|
Tourism In West Bengal
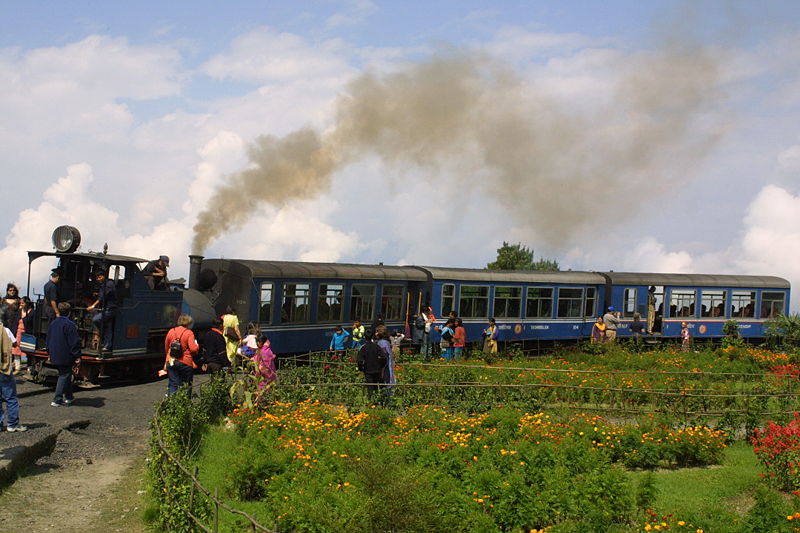
West Bengal is a state in the eastern region of India and is the nation's fourth-most populous. The state capital is Kolkata. The state encompasses two broad natural regions: the Gangetic Plain in the south and the sub-Himalayan and Himalayan area in the north. The tourism in West Bengal is maintained by WBTDCL, a state government owned enterprise. West Bengal, located on eastern bottleneck of India stretching from the Himalayas in the north to the Bay of Bengal in the south, presents some of marvelous landscape features and natural scenic beauty. Some of India's most preferred travel destinations like; the Darjeeling Himalayan hill region in the northern extreme of the state, the highest peak of the state Sandakphu () and the Sundarbans mangrove forests in the extreme south. During the British colonial era from 1700 to 1912, Kolkata enjoyed the privilege of being the capital of British India and witnessed a spate of frenzied construction of buildings, largely influenced by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East India
East India is a region of India consisting of the Indian states of Bihar, Jharkhand, Odisha and West Bengal and also the union territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. The region roughly corresponds to the historical region of Magadha from which it inherits its various Eastern Indo-Aryan languages. The states of Bihar and West Bengal lie on the Indo-Gangetic plain. Jharkhand is situated on the Chota Nagpur Plateau. Odisha lies on the Eastern Ghats and the Deccan Plateau. West Bengal's capital Kolkata is the largest city of this region. The Kolkata Metropolitan Area is the country's third largest. The region is bounded by Bhutan, Nepal and the state of Sikkim in the north, the states of Uttar Pradesh and Chhattisgarh on the west, the state of Andhra Pradesh in the south and the country of Bangladesh in the east. It is also bounded by the Bay of Bengal in the south-east. It is connected to the Seven Sister States of Northeast India by the narrow Siliguri Corrido ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bollywood
Hindi cinema, popularly known as Bollywood and formerly as Bombay cinema, refers to the film industry based in Mumbai, engaged in production of motion pictures in Hindi language. The popular term Bollywood, is a portmanteau of "Bombay" (former name of Mumbai) and " Hollywood". The industry is a part of the larger Indian cinema, which also includes South Cinema and other smaller film industries. In 2017, Indian cinema produced 1,986 feature films, of which the largest number, 364 have been from Hindi. , Hindi cinema represented 43 percent of Indian net box-office revenue; Tamil and Telugu cinema represented 36 percent, and the remaining regional cinema constituted 21 percent. Hindi cinema has overtaken the U.S. film industry to become the largest centre for film production in the world. In 2001 ticket sales, Indian cinema (including Hindi films) reportedly sold an estimated 3.6 billion tickets worldwide, compared to Hollywood's 2.6 billion tickets sold. Earlier Hindi film ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cooch Behar Palace
Cooch Behar Palace, is a landmark in Cooch Behar city, West Bengal. It was designed after the Italian Renaissance style of architecture and was built in 1887, during the reign of Maharaja Nripendra Narayan of Koch dynasty. It is currently a museum. History The Cooch Behar Palace is noted for its elegance and grandeur. It is a brick-built double-story structure in the Classical Italian style covering an area of . The whole structure is long and wide and is on rests above the ground. The Palace is fronted on the ground and first floors by a series of arcaded verandahs with their piers arranged alternately in single and double rows. At the southern and northern ends, the Palace projects slightly and in the center is a projected porch providing an entrance to the Durbar Hall. The Hall has an elegantly shaped metal dome which is topped by a cylindrical louver type ventilator. This is high from the ground and is in the style of the Renaissance architecture. The intros of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palanquin
The litter is a class of wheelless vehicles, a type of human-powered transport, for the transport of people. Smaller litters may take the form of open chairs or beds carried by two or more carriers, some being enclosed for protection from the elements. Larger litters, for example those of the Chinese emperors, may resemble small rooms upon a platform borne upon the shoulders of a dozen or more people. To most efficiently carry a litter, porters either place the carrying poles directly upon their shoulders or use a yoke to transfer the load from the carrying poles to the shoulders. Definitions A simple litter consists of a sling attached along its length to poles or stretched inside a frame. The poles or frame are carried by porters in front and behind. Such simple litters are common on battlefields and emergency situations, where terrain prohibits wheeled vehicles from carrying away the dead and wounded. Litters can also be created quickly by the lashing of poles to a chair. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Survey Of India
The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) is an Indian government agency that is responsible for archaeological research and the conservation and preservation of cultural historical monuments in the country. It was founded in 1861 by Alexander Cunningham who also became its first Director-General. History ASI was founded in 1861 by Alexander Cunningham who also became its first Director-General. The first systematic research into the subcontinent's history was conducted by the Asiatic Society, which was founded by the British Indologist William Jones on 15 January 1784. Based in Calcutta, the society promoted the study of ancient Sanskrit and Persian texts and published an annual journal titled ''Asiatic Researches''. Notable among its early members was Charles Wilkins who published the first English translation of the '' Bhagavad Gita'' in 1785 with the patronage of the then Governor-General of Bengal, Warren Hastings. However, the most important of the society's achieveme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nawab Of Bengal
The Nawab of Bengal ( bn, বাংলার নবাব) was the hereditary ruler of Bengal Subah in Mughal India. In the early 18th-century, the Nawab of Bengal was the ''de facto'' independent ruler of the three regions of Bengal, Bihar, and Orissa which constitute the modern-day sovereign country of Bangladesh and the Indian states of West Bengal, Bihar and Orissa. They are often referred to as the Nawab of Bengal, Bihar and Orissa ( bn, বাংলা, বিহার ও উড়িষ্যার নবাব). The Nawabs were based in Murshidabad which was centrally located within Bengal, Bihar, and Odisha. Their chief, a former prime minister, became the first Nawab. The Nawabs continued to issue coins in the name of the Mughal Emperor, but for all practical purposes, the Nawabs governed as independent monarchs. Bengal continued to contribute the largest share of funds to the imperial treasury in Delhi. The Nawabs, backed by bankers such as the Jagat Seth, became th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humayun Jah
Sayyid Mubarak Ali Khan ( bn, মুবারক আলী খান; 1759 – 6 September 1793), better known as Mubarak ud-Daulah (spelled also as: Mubarak ud-Daula), was the Nawab of Bengal and Bihar. He was the son of Mir Jafar and Babbu Begum. He ascended the throne on 21 March 1770 after his half-brother, Ashraf Ali Khan's death on 10 March 1770. Mubarak Ali Khan was succeeded by his son, Babar Ali Khan after his death on 6 September 1793. Life Early years Nawab Nazim Mubarak Ali Khan, better known as Mubarak ud-Daulah was the son of Mir Jafar by Babbu Begum. He succeeded his half brother, Ashraf Ali Khan, at the age of 12 years, after Ashraf Ali Khan's death on 24 March 1770. Warren Hastings appointed Mubarak ud-Daulah's stepmother, Munny Begum, his guardian though, his mother Babbu Begum was alive. The reason that why the guardianship was not given Babbu Begum has never been satisfactorily explained. Later years In 1790, the Queen of the Mughal Emperor Shah Alam II, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hazarduari Palace
Hazarduari Palace, earlier known as the ''Bara Kothi'', is located in the campus of Kila Nizamat in Murshidabad, in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is situated near the bank of river Ganges. It was built in the nineteenth century by architect Duncan Macleod, under the reign of Nawab Nazim Humayun Jah of Bengal, Bihar and Orissa (1824–1838). In 1985, the palace was handed over to the Archaeological Survey of India for better preservation. According to the Archaeological Survey of India as mentioned in the List of Monuments of National Importance in West Bengal, the Hazarduari Palace and Imambara ASI Listed Monuoments. Kila Nizamat Kila Nizamat or Nizamat Kila (Nizamat Fort) was the site of the old fort of Murshidabad. It was located on the present site of the Hazarduari Palace, on the banks of the Bhagirathi river. Etymology The name of the palace that is Hazarduari means "a palace with a thousand doors". ''Hazar'' means "thousand" and ''Duari'' means "the one with d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Temples In Bishnupur
This is a list of temples in Bishnupur, which are located in the Bankura district of West Bengal, India. The town is famous for the unique terracotta temples made from the locally available laterite stones. The Bishnupur kingdom, Malla rulers were Vaishnavites and built the famous terracotta temples during the 17th and 18th centuries at this place. See also *Mallabhum#Mallabhum_temples, Mallabhum temples {{Ancient-Medieval sites in Bengal Lists of Hindu temples in India, Bishnupur Mallabhum temples, Hindu temples in West Bengal, Bishnupur Krishna temples, Bishnupur Tourist attractions in Bankura district, Hindu temples Lists of buildings and structures in West Bengal, Temples in Bishnupur Lists of tourist attractions in West Bengal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Great Banyan
The Great Banyan is a banyan tree (''Ficus benghalensis'') located in Acharya Jagadish Chandra Bose Indian Botanic Garden, Shibpur, Howrah, near Kolkata, India. The great banyan tree draws more visitors to the garden than its collection of exotic plants from five continents. Its main trunk became infected by fungi after it was struck by two cyclones, so in 1925 the main trunk of the tree was amputated to keep the remainder healthy. A road was built around its circumference, but the tree continues to spread beyond it. It was recorded to be the largest tree specimen in the world in the ''Guinness Book of World Records'' in 1989. Botanical classification Botanically known as ''Ficus benghalensis'', and belonging to the family Moraceae, the tree is a native of India. The fruit is like a small fig and is eaten by some people. It tastes sweeter than fig. The banyan plant is seen sometimes growing from the little wet dust deposits on buildings because birds carry them around for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Howrah Bridge
The Howrah Bridge is a balanced cantilever bridge over the Hooghly River in West Bengal. Commissioned in 1943, the bridge was originally named the New Howrah Bridge, because it replaced a pontoon bridge at the same location linking the cities of Howrah and Kolkata (Calcutta). On 14 June 1965, it was renamed Rabindra Setu after the great Bengali poet Rabindranath Tagore, who was the first Indian and Asian Nobel laureate. It is still popularly known as the Howrah Bridge. The bridge is one of four on the Hooghly River and is a famous symbol of Kolkata and West Bengal. The other bridges are the Vidyasagar Setu (popularly called the Second Hooghly Bridge), the Vivekananda Setu and the relatively new Nivedita Setu. It carries a daily traffic of approximately 100,000 vehicles and possibly more than 150,000 pedestrians, easily making it the busiest cantilever bridge in the world. The third-longest cantilever bridge at the time of its construction, the Howrah Bridge is currently the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Times Of India
''The Times of India'', also known by its abbreviation ''TOI'', is an Indian English-language daily newspaper and digital news media owned and managed by The Times Group. It is the third-largest newspaper in India by circulation and largest selling English-language daily in the world. It is the oldest English-language newspaper in India, and the second-oldest Indian newspaper still in circulation, with its first edition published in 1838. It is nicknamed as "The Old Lady of Bori Bunder", and is an Indian " newspaper of record". Near the beginning of the 20th century, Lord Curzon, the Viceroy of India, called ''TOI'' "the leading paper in Asia". In 1991, the BBC ranked ''TOI'' among the world's six best newspapers. It is owned and published by Bennett, Coleman & Co. Ltd. (B.C.C.L.), which is owned by the Sahu Jain family. In the Brand Trust Report India study 2019, ''TOI'' was rated as the most trusted English newspaper in India. Reuters rated ''TOI'' as India's most trus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |