|
Tori Shogi
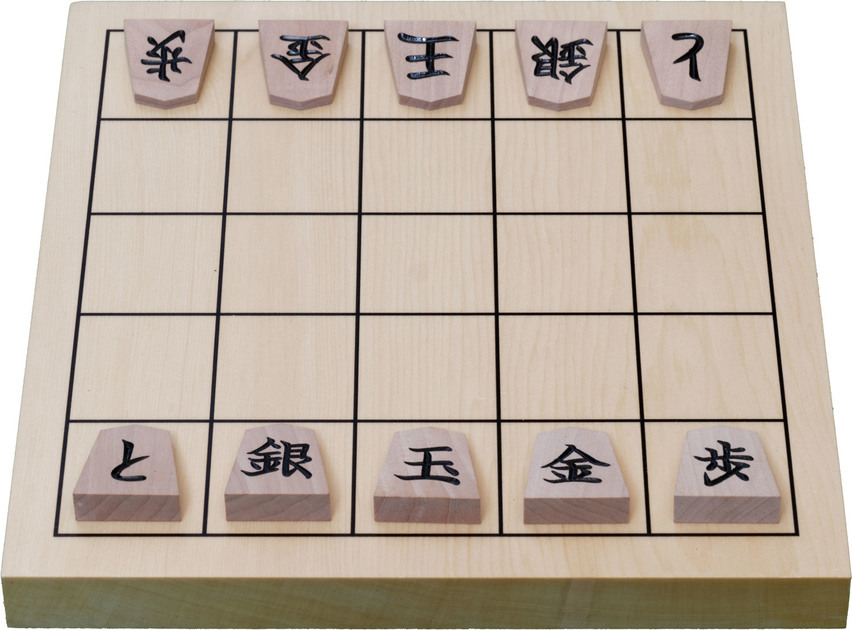
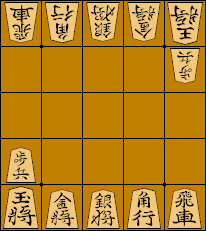
Tori shōgi (禽将棋 or 鳥将棋, 'bird chess') is a variant of shogi (Japanese chess), which was invented by Toyota Genryu in 1799 despite being traditionally attributed to his master Ōhashi Sōei. It was first published in 1828 and again in 1833. The game is played on a 7×7 board and uses the drop rule; it is the only traditional shogi variant, possibly besides wa shogi, to do so. This is one of the more popular shogi variants. There were tournaments in London and Royston in the 1990s and early 2000s. Rules of the game Objective The objective of the game is to capture your opponent's phoenix. Game equipment Two players, Black and White (or 先手 ''sente'' and 後手 ''gote),'' play on a board ruled into a grid of 7 ''ranks'' (rows) by 7 ''files'' (columns). The squares are undifferentiated by marking or color. Each player has a set of 16 wedge-shaped pieces, of slightly different sizes. From largest to smallest (or most to least powerful) they are: * 1 phoenix * 1 f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perpetual Check
In the game of chess, perpetual check is a situation in which one player can a draw by an unending series of checks. This typically arises when the player who is checking cannot deliver checkmate, and failing to continue the series of checks gives the opponent at least a chance to win. A draw by perpetual check is no longer one of the rules of chess; however, such a situation will eventually allow a draw claim by either threefold repetition or the fifty-move rule. Players usually agree to a draw long before that, however. Perpetual check can also occur in other forms of chess, although the rules relating to it might be different. For example, giving perpetual check is not allowed in shogi and xiangqi, where doing so leads to an automatic loss for the giver. Examples In this diagram, Black is ahead a rook, a bishop, and a pawn, which would normally be a decisive advantage. But White, to move, can draw by perpetual check: : 1. Qe8+ Kh7 : 2. Qh5+ Kg8 : 3. Qe8+ etc. The same po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Chess Variant Pages
''The Chess Variant Pages'' is a non-commercial website devoted to chess variants. It was created by Hans Bodlaender in 1995. The site is "run by hobbyists for hobbyists" and is "the most wide-ranging and authoritative web site on chess variants". The site contains a large compilation of games with published rules. The aims of the site are to educate readers about chess variants, encourage gameplay, and provide a place for free discussion. The site has featured game competitions as well as variant design competitions, and provides facilities for publishing documents. Numerous files are available for playing variants using the Zillions of Games proprietary software engine. The site also features The Game Courier software developed by Fergus Duniho which can be used to play almost any variant. There is also an extensive encyclopedia of fairy chess piece A fairy chess piece, variant chess piece, unorthodox chess piece, or heterodox chess piece is a chess piece not used in conventio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whale Shogi
Whale Shogi (鯨将棋 ''kujira shōgi)'' is a modern variant of shogi (Japanese chess). It is not, however, Japanese: it was invented by R. Wayne Schmittberger of the United States in 1981. The game is similar to Judkins shogi, but with more pieces, and the pieces are named after types of whale. Game rules Objective The objective of the game is to capture your opponent's white whale. Game equipment Two players, Black and White (or 先手 ''sente'' and 後手 ''gote),'' play on a board ruled into a grid of 6 ranks (rows) by 6 files (columns). The squares are undifferentiated by marking or color. Each player has a set of 12 wedge-shaped pieces, of slightly different sizes. From largest to smallest (most to least powerful) they are: *1 white whale (W) *1 porpoise (P) *1 humpback (H) *1 gray whale (G) *1 narwhal (N) *1 blue whale (B) *6 dolphins (D) Each piece has its initial written on its face. On the reverse side of the porpoise is another letter (K for 'killer whale'), often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yari Shogi
Yari shogi (槍将棋 ''yari shōgi'', spear chess, where 'spear' is another name for the lance piece) is a modern variant of shogi (Japanese chess); however, it is not Japanese. It was invented in 1981 by Christian Freeling of the Netherlands. This game accentuates shogi’s intrinsically forward range of direction by giving most of the pieces the ability to move any number of free squares orthogonally forward like a shogi lance. The opposite is true of promoted pieces which can move backward with the same power. Rules of the game Objective The objective of the game is to capture your opponent's general. Game equipment Two players, Black and White (or 先手 ''sente'' and 後手 ''gote''), play on a board ruled into a grid of 9 ''ranks'' (rows) by 7 ''files'' (columns). The squares are undifferentiated by markings or color. Each player has a set of 14 wedge-shaped pieces, of slightly different sizes. From largest to smallest (most to least powerful) they are: * 1 general * 2 y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannon Shogi
A shogi variant is a game related to or derived from shogi (Japanese chess). Many shogi variants have been developed over the centuries, ranging from some of the largest chess-type games ever played to some of the smallest. A few of these variants are still regularly played, though none are as popular as shogi itself. The drop rule, often considered the most notable feature of shogi, is absent from most shogi variants, which therefore play more like other forms of chess, with the board becoming less crowded as pieces are exchanged. This is especially true for variants larger than shogi itself − in fact, the largest well-known variant that features the drop rule is the 11×11 game wa shogi. Predecessors of modern shogi Some form of chess had almost certainly reached Japan by the 9th century, if not earlier, but the earliest surviving Japanese description of the rules of chess dates from the early 12th century, during the Heian period. Unfortunately, this description does not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kyoto Shogi
is a modern variant of shogi (Japanese chess). It was invented by Tamiya Katsuya c. 1976. Kyoto shogi is played like standard shogi, but with a reduced number of pieces on a 5×5 board. However, the pieces alternately promote and demote with every move, and the promotion values are entirely different from standard shogi. Rules of the game Game equipment Two players play on a board ruled into a grid of 5 ''ranks'' (rows) by 5 ''files'' (columns). The squares are undifferentiated by marking or color. Each player has a set of 5 wedge-shaped pieces, of slightly different sizes. From largest to smallest (most to least powerful) they are: * 1 king * 1 gold general * 1 silver general * 1 tokin * 1 pawn The names of the pieces combine their promoted and unpromoted values, and are puns in Japanese for words with the same pronunciations but different kanji. For example, the lance/tokin is homonymous with the name of the city 京都 Kyoto, and provides the name of the game. Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microshogi
Microshogi (五分摩訶将棋 ''gofun maka shōgi'' "5-minute (scarlet) poppy chess") is a modern variant of shogi (Japanese chess), with very different rules for promotion, and demotion. Kerry Handscomb of NOSTNOST (kNights of the Square Table), a (now defunct) correspondence game club formed in 1960 by Bob Lauzon and Jim France, enjoyed several hundred active members. gave it this English name. Although not confirmed, he credits its invention to the late Oyama Yasuharu, a top level shogi player. The game was invented before 1982. Equipment Two players play on a board ruled into a grid of 5 ranks (rows) by 4 files (columns). The squares are undifferentiated by marking or color. Each player has a set of 5 wedge-shaped pieces. The pieces are of slightly different sizes. From largest to smallest (or most to least powerful) they are: *1 king *1 bishop *1 gold general *1 silver general *1 pawn Game rules The game is identical to standard shogi with the following exceptions. Setu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judkins Shogi
Judkins shogi (ジャドケンス将棋 ''Jadokensu shōgi'' "Judkins chess") is a modern variant of shogi (Japanese chess), however it is not Japanese. Credit for its invention has been given to Paul Judkins of Norwich, UK, prior to April 1998. Rules of the game Objective The objective of the game is to capture your opponent's king. Game equipment Two players, Black and White (or 先手 ''sente'' and 後手 ''gote''), play on a board ruled into a grid of 6 ''ranks'' (rows) by 6 ''files'' (columns). The squares are undifferentiated by marking or color. Each player has a set of 7 wedge-shaped pieces, of slightly different sizes. From largest to smallest (most to least powerful) they are: * 1 king * 1 rook * 1 bishop * 1 gold general * 1 silver general * 1 knight * 1 pawn Most of the English-language names are chosen to correspond to rough equivalents in Western chess, rather than as translations of the Japanese names. Each piece has its name in the form of two kanji written ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minishogi
Minishogi (5五将棋 ''gogo shōgi'' "5V chess" or "5×5 chess") is a modern variant of shogi (Japanese chess). The game was invented (or rediscovered) around 1970 by Shigenobu Kusumoto of Osaka, Japan. The rules are nearly identical to those of standard shogi, with the exception that it is played on a 5x5 board with a reduced number of pieces, and each player's promotion zone consists only of the rank farthest from the player. Rules of the game Objective Like in standard shogi, each player aims to checkmate the opponent's king. Game equipment Two players play on a board ruled into a grid of five ranks (rows) by five files (columns). The squares are undifferentiated by marking or color. Each player begins with a set of 6 wedge-shaped pieces; these are: *1 king *1 rook *1 bishop *1 gold general *1 silver general *1 pawn Their movements are identical to those of their namesakes in standard shogi. Setup Each player places their pieces in the positions shown below, point ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shogi Variant
A shogi variant is a game related to or derived from shogi (Japanese chess). Many shogi variants have been developed over the centuries, ranging from some of the largest chess-type games ever played to some of the smallest. A few of these variants are still regularly played, though none are as popular as shogi itself. The drop rule, often considered the most notable feature of shogi, is absent from most shogi variants, which therefore play more like other forms of chess, with the board becoming less crowded as pieces are exchanged. This is especially true for variants larger than shogi itself − in fact, the largest well-known variant that features the drop rule is the 11×11 game wa shogi. Predecessors of modern shogi Some form of chess had almost certainly reached Japan by the 9th century, if not earlier, but the earliest surviving Japanese description of the rules of chess dates from the early 12th century, during the Heian period. Unfortunately, this description does not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellipsis
The ellipsis (, also known informally as dot dot dot) is a series of dots that indicates an intentional omission of a word, sentence, or whole section from a text without altering its original meaning. The plural is ellipses. The term originates from the grc, ἔλλειψις, meaning 'leave out'. Opinions differ as to how to render ellipses in printed material. According to ''The Chicago Manual of Style'', it should consist of three periods, each separated from its neighbor by a non-breaking space: . According to the ''AP Stylebook'', the periods should be rendered with no space between them: . A third option is to use the Unicode character U+2026 . Background The ellipsis is also called a suspension point, points of ellipsis, periods of ellipsis, or (colloquially) "dot-dot-dot".. According to Toner it is difficult to establish when the "dot dot dot" phrase was first used. There is an early instance, which is perhaps the first in a piece of fiction, in Virginia Woolf's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_gegen_Fischer_(USA).jpg)