|
Toramana
Toramana also called Toramana Shahi Jauvla ( Gupta script: ''Toramāṇa'', ruled circa 493-515 CE) was a king of the Alchon Huns who ruled in northern India in the late 5th and the early 6th century CE. Toramana consolidated the Hephthalite power in Punjab (present-day Pakistan and northwestern India), and conquered northern and central India including Eran in Madhya Pradesh. Toramana used the title "Great King of Kings" (''Mahārājadhirāja'' ), equivalent to "Emperor", in his inscriptions, such as the Eran boar inscription. The Sanjeli inscription of Toramana speaks of his conquest and control over Malwa and Gujarat. His territory also included Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan and Kashmir. He probably went as far as Kausambi, where one of his seals was discovered. According to the Rīsthal inscription, discovered in 1983, the Aulikara king Prakashadharma of Malwa defeated him.Ojha, N.K. (2001). ''The Aulikaras of Central India: History and Inscriptions'', Chandigarh: Arun Publish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alchon Huns
The Alchon Huns, ( Bactrian: αλχον(ν)ο ''Alchon(n)o'') also known as the Alchono, Alxon, Alkhon, Alkhan, Alakhana and Walxon, were a nomadic people who established states in Central Asia and South Asia during the 4th and 6th centuries CE. They were first mentioned as being located in Paropamisus, and later expanded south-east, into the Punjab and central India, as far as Eran and Kausambi. The Alchon invasion of the Indian subcontinent eradicated the Kidarite Huns who had preceded them by about a century, and contributed to the fall of the Gupta Empire, in a sense bringing an end to Classical India. The invasion of India by the Huna peoples follows invasions of the subcontinent in the preceding centuries by the Yavana (Indo-Greeks), the Saka (Indo-Scythians), the Palava (Indo-Parthians), and the Kushana (Yuezhi). The Alchon Empire was the third of four major Huna states established in Central and South Asia. The Alchon were preceded by the Kidarites and succeeded by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eran Boar Inscription Of Toramana
The Eran boar inscription of Toramana, is a stone inscription found in Eran in the Malwa region of Madhya Pradesh, India. It is 8 lines of Sanskrit, the first three of which are in meter and the rest in prose, written in a North Indian script. It is carved on the neck of a freestanding high red sandstone Varaha statue, a zoomorphic iconography of Vishnu avatar, and dated to the 6th century. The inscription names king Toramana, ruler of the Alchon Huns, as ruling over Malwa ("governing the earth") and records that a Dhanyavishnu is dedicating a stone temple to Narayana (Vishnu). Date The inscription does not give any date, but mentions Toramana is "governing the earth", which is interpreted to mean the Malwa region site where this inscription is found. According to Radhakumud Mookerji, this means that the inscription was made after 510 CE when the Gupta king Bhanugupta and his local chief Goparaja had lost Malwa region after Toramana's invasion. It must be before 513 CE, because Tor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rīsthal Inscription
The Rīsthal inscription is a stone-slab inscription which was discovered in 1983 in the area of Rīsthal near Mandsaur in Madhya Pradesh, India. The inscription describes the event in the year 515 CE, when the Aulikara king Prakashadharma of Malwa finally defeated the Alchon Huns ruler Toramana in his campaigns into Central India, and how he took away the tusks of his elephants and his harem.Ojha, N.K. (2001). ''The Aulikaras of Central India: History and Inscriptions'', Chandigarh: Arun Publishing House, , pp.48-50Hans Bakkerbr>24th Gonda lecture/ref> The portion of the inscription related to Toramana reads: This ended the First Hunnic War in Indian territory, until Toramana's son Mihirakula would again attack Central India a few years later. Full inscription The purpose of the inscription is to record the construction of a tank, as well as the dedication of a Temple to Shiva by the Rajasthaniya Bagavaddosha in the reign of king Prakasadharma. The inscription documents one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanjeli Inscriptions
The Sanjeli inscriptions consist in three copperplate charters found in Sanjeli in northern Gujarat, dated to 499 CE, 502 CE and 515 CE respectively: they are the "Sanjeli Charter of the Merchants", "Sanjeli Charter of Bhūta" and the "Sanjeli Charter of Mātṛdāsa". The copperplates mention the rule of Alchon Huns king Toramana in the area, as ''mahārājādhirājaśrī toramāṇe'' ("Great King of Kings Toramana", in the Sanjeli Charter of the Merchants). The first copperplate refers to the 3rd year of the reign of Toramana, and describes pious gifts made by merchants in the area of Vadrapali in the district of Sivabhagapura. The copperplates also describes how the local king Maharaja Bhuta in Sanjeli was made Governor (visayapati) of the district of Sivabhagapura (northern Gujarat) by the grace of Toramana. The Sanjeli inscriptions indicate that Toramana penetrated at least as far as northern Gujarat, and possibly to the trading port of Bharukaccha.The World of the Skanda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mihirakula
Mihirakula (Gupta script: , ''Mi-hi-ra-ku-la'', Chinese: 摩酰逻矩罗 ''Mo-hi-lo-kiu-lo''), sometimes referred to as Mihiragula or Mahiragula, was the second and last Alchon Hun king of northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent between 502 and 530 CE. He was a son of and successor to Toramana of Huna heritage. His father ruled the Indian part of the Hephthalite Empire. Mihirakula ruled from his capital of Sagala (modern-day Sialkot, Pakistan). In around 520 CE, the Chinese monk Song Yun met with Mihirakula. According to the 7th-century travelogue of the Chinese Buddhist pilgrim and student Xuanzang, Mihirakula ruled several hundreds of years before his visit, was initially interested in Buddhism, and sought a Buddhist teacher from monasteries in his domain. They did not send him a learned Buddhist scholar. Feeling insulted, he became anti-Buddhist and destroyed the monasteries in his kingdom.Li Rongxi (1996), ''The Great Tang Dynasty Record of the Western Regions'', B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eran
Eran is an ancient town and archaeological site in the Sagar district of Madhya Pradesh, India. It was one of the ancient mints for Indian dynasties as evidenced by the diverse coins excavated here. The site has 5th and 6th-century Gupta era temples and monuments, particularly the colossal stone boar with sages and scholars depicted on the body of the sculpture. The inscription stones found at Eran are important to reconstructing the chronology of Gupta Empire history. Eran or Erakina was the capital of ''Erakina (Airikina) Pradesha'' or ''Airkina Vishaya'', an administrative division of the Gupta empire. Etymology The ancient name of Eran ( sa, ऐरण), ''Erakaina'', ''Erakanya'' or ''Erakina'' (as mentioned in the inscriptions); ''Airikina'' ( sa, ऐरिकिण, as mentioned in the inscription of Samudragupta) or ''Erikina'' (as mentioned in the inscription of Toramana) is derived from ''Eraka''. The word ''erakā'' probably refers to a tall grass commonly called the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gwalior Inscription Of Mihirakula
The Gwalior Inscription of Mihirakula is a Sanskrit inscription recording the construction of a Surya temple from stone on the Gopa hill of Gwalior. Though now referred with the name of Mihirakula, the temple and the inscription was commissioned by Matricheta. The original temple is lost, and the inscribed red-sandstone slab was found in 1861 by Alexander Cunningham in the porch of another temple, and published in 1861. This inscribed stone from Gwalior was moved shortly after its discovery to the Kolkata museum for preservation. Several translations of it have been published thereafter. It is damaged, its script is the northern class of ancient Gupta script and the entire composition is in poetic verse. It is notable for mentioning a Sun temple in the first part of the sixth century CE, and the rule of the two Hūṇa kings Toramana and Mihirakula. Location Gwalior is located in northern Madhya Pradesh, India. The shrine probably stood on the edge of the tank known as Surāj Kuṇ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aulikaras
The Aulikaras (Late Brahmi script: ''Au-li-ka-rā''), also referred to as Aulikara dynasty or Olikara dynasty, were an ancient Indian clan from the Maurya era, that emerged into a kingdom between the 4th-century CE and 6th-century CE. They were based in the Malwa (Malawa) region of central India near Mandsaur, with their power center near what is now western Madhya Pradesh, southeastern Rajasthan and northeastern Gujarat. Two royal houses belonging to this clan ruled over the present-day western Malwa region of Madhya Pradesh state from c. 350 CE to 550 CE, much of it as feudatories of the Gupta Empire. Several major and important inscriptions of Aulikaras are known. These inscriptions suggest that they were Hindus who built several notable temples in the Gupta-style to Shiva, Surya and Vishnu, as well as Buddhist monasteries, in western Madhya Pradesh and east Rajasthan. Among these, the notable ruins are in the region near Mandsaur and the Dara Mukundara valley passage betw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt Range
The Salt Range ( pnb, ) is a mountain range in the north of Punjab province of Pakistan, deriving its name from its extensive deposits of rock salt. The range extends along the south of the Potohar Plateau and the north of the Jhelum River. The Salt Range contains the great mines of Khewra, Kalabagh and Warcha which yield vast supplies of salt. Coal of a medium quality is also found. In the Himalayan and Salt Range, rock containing fossil of marine life go back to the Ediacaran period (up to 570 million years ago), which shows these rocks have developed out of sea sediments, and that where we have the Himalayas now was once a sea. *Sakaser is the highest peak of Salt Range. *Namal Lake, Khabikki Lake and Uchhali Lake are lakes in the Salt Range. History An inscription found at Kura in the Salt Range records the building of a Buddhist monastery by a person named Rotta Siddhavriddhi during the reign of the Huna ruler Toramana. The donor expresses the wish that the religious mer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mehama
Mehama ( Bactrian: ''Meyam'', Brahmi: ''Me-ha-ma''), ruled c.461-493, was a king of Alchon Huns dynasty. He is little known, but the Talagan copper scroll mentions him as an active ruler making a donation to a Buddhist stupa in 492/93.For an image of the copper scroll: Coin Cabinet of the Kunsthistorisches Museum ViennShowcase 8/ref> At that time, it is considered that the Alchon Huns were firmly in charge of the Buddhist region around Taxila, but had not yet started to conquer the Indian mainland. Mehama is named ''Maha Shahi Mehama'' (Great Lord Mehama) in the Talagan copper scroll. Mehama appears in a letter in the Bactrian language he wrote in 461-462 CE. The letter comes from the archives of the Kingdom of Rob, located in southern Bactria. In this letter he presents himself as: Kadag is Kadagstan, an area in southern Bactria, in the region of Baghlan. Significantly, he presents himself as a vassal of the Sasanian Empire king Peroz I. Mehama (r.461-493) allied with Sasa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
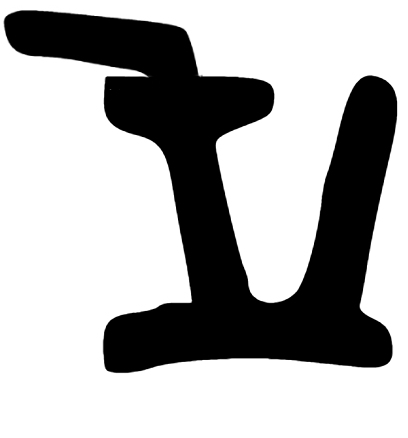
Gupta Allahabad J
Gupta () is a common surname or last name of Indian origin. It is based on the Sanskrit word गोप्तृ ''goptṛ'', which means 'guardian' or 'protector'. According to historian R. C. Majumdar, the surname ''Gupta'' was adopted by several different communities in northern and eastern India at different times. In Bengal The Rāmpāl plate of Srichandra mentions a line of Brahmins who had Gupta as their surname. In Bengal region, the surname is found among Baidyas (mainly) as well as Kayasthas. In Northern India The Gupta surname is also used by Banias and Jains in the northern part of India. Notables Monarchs *Gupta (king), founder of the Gupta dynasty *Ghatotkacha (king) *Chandragupta I *Samudragupta *Chandragupta II, also known as Chandragupta Vikramaditya *Kumaragupta I *Skandagupta, last Gupta emperor *Vishnugupta (Gupta Empire) *Budhagupta Academic *Akhil Gupta (born 1959), professor at the University of California, Los Angeles, in the field of social ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gupta Ashoka Haa
Gupta () is a common surname or last name of Indian origin. It is based on the Sanskrit word गोप्तृ ''goptṛ'', which means 'guardian' or 'protector'. According to historian R. C. Majumdar, the surname ''Gupta'' was adopted by several different communities in northern and eastern India at different times. In Bengal The Rāmpāl plate of Srichandra mentions a line of Brahmins who had Gupta as their surname. In Bengal region, the surname is found among Baidyas (mainly) as well as Kayasthas. In Northern India The Gupta surname is also used by Banias and Jains in the northern part of India. Notables Monarchs *Gupta (king), founder of the Gupta dynasty *Ghatotkacha (king) *Chandragupta I *Samudragupta *Chandragupta II, also known as Chandragupta Vikramaditya *Kumaragupta I *Skandagupta, last Gupta emperor *Vishnugupta (Gupta Empire) *Budhagupta Academic *Akhil Gupta (born 1959), professor at the University of California, Los Angeles, in the field of social ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |