|
Tom Gehrels
Anton M.J. "Tom" Gehrels (February 21, 1925 – July 11, 2011) was a Dutch–American astronomer, Professor of Planetary Sciences, and Astronomer at the University of Arizona, Tucson. Biography Youth and education Gehrels was born at Haarlemmermeer, the Netherlands on February 21, 1925. He was born in bible-belt Netherlands, and was forced to attend church regularly, an act he despised. When he was older he rejoiced when he found out his childhood church had been destroyed. During World War II he was, as a teenager, active in the Dutch Resistance. After he escaped to England, he was sent back by parachute as an organizer for Special Operations Executive SOE committing sabotage against the German forces. After the war, he attended the University of Leiden where he graduated with a degree in physics and astronomy in 1951. He continued his education at the University of Chicago where he obtained his doctorate in astronomy and astrophysics in 1956 under Professor Gerard P. K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
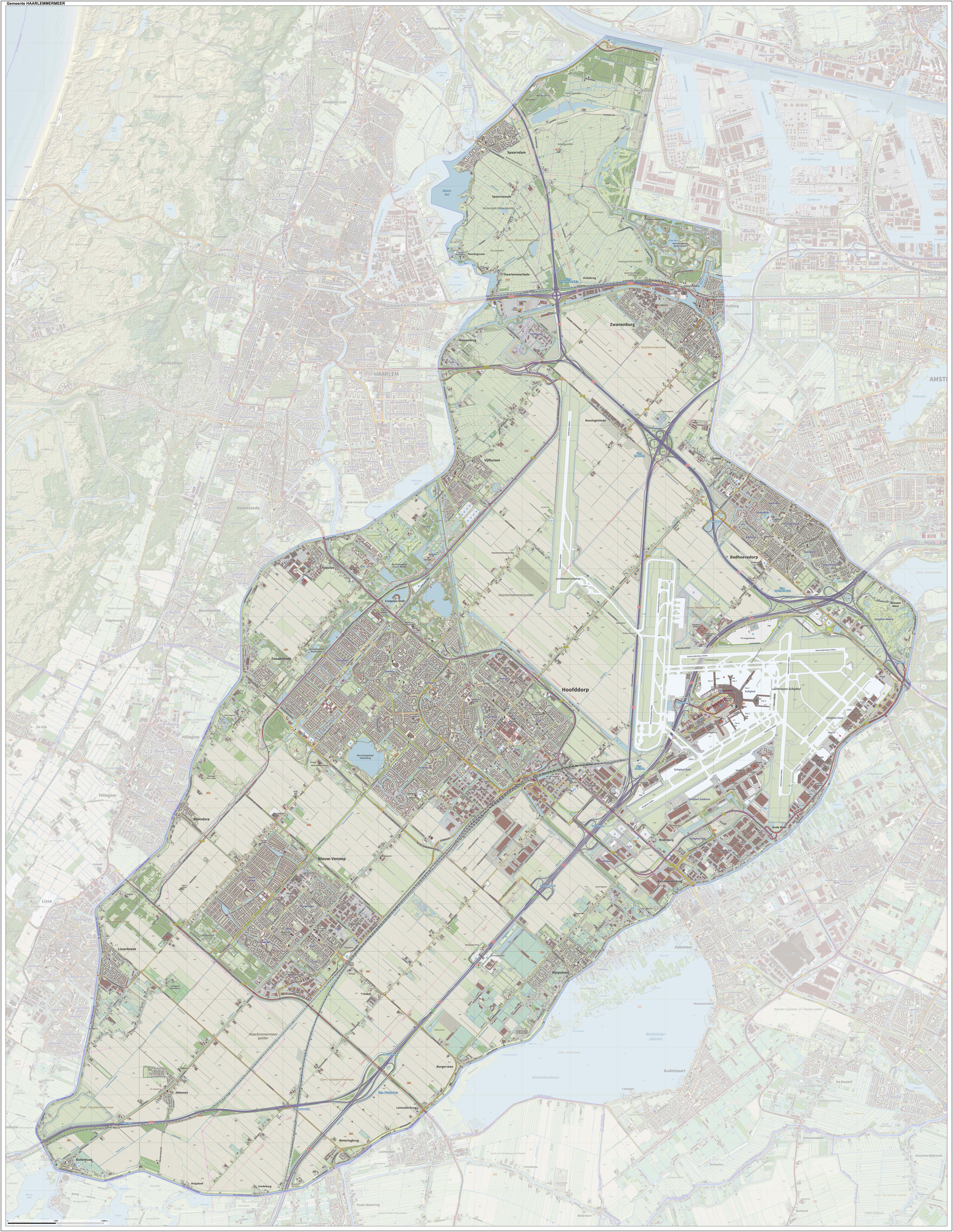
Haarlemmermeer
Haarlemmermeer () is a municipality in the west of the Netherlands, in the province of North Holland. Haarlemmermeer is a polder, consisting of land reclaimed from water. The name Haarlemmermeer means ' Haarlem's lake', referring to the body of water from which the region was reclaimed in the 19th century. Haarlemmermeer's main town is Hoofddorp, which has a population of 76,660. Hoofddorp, along with the rapidly growing towns of Nieuw-Vennep and Badhoevedorp, are part of the Randstad agglomeration. The main international airport of the Netherlands, Schiphol, is located in Haarlemmermeer. History The original Haarlemmermeer lake is said to have been mostly a peat bog, a relic of a northern arm of the Rhine which passed through the district in Roman times. In 1531, the original Haarlemmermeer had an area of , and near it were three smaller lakes: the Leidsche Meer (Leiden Lake), the Spiering Meer, and the Oude Meer (Old Lake), with a combined area of about . The four lakes w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polarization (waves)
Polarization ( also polarisation) is a property applying to transverse waves that specifies the geometrical orientation of the oscillations. In a transverse wave, the direction of the oscillation is perpendicular to the direction of motion of the wave. A simple example of a polarized transverse wave is vibrations traveling along a taut string ''(see image)''; for example, in a musical instrument like a guitar string. Depending on how the string is plucked, the vibrations can be in a vertical direction, horizontal direction, or at any angle perpendicular to the string. In contrast, in longitudinal waves, such as sound waves in a liquid or gas, the displacement of the particles in the oscillation is always in the direction of propagation, so these waves do not exhibit polarization. Transverse waves that exhibit polarization include electromagnetic waves such as light and radio waves, gravitational waves, and transverse sound waves ( shear waves) in solids. An electromagneti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet of the Solar System#Inner solar system, inner Solar System. Sizes and shapes of asteroids vary significantly, ranging from 1-meter rocks to a dwarf planet almost 1000 km in diameter; they are rocky, metallic or icy bodies with no atmosphere. Of the roughly one million known asteroids the greatest number are located between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, approximately 2 to 4 astronomical unit, AU from the Sun, in the main asteroid belt. Asteroids are generally classified to be of three types: C-type asteroid, C-type, M-type asteroid, M-type, and S-type asteroid, S-type. These were named after and are generally identified with carbonaceous, metallic, and silicaceous compositions, respectively. The size of asteroids varies greatly; the largest, Ceres (dwarf planet), Ceres, is almost across and qualifies as a dwarf planet. The total mass of all the asteroids combined is only 3% that of Earth's Moon. The majority of main belt asteroids follow slig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photometry (astronomy)
Photometry, from Greek '' photo-'' ("light") and '' -metry'' ("measure"), is a technique used in astronomy that is concerned with measuring the flux or intensity of light radiated by astronomical objects. This light is measured through a telescope using a photometer, often made using electronic devices such as a CCD photometer or a photoelectric photometer that converts light into an electric current by the photoelectric effect. When calibrated against standard stars (or other light sources) of known intensity and colour, photometers can measure the brightness or apparent magnitude of celestial objects. The methods used to perform photometry depend on the wavelength region under study. At its most basic, photometry is conducted by gathering light and passing it through specialized photometric optical bandpass filters, and then capturing and recording the light energy with a photosensitive instrument. Standard sets of passbands (called a photometric system) are defined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
:Category:Discoveries By Tom Gehrels
This is a category for discoveries by Dutch–American astronomer Tom Gehrels Anton M.J. "Tom" Gehrels (February 21, 1925 – July 11, 2011) was a Dutch–American astronomer, Professor of Planetary Sciences, and Astronomer at the University of Arizona, Tucson. Biography Youth and education Gehrels was born at Haa .... See parent category for proper sortkey usage instructions. Gehrels, Tom History of science and technology in the Netherlands Astronomy in the Netherlands {{CatAutoTOC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2247 Hiroshima
47, 47 or forty-seven may refer to: *47 (number) *47 BC *AD 47 *1947 * 2047 *'47 (brand), an American clothing brand * ''47'' (magazine), an American publication * 47 (song), a song by Sidhu Moose Wala *47, a song by New Found Glory from the album ''Not Without a Fight'' *"Forty Seven", a song by Karma to Burn from the album '' V'', 2011 * +47, the international calling code for Norway *4seven, a television channel *Agent 47, protagonist of the ''Hitman'' video game series *''47'', a young adult novel by Walter Mosley See also * List of highways numbered 47 * Channel 47 (other) * M47 (other), including "Model 47" (M47) * Forty-seven Ronin (other) * A47 (other) A47 may refer to: * Queen's Indian Defense, ''Encyclopaedia of Chess Openings'' code * Focke-Wulf A.47, a meteorological aircraft developed in Germany in 1931 ; roads * A47 road, a road connecting Birmingham and Lowestoft in England ... * Capital Steez {{number disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1979 Sakharov
1979 Sakharov, provisionally designated , is a stony Vestian asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 4.5 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered during the Palomar–Leiden survey in 1960, and named after Russian physicist Andrei Sakharov. Discovery ''Sakharov'' was discovered on 24 September 1960, by the Dutch astronomers Ingrid and Cornelis van Houten, on photographic plates taken by Dutch–American astronomer Tom Gehrels at the U.S. Palomar Observatory in California. Survey designation The survey designation "P-L" stands for ''Palomar–Leiden'', named after Palomar Observatory and Leiden Observatory, which collaborated on the fruitful Palomar–Leiden survey in the 1960s. Gehrels used Palomar's Samuel Oschin telescope (also known as the 48-inch Schmidt Telescope), and shipped the photographic plates to Ingrid and Cornelis van Houten at Leiden Observatory where astrometry was carried out. The trio are credited with the discovery of several t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1873 Agenor
1873 Agenor ( ''prov. designation'': ) is a dark Jupiter trojan from the Trojan camp, approximately in diameter. It was discovered during the Palomar–Leiden Trojan survey in 1971, and later named after Agenor from Greek mythology. The dark Jovian asteroid belongs to the 100 largest Jupiter trojans and has a rotation period of 20.60 hours. Discovery ''Agenor'' was discovered on 25 March 1971, by Dutch astronomer couple Ingrid and Cornelis van Houten at Leiden, on photographic plates taken by Dutch–American astronomer Tom Gehrels at Palomar Observatory in the Palomar Mountain Range, southeast of Los Angeles. Palomar–Leiden survey The discovery was made in a survey of faint Trojans, one night after the discovery of 1870 Glaukos. The trio of Dutch and Dutch–American astronomers also collaborated on the productive Palomar–Leiden survey in the 1960s, using the same procedure as for this (smaller) survey: Tom Gehrels used Palomar's Samuel Oschin telescope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1864 Daedalus
1864 Daedalus, provisional designation , is a stony asteroid and near-Earth object of the Apollo group, approximately 3 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 24 March 1971, by Dutch–American astronomer Tom Gehrels at Palomar Observatory, California, and named after Daedalus from Greek mythology. Orbit and classification ''Daedalus'' is a member of the Apollo asteroids, a group of near-Earth object with an Earth-crossing orbit. It orbits the Sun in the inner main-belt at a distance of 0.6–2.4 AU once every 1 years and 9 months (645 days). Its orbit has an eccentricity of 0.61 and an inclination of 22 ° with respect to the ecliptic. It has an Earth ''Minimum orbit intersection distance'' ( MOID) of 0.2693 AU. Physical characteristics ''Daedalus'' is a stony asteroid, characterized as an SQ and Sr spectral type in the Tholen and SMASS taxonomy. Diameter and albedo According to the survey carried out by NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1778 Alfvén
1778 Alfvén, also designated , is a carbonaceous Themistian asteroid from the outer region of the asteroid belt, approximately 20 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 26 September 1960, by astronomers Cornelis van Houten, Ingrid van Houten-Groeneveld and Tom Gehrels at the U.S. Palomar Observatory, in California. It was later named after Swedish Nobelist Hannes Alfvén. Orbit and classification The dark C-type asteroid is a member of the Themis family, a dynamical family of outer-belt asteroids with nearly coplanar ecliptical orbits. ''Alfvén'' orbits the Sun in the outer main-belt at a distance of 2.7–3.6 AU once every 5 years and 7 months (2,038 days). Its orbit has an eccentricity of 0.13 and an inclination of 2 ° with respect to the ecliptic. A first precovery was taken at Lowell Observatory in 1906, extending the body's observation arc by 54 years prior to its official discovery observation. Physical characteristics Rotation period In February ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minor Planet
According to the International Astronomical Union (IAU), a minor planet is an astronomical object in direct orbit around the Sun that is exclusively classified as neither a planet nor a comet. Before 2006, the IAU officially used the term ''minor planet'', but that year's meeting reclassified minor planets and comets into dwarf planets and small Solar System bodies (SSSBs).Press release, IAU 2006 General Assembly: Result of the IAU Resolution votes International Astronomical Union, August 24, 2006. Accessed May 5, 2008. Minor planets include s ( ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |