|
Torok Formation
The Torok Formation is a geologic formation in the National Petroleum Reserve in Alaska (NPR-A). It preserves fossils dating back to the Cretaceous period. Geology The Torok Formation lies 2,000–4,000 feet deeper than the Nanushuk Formation. They form a huge wedge of sediment deposited in a deep water basin and stretch from north of the Brooks Range beneath the Alaska North Slope to the adjacent offshore. It contains reservoirs in turbidite sandstone and is very porous. The USGS found large-scale folds and faults in the South of the formation and evidence, that the rocks have been heated to temperatures at which oil is converted to natural gas. The Torok Formation was deposited on the floor of the Alaska North Slope basin. History of oil exploration In 2016, oil discovery in the deeper Torok Formation of more than 1,000 MMBO was announced at Smith Bay, less than 1 mile offshore from the NPR-A. It came at the same time as ConocoPhillips discovery of Willow project The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formation (stratigraphy)
A geological formation, or simply formation, is a body of rock having a consistent set of physical characteristics (lithology) that distinguishes it from adjacent bodies of rock, and which occupies a particular position in the layers of rock exposed in a geographical region (the stratigraphic column). It is the fundamental unit of lithostratigraphy, the study of strata or rock layers. A formation must be large enough that it can be mapped at the surface or traced in the subsurface. Formations are otherwise not defined by the thickness (geology), thickness of their rock strata, which can vary widely. They are usually, but not universally, tabular in form. They may consist of a single lithology (rock type), or of alternating beds of two or more lithologies, or even a heterogeneous mixture of lithologies, so long as this distinguishes them from adjacent bodies of rock. The concept of a geologic formation goes back to the beginnings of modern scientific geology. The term was used by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
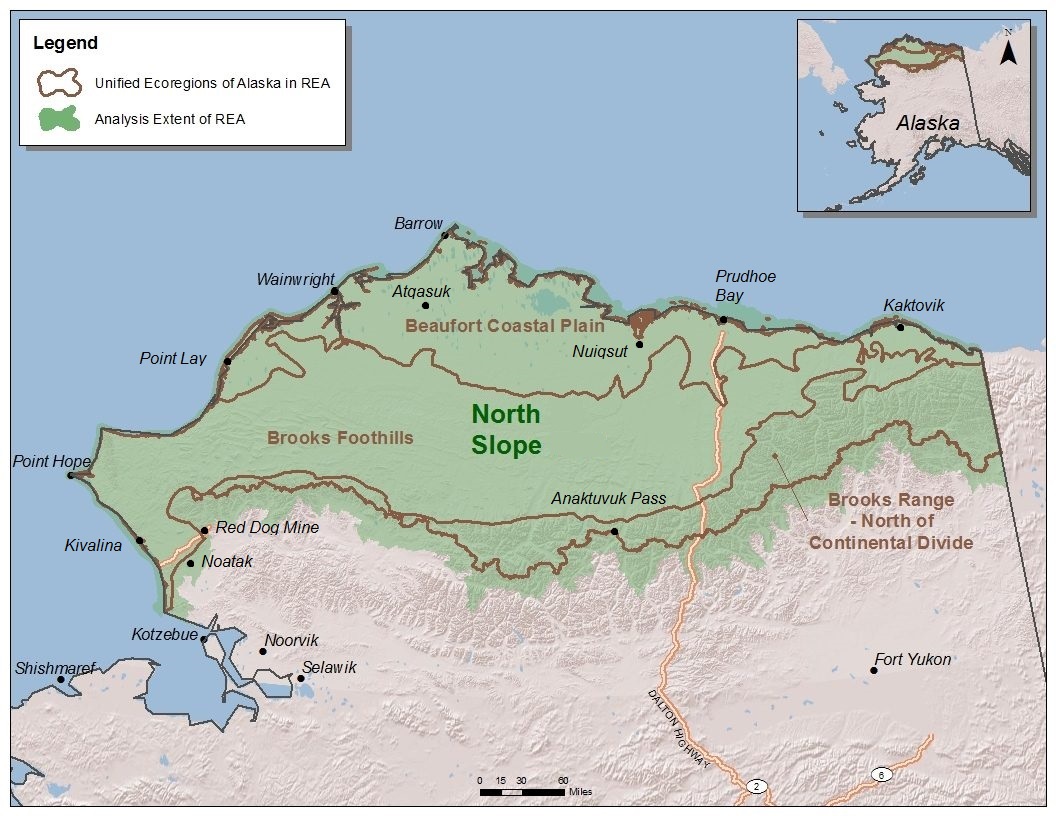
North Slope Borough, Alaska
The North Slope Borough is the northernmost borough in the US state of Alaska and thus, the northernmost county or equivalent of the United States as a whole. As of the 2020 census, the population was 11,031. The borough seat and largest city is Utqiaġvik (known as Barrow from 1901 to 2016), which is also the northernmost settlement in the United States. History The borough was established in 1972 by an election of the majority Indigenous people in the region, following Congressional passage of the Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act. Most are Inupiat. The borough was named for the Alaska North Slope basin. In 1974 it adopted a Home Rule Charter, enabling it to exercise any legitimate governmental power. The borough has first-class status and exercises the powers of planning, zoning, taxation, and schools."Your Government" North Slope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Fossiliferous Stratigraphic Units In Alaska
This article contains a list of fossil-bearing stratigraphic units in the state of Alaska, U.S. Sites See also * Paleontology in Alaska References * {{DEFAULTSORT:Fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Alaska Stratigraphic Units Alaska Stratigraphic Units A stratigraphic unit is a volume of Rock (geology), rock of identifiable origin and relative age range that is defined by the distinctive and dominant, easily mapped and recognizable petrology, petrographic, lithology, lithologic or paleontology, p ... Stratigraphy of Alaska United States geology-related lists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willow Project
The Willow project is an oil drilling project by ConocoPhillips located on the plain of the North Slope of Alaska in the National Petroleum Reserve in Alaska entirely on wetlands. The project was originally to construct and operate up to five drill pads for a total of 250 oil wells. Associated infrastructure includes access and infield roads, airstrips, pipelines, a gravel mine and a temporary island to facilitate module delivery via sealift barges on permafrost and between waters managed by the state of Alaska. Oil was discovered in the Willow prospect area west of Alpine, Alaska, in 2016, and in October 2020, the Bureau of Land Management (BLM) approved ConocoPhillips' Willow development project in its Record of Decision. After a court challenge in 2021, the BLM issued its final supplemental environmental impact statement (SEIS) in February 2023. Alaskan lawmakers from both parties, as well as the Arctic Slope Regional Corporation, have supported the Willow project. In Mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ConocoPhillips
ConocoPhillips Company is an American multinational corporation engaged in hydrocarbon exploration and production. It is based in the Energy Corridor district of Houston, Texas. The company has operations in 15 countries and has production in the United States (49% of 2019 production), Norway (10% of 2019 production), Canada (5% of 2019 production), Australia (12% of 2019 production), Indonesia (4% of 2019 production), Malaysia (4% of 2019 production), Libya (3% of 2019 production), China (3% of 2019 production), and Qatar (6% of 2019 production). The company's production in the United States included production in Alaska, the Eagle Ford Group, the Permian Basin (North America), Permian Basin, the Bakken Formation, the Gulf of Mexico and the Anadarko Basin. Approximately 1/3 of the company's U.S. production is in Alaska, where it has operations in the Cook Inlet Area, the Alpine oil field off the Colville River (Alaska), Colville River, and the Kuparuk oil field and Prudhoe Bay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
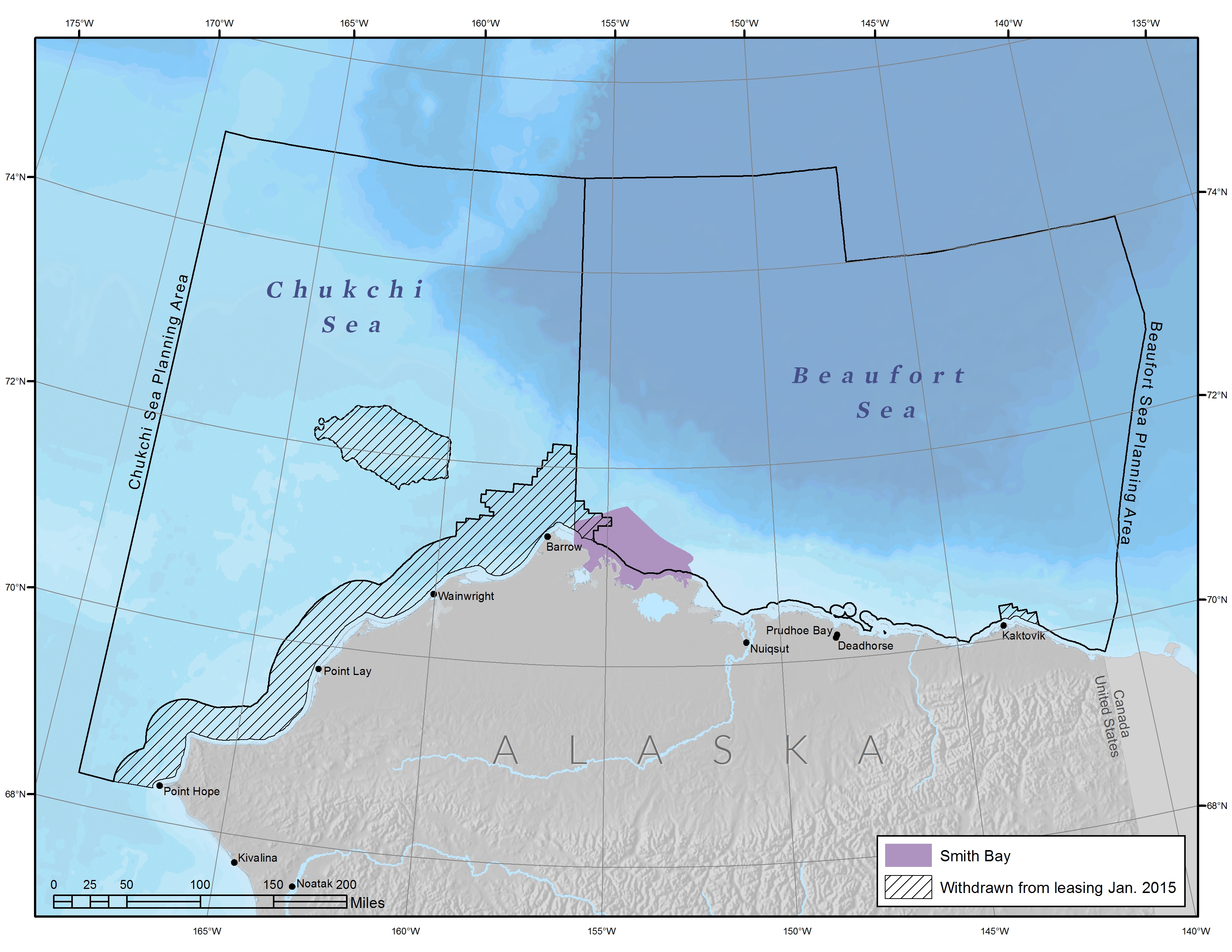
Smith Bay
Smith Bay is an estuary in the Beaufort Sea that supports a wide range of fish, birds, and marine mammals. It is located northeast of Point Barrow, Alaska. The Bureau of Ocean Energy Management recognizes the southeastern portion of Barrow Canyon, which covers some, but not all, of Smith Bay, as an Environmentally Important Area. Geography Approximately 150 miles west of Prudhoe Bay, Alaska, Smith Bay stretches from Dease Inlet, Alaska to Cape Halkett, Alaska. Bordered by barrier islands that separate the shallow, brackish waters from the Beaufort Sea, several slow-moving rivers flow into this region. Along with its adjacent waters, Smith Bay is a shallow-water estuary. Fauna Smith Bay is a significant hotspot for pinnipeds. The nearshore areas are important habitat for ringed seals that come to the landfast ice during the winter and spring to give birth. Polar bears and bowhead whales rely on Smith Bay for important foraging habitat. Polar bears have been observed using Sm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaska North Slope Basin
The Alaskan North Slope (ANS) is a foreland basin located on the northern edge of the Brooks Range. The Alaska North Slope is bounded on the north by the Beaufort Sea and runs from the Canadian border to the maritime boundary with Russia in the west. The western edge extends into the Chukchi Sea and Chukchi platform where the basin is at its widest. As the basin moves east it narrows towards the Canadian border. The basin is 1000 km long, 600 km at its widest, and covers a total area of 240,000 km2. Basin formation The ANS is broken into three provinces the Brooks Range, the Northern Foothills, and the Coastal Plain. The foothills province has severe to gently deformed rock. The southern edge, closest to the Brooks Range, consists of folded and faulted Lower Cretaceous deposits. This region is home to the deepest section of the basin the Colville trough, with a maximum depth around 30,000 ft. The northern foothills province is made up of numerous elongated det ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
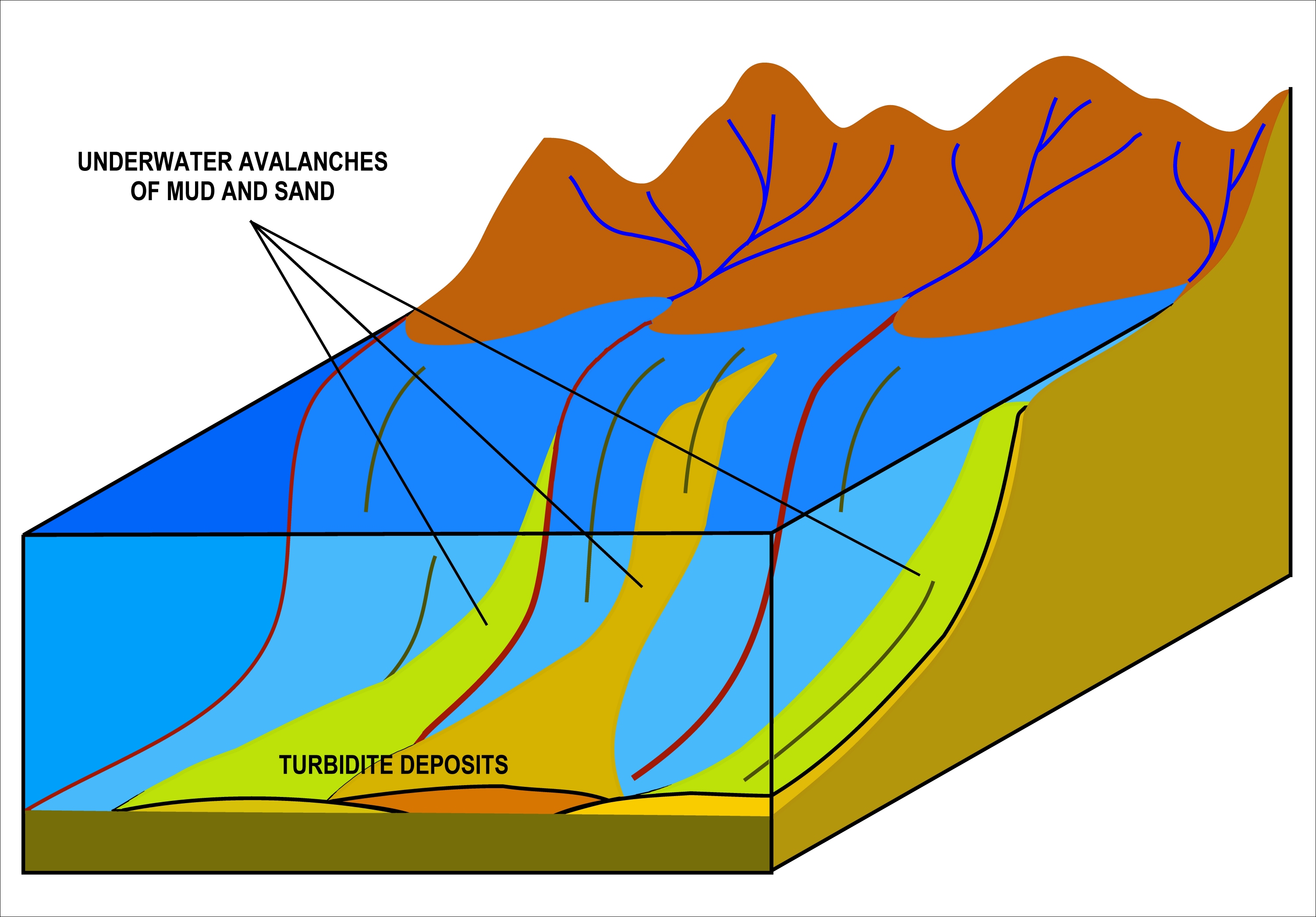
Turbidite
A turbidite is the geologic deposit of a turbidity current, which is a type of amalgamation of fluidal and sediment gravity flow responsible for distributing vast amounts of clastic sediment into the deep ocean. Sequencing Turbidites were first properly described by Arnold H. Bouma (1962), who studied deepwater sediments and recognized particular "fining-up intervals" within deep water, fine-grained shales, which were anomalous because they started at pebble conglomerates and terminated in shales. This was anomalous because within the deep ocean it had historically been assumed that there was no mechanism by which tractional flow could carry and deposit coarse-grained sediments into the abyssal depths. Bouma cycles begin with an erosional contact of a coarse lower bed of pebble to granule conglomerate in a sandy matrix, and grade up through coarse then medium plane parallel sandstone; through cross-bedded sandstone; rippled cross-bedded sand/silty sand, and finally lami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brooks Range
The Brooks Range ( Gwich'in: ''Gwazhał'') is a mountain range in far northern North America stretching some from west to east across northern Alaska into Canada's Yukon Territory. Reaching a peak elevation of on Mount Isto, the range is believed to be approximately 126 million years old. In the United States, these mountains are considered a subrange of the Rocky Mountains, whereas in Canada they are considered separate, as the northern border of the Rocky Mountains is considered to be the Liard River far to the south in the province of British Columbia. While the range is mostly uninhabited, the Dalton Highway and Trans-Alaska Pipeline System run through the Atigun Pass (1,415 m, 4,643 ft) on their way to the oil fields at Prudhoe Bay on Alaska's North Slope. The Alaska Native villages of Anaktuvuk and Arctic Village, as well as the very small communities of Coldfoot, Wiseman, Bettles, and Chandalar, are the range's only settlements. In the far west, near the Wul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic. The name is derived from the Latin ''creta'', "chalk", which is abundant in the latter half of the period. It is usually abbreviated K, for its German translation ''Kreide''. The Cretaceous was a period with a relatively warm climate, resulting in high eustatic sea levels that created numerous shallow inland seas. These oceans and seas were populated with now- extinct marine reptiles, ammonites, and rudists, while dinosaurs continued to dominate on land. The world was ice free, and forests extended to the poles. During this time, new groups of mammals and birds appeared. During the Early Cretaceous, flowering plants appeared and began to rapidly diversify, becoming the dominant group of plants across the Earth b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanushuk Formation
The Nanushuk Group or Nanushuk formation is a geologic group in Alaska in westernmost National Petroleum Reserve in Alaska (NPR-A). Oil in these rocks likely was generated beneath Western North Slope and migrated northeastward into NPR-A. It preserves fossils dating back to the Cretaceous period. Underneath the Nanushuk lies the Torok Formation. Geology The Nanushuk Formation together with the Torok Formation below it forms a huge wedge of sediment deposited in a deep water basin and stretches from north of the Brooks Range beneath the Alaska North Slope to the adjacent offshore. It was deposited in shallow water and includes potential reservoirs in deltaic, shoreface, and fluvial sandstones. The USGS found large-scale folds and faults in the South of the formation and evidence, that the rocks have been heated to temperatures at which oil is converted to natural gas. History Before 2015, over a period of more than 50 years about 150 oil exploration wells had been drilled into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Period (geology)
The geologic time scale, or geological time scale, (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochronology (scientific branch of geology that aims to determine the age of rocks). It is used primarily by Earth scientists (including geologists, paleontologists, geophysicists, geochemists, and paleoclimatologists) to describe the timing and relationships of events in geologic history. The time scale has been developed through the study of rock layers and the observation of their relationships and identifying features such as lithologies, paleomagnetic properties, and fossils. The definition of standardized international units of geologic time is the responsibility of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), a constituent body of the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS), whose primary objective is to precisely define ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |