|
Tombstone Junction
Tombstone Junction was a small, Western-town-themed park located on Kentucky Route 90 in McCreary County, Kentucky near the Cumberland Falls State Resort Park. It began operating in the 1960s and continued uninterrupted until it was heavily damaged by fire in 1989. The park continued with limited operation until it was completely destroyed by a second fire in 1991. The venue featured a recreation of a small, Western frontier town complete with train station, working saloon, dance hall, jailhouse, shanties, and shops. There was also an outdoor amphitheater that hosted live shows featuring country and western music of the period. The leading attraction at Tombstone Junction was a 2 1/2 mile ride aboard a full-sized standard gauge, standard-gauge operating Steam locomotive, steam train. Background The park developed from the building and operation of a tourist railroad attraction called the "Cumberland Falls Scenic Railroad" in the 1960s. The railroad was built by Millard and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loretta Lynn
Loretta Lynn (; April 14, 1932 – October 4, 2022) was an American country music singer and songwriter. In a career spanning six decades, Lynn released multiple gold albums. She had numerous hits such as " You Ain't Woman Enough (To Take My Man)", " Don't Come Home A-Drinkin' (With Lovin' on Your Mind)", "One's on the Way", "Fist City", and " Coal Miner's Daughter". In 1980, the film '' Coal Miner's Daughter'' was made based on her life. Lynn received many awards and other accolades for her groundbreaking role in country music, including awards from both the Country Music Association and Academy of Country Music as a duet partner and an individual artist. She was nominated 18 times for a Grammy Award, and won three times. , Lynn was the most awarded female country recording artist, and the only female ACM Artist of the Decade (1970s). Lynn scored 24 No. 1 hit singles and 11 number one albums. She ended 57 years of touring on the road after she suffered a stroke in 2017 and br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kentucky Railway Museum
The Kentucky Railway Museum, now located in New Haven, Kentucky, United States, is a non-profit railroad museum dedicated to educating the public regarding the history and heritage of Kentucky's railroads and the people who built them. Originally created in 1954 in Louisville, Kentucky, the museum is at its third location, in extreme southern Nelson County. It is one of the oldest railroad stations in the United States.Kleber p.478 The museum owns four steam locomotives, twelve diesel locomotives and over a hundred pieces of rolling stock. Four of the pieces are separately on the National Register of Historic Places: the Louisville and Nashville Steam Locomotive No. 152, the Louisville and Nashville Combine Car Number 665, the Mt. Broderick Pullman Lounge-Obs-Sleeping Car, and the Frankfort and Cincinnati Model 55 Rail Car. History The site of the current museum was built by the Louisville and Nashville Railroad from 1856 to 1857, on their old line, which ran to Lebanon, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltimore And Ohio Railroad
The Baltimore and Ohio Railroad was the first common carrier railroad and the oldest railroad in the United States, with its first section opening in 1830. Merchants from Baltimore, which had benefited to some extent from the construction of the National Road early in the century, wanted to do business with settlers crossing the Appalachian Mountains. The railroad faced competition from several existing and proposed enterprises, including the Albany-Schenectady Turnpike, built in 1797, the Erie Canal, which opened in 1825, and the Chesapeake and Ohio Canal. At first, the B&O was located entirely in the state of Maryland; its original line extending from the port of Baltimore west to Sandy Hook, Maryland, opened in 1834. There it connected with Harper's Ferry, first by boat, then by the Wager Bridge, across the Potomac River into Virginia, and also with the navigable Shenandoah River. Because of competition with the C&O Canal for trade with coal fields in western Maryland, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Block Letters
Block letters (known as printscript, manuscript, print writing or ball and stick in academics) are a sans-serif (or "gothic") style of writing Latin script in which the letters are individual glyphs, with no joining. Elementary education in English-speaking countries typically introduces children to the literacy of handwriting using a method of block letters, which may later advance to cursive (joined) penmanship. The policy of teaching cursive in American elementary schools has varied over time, from strict endorsement such as the Palmer method in the early 20th century, to removal by Common Core in 2010, to being reinstated. On official forms, one is often asked to "please print". This is because cursive handwriting is harder to read, and the glyphs are joined so they do not fit neatly into separate boxes. Block letters may also be used as a synonym of block capitals, which means writing in all capital letters or in large and small capital letters, imitating the style of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livery
A livery is an identifying design, such as a uniform, ornament, symbol or insignia that designates ownership or affiliation, often found on an individual or vehicle. Livery will often have elements of the heraldry relating to the individual or corporate body feature in the livery. Alternatively, some kind of a personal emblem or badge, or a distinctive colour, is featured. The word itself derives from the French ''livrée'', meaning ''dispensed, handed over''. Most often it would indicate that the wearer of the livery was a servant, dependant, follower or friend of the owner of the livery, or, in the case of objects, that the object belonged to them. In the late medieval phenomenon of bastard feudalism, livery badges worn by the "retainers" of great lords, sometimes in effect private armies, became a great political concern in England. Etymology "In the ''Black'' Book of 1483, it was laid down that each person should receive "... for his Livery at night, half a chet loaf, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stearns, Kentucky
Stearns is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in McCreary County, Kentucky, United States. The population was 1,365 at the 2020 census. It was founded by Justus Smith Stearns. Geography Stearns is located in south-central McCreary County at (36.697976, -84.476776). It is bordered to the north by Whitley City, the county seat, and to the south by Pine Knot. The unincorporated community of Revelo is partly within the Stearns CDP, along its southern border. U.S. Route 27 runs along the eastern edge of Stearns, leading north through Whitley City to Somerset and south to Oneida, Tennessee. Kentucky Route 92 passes through the center of Stearns and leads west to Monticello. Eastbound KY 92 joins US 27 south to Pine Knot, then turns east to lead to Williamsburg. According to the United States Census Bureau, the Stearns CDP has a total area of , of which , or 0.84%, are water. The community is drained to the west by tributaries of Roaring Paunch Creek, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kentucky And Tennessee Railway
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper South. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north; West Virginia and Virginia to the east; Tennessee to the south; and Missouri to the west. Its northern border is defined by the Ohio River. Its capital is Frankfort, and its two largest cities are Louisville and Lexington. Its population was approximately 4.5 million in 2020. Kentucky was admitted into the Union as the 15th state on June 1, 1792, splitting from Virginia in the process. It is known as the "Bluegrass State", a nickname based on Kentucky bluegrass, a species of green grass found in many of its pastures, which has supported the thoroughbred horse industry in the center of the state. Historically, it was known for excellent farming conditions for this reason and the development of large tobacco plantations akin to those in Virginia and North Carolina in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morehead, Kentucky
Morehead is a list of Kentucky cities, home rule-class city located along U.S. Route 60 in Kentucky, US 60 (the historic Midland Trail) and Interstate 64 in Kentucky, Interstate 64 in Rowan County, Kentucky, Rowan County, Kentucky, in the United States. It is the county seat, seat of its county. The population was 6,845 at the time of the 2010 U.S. census. It was the focal point of the Rowan County War and is the home of Morehead State University. History Initial settlement The first European settlers came to Rowan County from Virginia following the end of the American Revolutionary War in 1783. In 1854, Morehead became the third community to be settled in the county. Colonel John Hargis (Kentucky settler), John Hargis founded the city after purchasing land in the area. The city was named after James Turner Morehead (Kentucky politician), James T Morehead, a politician who served as governor of Kentucky from 1834 to 1836. Rowan County came into existence in May 1856, seceding fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Locomotive Company
The American Locomotive Company (often shortened to ALCO, ALCo or Alco) was an American manufacturer of locomotives, diesel generators, steel, and tanks that operated from 1901 to 1969. The company was formed by the merger of seven smaller locomotive manufacturers and Schenectady Locomotive Works, Schenectady Locomotive Engine Manufactory of Schenectady, New York. A subsidiary, American Locomotive Automobile Company, designed and manufactured automobiles under the Alco brand from 1905 to 1913. ALCO also produced nuclear reactors from 1954 to 1962. The company changed its name to Alco Products, Incorporated in 1955. In 1964, the Worthington Corporation acquired the company. The company went out of business in 1969. The ALCO name is currently being used by Fairbanks-Morse, Fairbanks Morse Engine for their FM, ALCO line. Foundation and early history The company was created in 1901 from the merger of seven smaller locomotive manufacturers with Schenectady Locomotive Works, Schenect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
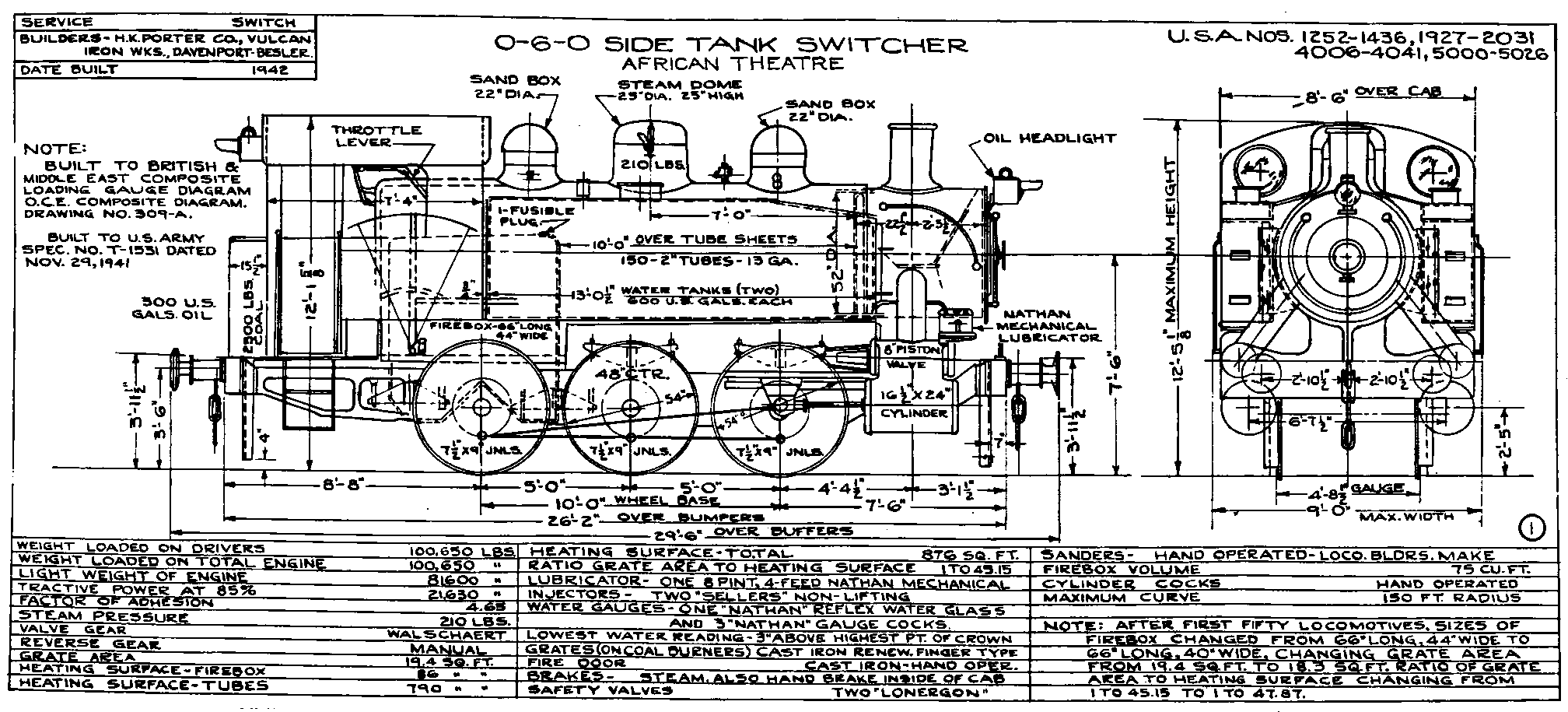
United States Army Transportation Corps Class S100
The United States Army Transportation Corps (USATC) S100 Class is a 0-6-0 steam locomotive that was designed for switching (shunting) duties in Europe and North Africa during World War II. After the war, they were used on railways in Austria, China, Egypt, France, Great Britain, Greece, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Italy, the Netherlands, Palestine, the United States, and Yugoslavia. Wartime development and use The S100 is a side tank design by Col. Howard G. Hill. In 1942, the USATC ordered 382 S100s from Davenport Locomotive Works of Iowa, H. K. Porter, Inc, of Pittsburgh and Vulcan Iron Works of Wilkes-Barre. They were shipped to Great Britain in 1943, where they were stored until 1944. After D-Day, they were shipped to Continental Europe. Construction Use after the Second World War After the Second World War, SNCF bought 77 S100's and designated them class 030TU. Jugoslovenske železnice (Yugoslav State Railways) bought many S100's and designated them class 62. In the 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locomotive
A locomotive or engine is a rail transport vehicle that provides the Power (physics), motive power for a train. If a locomotive is capable of carrying a payload, it is usually rather referred to as a multiple unit, Motor coach (rail), motor coach, railcar or power car; the use of these self-propelled vehicles is increasingly common for passenger trains, but rare for freight (see CargoSprinter). Traditionally, locomotives pulled trains from the front. However, Push-pull train, push-pull operation has become common, where the train may have a locomotive (or locomotives) at the front, at the rear, or at each end. Most recently railroads have begun adopting DPU or distributed power. The front may have one or two locomotives followed by a mid-train locomotive that is controlled remotely from the lead unit. __TOC__ Etymology The word ''locomotive'' originates from the Latin language, Latin 'from a place', Ablative case, ablative of 'place', and the Medieval Latin 'causing mot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_train.jpg)
.jpg)