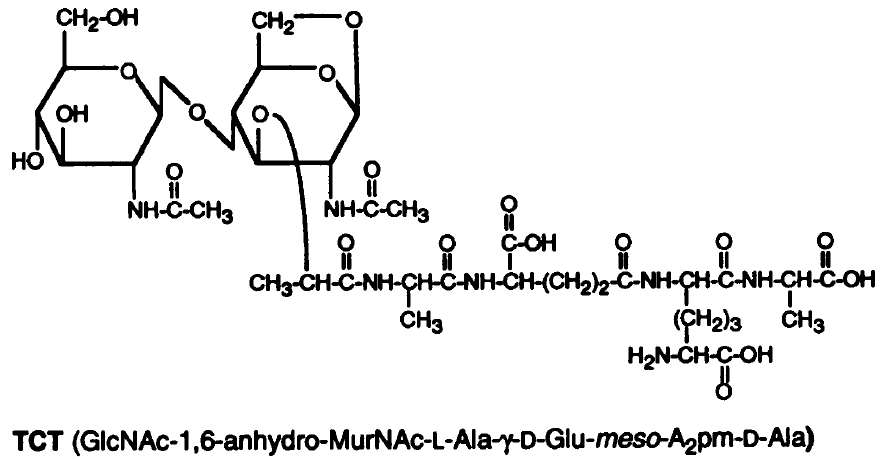
Tracheal cytotoxin (TCT) is a 921 dalton glycopeptide released by ''Bordetella pertussis'', ''Vibrio fischeri ''Aliivibrio fischeri'' (also called ''Vibrio fischeri'') is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium found globally in marine environments. This species has bioluminescent properties, and is found predominantly in symbiosis with various marine anim ...'' (as a symbiosis chemical), and ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae'' (among other peptidoglycan-derived cytotoxins it produces). It is a soluble piece of peptidoglycan (PGN) found in the cell wall of all gram-negative bacteria, but only some bacteria species release TCT due to inability to recycle this piece of anhydromuropeptide. History In 1980, it was discovered that ''B. pertussis'' could attach to hamster tracheal epithelial (HTE) cell (biology), cells, and also, that the supernatant from the cultured bacterium could disrupt the cell cycle of uninfected cell (biology), cells. This prompted the scientists W. E. Goldman, D. G. Klap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |