|
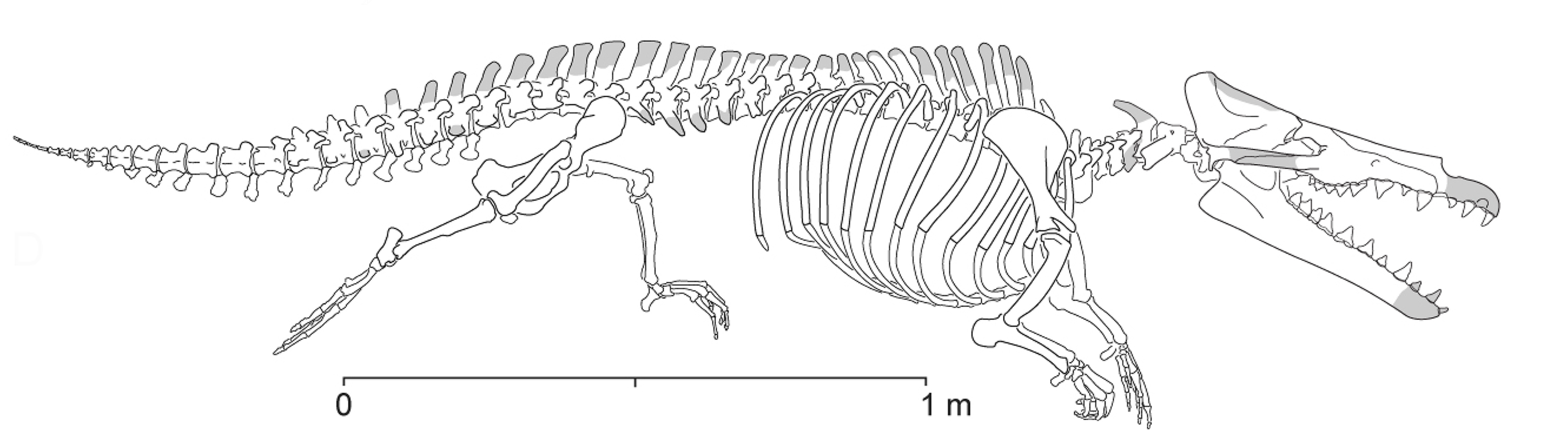
Togocetus
''Togocetus'' (“Togo whale”) is a genus of extinct cetacean from the Lutetian (lower Eocene) of Togo, known from a fossilized skeleton discovered a few kilometers north-east of Lomé. Discovery and description The skeleton was found in a phosphate mining area, Kpogamé-Hahotoé, which is located just north of Lake Togo. It was embedded in a phospharenite bone bed dating back to 46 – 44 million years ago, and overlying an older rock unit, the Tabligbo Group. The remains were described in 2014 by Philip D. Gingerich and Henri Cappetta, who established for it the new monotypic genus ''Togocetus'' and the new species ''T. traversei'', dedicated to Michel Traverse. According to the two authors, ''Togocetus'' was a semiaquatic animal which must have weighed around . It was a protocetid with rather primitive traits such as a still quite long neck, a digitigrade manus and a swim-specialized pes. It shared many similarities with the protocetid genera '' Protocetus'' a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protocetidae
Protocetidae, the protocetids, form a diverse and heterogeneous group of extinct cetaceans known from Asia, Europe, Africa, South America, and North America. Description There were many genera, and some of these are very well known (e.g., '' Rodhocetus''). Known protocetids had large fore- and hindlimbs that could support the body on land, and it is likely that they lived amphibiously: in the sea and on land. It is unclear at present whether protocetids had flukes (the horizontal tail fin of modern cetaceans). However, what is clear is that they are adapted even further to an aquatic life-style. In '' Rodhocetus'', for example, the sacrum – a bone that in land-mammals is a fusion of five vertebrae that connects the pelvis with the rest of the vertebral column – was divided into loose vertebrae. However, the pelvis retain a sacroiliac joint. Furthermore, the nasal openings are now halfway up the snout; a first step towards the telescoped condition in modern whale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', " dawn") and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in comparison with the more common isotope 12C. The end is set at a major extinction event called the ''Grande Coupure'' (the "Great Break" in continuity) or the Eocene–Oligocene extinction event, which may be related to the impact of one or more large bolides in Siberia and in what is now Chesapeake Bay. As with other geologic periods, the strata that define the start and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquatic Locomotion
Aquatic locomotion or swimming is biologically propelled motion through a liquid medium. The simplest propulsive systems are composed of cilia and flagella. Swimming has evolved a number of times in a range of organisms including arthropods, fish, molluscs, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals. Evolution of swimming Swimming evolved a number of times in unrelated lineages. Supposed jellyfish fossils occur in the Ediacaran, but the first free-swimming animals appear in the Early to Middle Cambrian. These are mostly related to the arthropods, and include the Anomalocaridids, which swam by means of lateral lobes in a fashion reminiscent of today's cuttlefish. Cephalopods joined the ranks of the nekton in the late Cambrian, and chordates were probably swimming from the Early Cambrian. Many terrestrial animals retain some capacity to swim, however some have returned to the water and developed the capacities for aquatic locomotion. Most apes (including humans), howeve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene Mammals Of Africa
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', "dawn") and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in comparison with the more common isotope 12C. The end is set at a major extinction event called the ''Grande Coupure'' (the "Great Break" in continuity) or the Eocene–Oligocene extinction event, which may be related to the impact of one or more large bolides in Siberia and in what is now Chesapeake Bay. As with other geologic periods, the strata that define the start and end of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elsevier Science Direct
ScienceDirect is a website which provides access to a large bibliographic database of scientific and medical publications of the Dutch publisher Elsevier. It hosts over 18 million pieces of content from more than 4,000 academic journals and 30,000 e-books of this publisher. The access to the full-text requires subscription, while the bibliographic metadata is free to read. ScienceDirect is operated by Elsevier. It was launched in March 1997. Usage The journals are grouped into four main sections: ''Physical Sciences and Engineering'', ''Life Sciences'', ''Health Sciences'', and ''Social Sciences and Humanities''. Article abstracts are freely available, and access to their full texts (in PDF and, for newer publications, also HTML) generally requires a subscription or pay-per-view purchase unless the content is freely available in open access. Subscriptions to the overall offering hosted on ScienceDirect, rather than to specific titles it carries, are usually acquired through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Paleontology
The ''Journal of Paleontology'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering the field of paleontology. It is published by the Paleontological Society. Indexing The ''Journal of Paleontology'' is indexed in: *BIOSIS Previews *Science Citation Index *The Zoological Record *GeoRef __NOTOC__ The GeoRef database is a bibliographic database that indexes scientific literature in the geosciences, including geology. Coverage ranges from 1666 to the present for North American literature, and 1933 to the present for the rest of t ... References Paleontology journals Publications established in 1927 Academic journals published by learned and professional societies Cambridge University Press academic journals Bimonthly journals Paleontological Society {{paleo-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annales De Paléontologie
''Annales de Paléontologie'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering paleontology. It is published by Elsevier. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', its 2020 impact factor is 0.702. The journal is abstracted and indexed in BIOSIS Previews, PASCAL, FRANCIS, and Scopus. , the editor-in-chief An editor-in-chief (EIC), also known as lead editor or chief editor, is a publication's editorial leader who has final responsibility for its operations and policies. The highest-ranking editor of a publication may also be titled editor, managing ... is Didier Neraudeau. References English-language journals Online-only journals Earth and atmospheric sciences journals {{paleontology-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ear Ossicle
The ossicles (also called auditory ossicles) are three bones in either middle ear that are among the smallest bones in the human body. They serve to transmit sounds from the air to the fluid-filled labyrinth (cochlea). The absence of the auditory ossicles would constitute a moderate-to-severe hearing loss. The term "ossicle" literally means "tiny bone". Though the term may refer to any small bone throughout the body, it typically refers to the malleus, incus, and stapes (hammer, anvil, and stirrup) of the middle ear. Structure The ossicles are, in order from the eardrum to the inner ear (from superficial to deep): the malleus, incus, and stapes, terms that in Latin are translated as "the hammer, anvil, and stirrup". * The malleus ( la, "hammer") articulates with the incus through the incudomalleolar joint and is attached to the tympanic membrane (eardrum), from which vibrational sound pressure motion is passed. * The incus ( la, "anvil") is connected to both the other bones. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Systematic Palaeontology
The ''Journal of Systematic Palaeontolog'y'' (Print: , online: ) is a peer-reviewed scientific journal of palaeontology published by Taylor & Francis on behalf of the British Natural History Museum. , the editor-in-chief is Paul D. Taylor. The journal covers papers on new or poorly known faunas and floras and new approaches to systematics Biological systematics is the study of the diversification of living forms, both past and present, and the relationships among living things through time. Relationships are visualized as evolutionary trees (synonyms: cladograms, phylogenetic tre .... It was established in 2003. According to the '' Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2014 impact factor of 3.727, ranking it second out of 49 journals in the category 'Paleontology'. References External links * Paleontology journals Taylor & Francis academic journals Quarterly journals Publications established in 2003 English-language journals {{paleo-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trigonid
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone tooth", from ''mola'', millstone and ''dens'', tooth. Molars show a great deal of diversity in size and shape across mammal groups. The third molar of humans is sometimes vestigial. Human anatomy In humans, the molar teeth have either four or five cusps. Adult humans have 12 molars, in four groups of three at the back of the mouth. The third, rearmost molar in each group is called a wisdom tooth. It is the last tooth to appear, breaking through the front of the gum at about the age of 20, although this varies from individual to individual. Race can also affect the age at which this occurs, with statistical variations between groups. In some cases, it may not even erupt at all. The human mouth contains upper (maxillary) and lower (man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligament Of Head Of Femur
In human anatomy, the ligament of the head of the femur (round ligament of the femur, ligamentum teres femoris, the foveal ligament, or Fillmore’s ligament) is a ligament located in the hip. It is triangular in shape and somewhat flattened. The ligament is implanted by its apex into the antero-superior part of the fovea capitis femoris and its base is attached by two bands, one into either side of the acetabular notch, and between these bony attachments it blends with the transverse ligament.'' Gray's Anatomy'' (1918), see infobox It is ensheathed by the synovial membrane The synovial membrane (also known as the synovial stratum, synovium or stratum synoviale) is a specialized connective tissue that lines the inner surface of capsules of synovial joints and tendon sheath A tendon sheath is a layer of synovial m ..., and varies greatly in strength in different subjects; occasionally only the synovial fold exists, and in rare cases even this is absent. The ligament of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fovea Capitis Femoris
The femoral head (femur head or head of the femur) is the highest part of the thigh bone (femur). It is supported by the femoral neck. Structure The head is globular and forms rather more than a hemisphere, is directed upward, medialward, and a little forward, the greater part of its convexity being above and in front. The femoral head's surface is smooth. It is coated with cartilage in the fresh state, except over an ovoid depression, the fovea capitis, which is situated a little below and behind the center of the femoral head, and gives attachment to the ligament of head of femur. The thickest region of the articular cartilage is at the centre of the femoral head, measuring up to 2.8 mm. The diameter of the femoral head is usually larger in men than in women. Fovea capitis The fovea capitis is a small, concave depression within the head of the femur that serves as an attachment point for the ligamentum teres (Saladin). It is slightly ovoid in shape and is oriented "superior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |