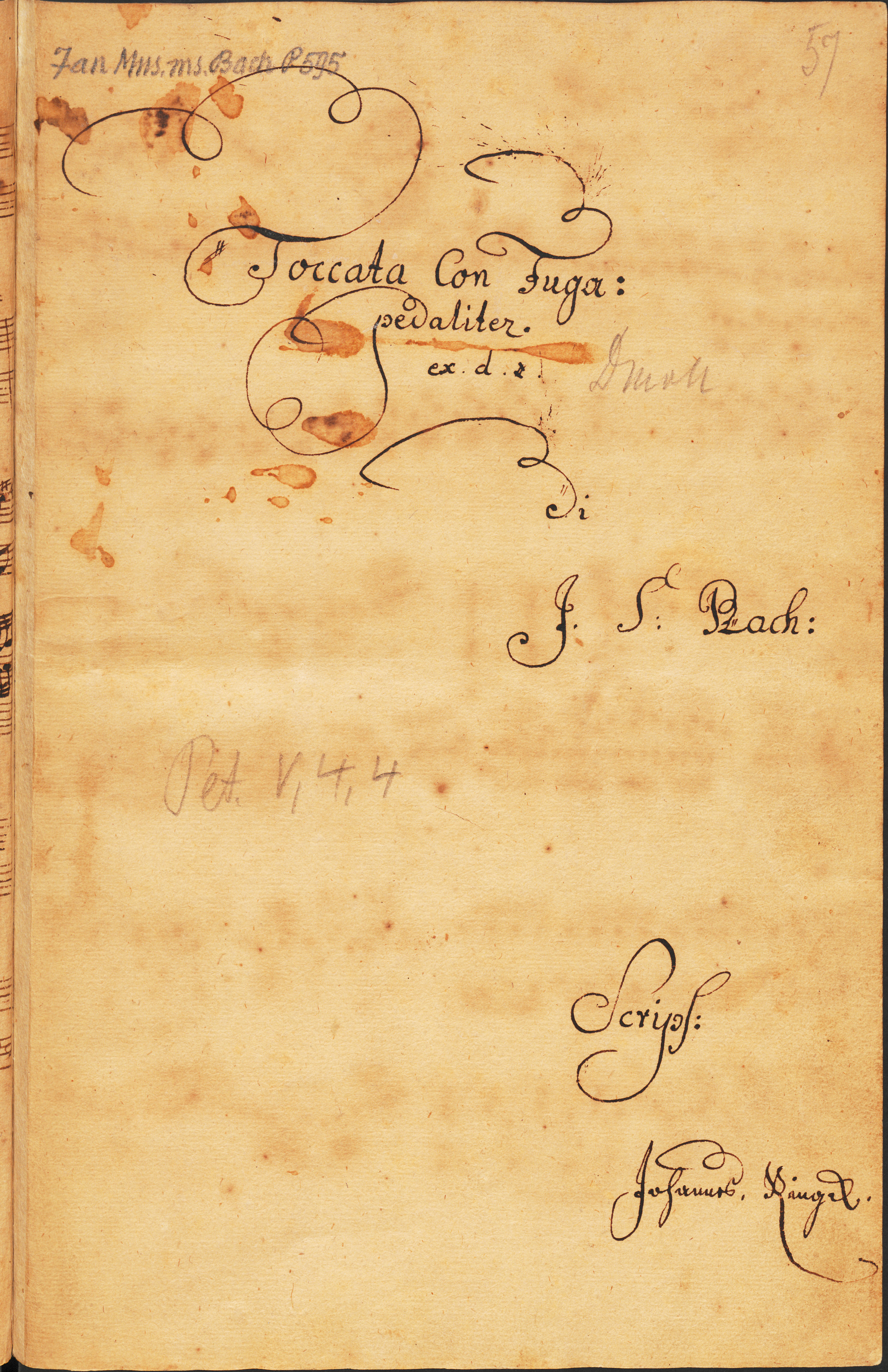|
Toccata And Fugue In D Minor, BWV 565
The Toccata and Fugue in D minor, BWV 565, is a piece of organ music written, according to its oldest extant sources, by Johann Sebastian Bach (1685–1750). The piece opens with a toccata section, followed by a fugue that ends in a coda. Scholars differ as to when it was composed. It could have been as early as . Alternatively, a date as late as the 1750s has been suggested. To a large extent, the piece conforms to the characteristics deemed typical of the north German organ school of the Baroque era with divergent stylistic influences, such as south German characteristics. Despite a profusion of educated guesswork, there is not much that can be said with certainty about the first century of the composition's existence other than that it survived that period in a manuscript written by Johannes Ringk. The first publication of the piece, in the Bach Revival era, was in 1833, through the efforts of Felix Mendelssohn, who also performed the piece in an acclaimed concert in 1840. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ringk Copy - First Page Fragment
Johannes Ringk, or Ringck (26 June 1717 – 24 August 1778), was a German composer and organist. He was born in Frankenhain, in present-day Thuringia, and studied organ with Johann Peter Kellner in Gräfenroda and Gottfried Heinrich Stölzel in Gotha. From 1740 he was a music teacher in Berlin, and in 1754 he was appointed organist of the Marienkirche, where he remained until his death. Contemporaries held a high opinion of his organ playing and ability at fugal extemporisation. He composed organ works, concertos and possibly an opera, but is most remembered today for the numerous copies he made, often the only ones now remaining, of works by more notable composers. Amongst these copies in his hand are Johann Sebastian Bach's cantata ''Weichet nur, betrübte Schatten, BWV 202 ''Weichet nur, betrübte Schatten'' (Dissipate, you troublesome shadows), BWV202, is a secular cantata by Johann Sebastian Bach. It was likely composed for a wedding, but scholars disagree on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absolute Music
Absolute music (sometimes abstract music) is music that is not explicitly 'about' anything; in contrast to program music, it is non- representational.M. C. Horowitz (ed.), ''New Dictionary of the History of Ideas'', , vol.1, p. 5 The idea of absolute music developed at the end of the 18th century in the writings of authors of early German Romanticism, such as Wilhelm Heinrich Wackenroder, Ludwig Tieck and E. T. A. Hoffmann but the term was not coined until 1846 where it was first used by Richard Wagner in a programme to Beethoven's Ninth Symphony. The aesthetic ideas underlying absolute music derive from debates over the relative value of what was known in the early years of aesthetic theory as the fine arts. Kant, in his ''Critique of Judgment'', dismissed music as "more a matter of enjoyment than culture" and "less worth in the judgement of reason than any other of the fine arts" because of its lack of conceptual content, thus treating as a deficit the very feature of music ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gräfenroda
Gräfenroda is a village and a former municipality in the Ilm-Kreis district, in Thuringia, Germany. Since 1 January 2019, it is part of the municipality Geratal. It was the administrative seat of the former ''Verwaltungsgemeinschaft'' Oberes Geratal. Geography The municipal area stretches along the valley of the Wilde Gera river and its Lütsche tributary, northeast of the Thuringian Forest mountain range and the Rennsteig ridge. The Lütsche Reservoir built in 1935-38 is located west of the settlement. The municipality has access to the Bundesautobahn 71 near the Rennsteig Tunnel at Gräfenroda junction, about to the southeast. With a population of about 3200, Gräfenroda is the district's fourth-largest municipality, though without town privileges. History Gräfenroda was first mentioned in a 1290 deed, located on an important trade route from Arnstadt to Suhl. From the early 14th century onwards, the local estates were held by the Thuringian noble house of Schwarzburg. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Peter Kellner
Johann Peter Kellner (variants: Keller, Kelner) (28 September 1705 – 19 April 1772) was a German organist and composer. He was the father of Johann Christoph Kellner. Biography He was born in Gräfenroda, Thuringia, and was intended by his parents to follow his father into a career as a lamp-black merchant. He was devoted to music from childhood, and first learnt singing from the cantor Johann Peter Nagel and keyboard from his son Johann Heinrich Nagel. He studied for a year from 1720 with the organist Johann Schmidt in Zella, followed by a year with the organist Hieronymus Florentius Quehl (or Kehl) in Suhl, during which time he also studied composition. He knew Johann Sebastian Bach well, although it is not known whether he was taught by him. He was also acquainted with George Frideric Handel. In 1722, he returned to work as a tutor at Gräfenroda for three years. He was appointed cantor of Frankenhain in October 1725, returning to Gräfenroda in December 1727 as assistan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Claude Zehnder
Jean-Claude Zehnder (born 1941) is a Swiss organist in church and concert, harpsichordist, and musicologist. In research and playing, he is focused on Baroque music, and has played and recorded at historic organs in Europe. He led the department for organ at the Schola Cantorum Basiliensis from 1972 to 2006. His publications include books and music editions, such as organ works by Johann Sebastian Bach. Career Born in Winterthur, Zehnder studied at the conservatory of his hometown, at the University of Zurich, at the Musikakademie Wien with Anton Heiller, and in Amsterdam with Gustav Leonhardt. He was from 1966 church musician (organist and choral conductor) at the Protestant church in Frauenfeld, and taught organ and harpsichord at the Konservatorium Winterthur. He directed the organ class of the Schola Cantorum Basiliensis from 1972 to 2006. He is the organist of the Silbermann organ at the Dom zu Arlesheim. His publications focus on topics such as the early works ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breitkopf & Härtel
Breitkopf & Härtel is the world's oldest music publishing house. The firm was founded in 1719 in Leipzig by Bernhard Christoph Breitkopf. The catalogue currently contains over 1,000 composers, 8,000 works and 15,000 music editions or books on music. The name "Härtel" was added when Gottfried Christoph Härtel took over the company in 1795. In 1807, Härtel began to manufacture pianos, an endeavour which lasted until 1870. The Breitkopf pianos were highly esteemed in the 19th century by pianists like Franz Liszt and Clara Schumann. In the 19th century the company was for many years the publisher of the '' Allgemeine musikalische Zeitung'', an influential music journal. The company has consistently supported contemporary composers and had close editorial collaboration with Beethoven, Haydn, Mendelssohn, Schumann, Chopin, Liszt, Wagner and Brahms. In the 19th century they also published the first "complete works" editions of various composers, for instance Bach (the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Bach Edition
The New Bach Edition (NBE) (german: Neue Bach-Ausgabe; NBA), is the second complete edition of the music of Johann Sebastian Bach, published by Bärenreiter. The name is short for Johann Sebastian Bach (1685–1750): New Edition of the Complete Works (''Johann Sebastian Bach (1685–1750): Neue Ausgabe sämtlicher Werke''). It is a historical-critical edition (German: ''historisch-kritische Ausgabe'') of Bach's complete works by the Johann Sebastian Bach Institute (Johann-Sebastian-Bach-Institut) in Göttingen and the Bach Archive (Bach-Archiv) in Leipzig, When Bach died most of his work was unpublished. The first complete edition of Bach's music was published in the second half of the nineteenth century by the Bach Gesellschaft (Bach-Gesellschaft Ausgabe, BGA). The second complete edition includes some discoveries made since 1900, but there are relatively few such scores. The significance of the NBE lies more in its incorporation of the latest scholarship. Although the NBE is an u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dietrich Kilian
Dietrich Kilian (3 May 1928 – 6 September 1984) was a German musicologist. Career Kilian was born in Roßlau. He studied at the Freie Universität Berlin and earned the doctorate in 1956 with a thesis "Das Vokalwerk D. Buxtehudes – Quellenstudien zu seiner Überlieferung und Verwendung" (The vocal works by D. Buxtehude – study of the sources regarding tradition and use). He was from 1958 an editor of the Neue Bach-Ausgabe, the critical edition of the complete works by Johann Sebastian Bach, editing, including critical reports, for the rest of his life, on the cantatas (I/13), the orchestral works (VII/3) and the organ works (IV/5–7). With Alfred Dürr and Klaus Hofmann and others, he authored ''Kritischer Bericht'' (Critical Commentary). He rediscovered and published in 1963 the prelude in C major by Buxtehude (BuxWV 138). Selected works *''Neue Ausgabe sämtlicher Werke: Serie 1, Kantaten. Bd. 13. Kantaten zum 1. Pfingsttag. Kritischer Bericht'', Deutscher Ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ringk (score)
Johannes Ringk, or Ringck (26 June 1717 – 24 August 1778), was a German composer and organist. He was born in Frankenhain, in present-day Thuringia, and studied organ with Johann Peter Kellner in Gräfenroda and Gottfried Heinrich Stölzel in Gotha. From 1740 he was a music teacher in Berlin, and in 1754 he was appointed organist of the Marienkirche, where he remained until his death. Contemporaries held a high opinion of his organ playing and ability at fugal extemporisation. He composed organ works, concertos and possibly an opera, but is most remembered today for the numerous copies he made, often the only ones now remaining, of works by more notable composers. Amongst these copies in his hand are Johann Sebastian Bach's cantata ''Weichet nur, betrübte Schatten, BWV 202 ''Weichet nur, betrübte Schatten'' (Dissipate, you troublesome shadows), BWV202, is a secular cantata by Johann Sebastian Bach. It was likely composed for a wedding, but scholars disagree on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Répertoire International Des Sources Musicales
A repertoire () is a list or set of dramas, operas, musical compositions or roles which a company or person is prepared to perform. Musicians often have a musical repertoire. The first known use of the word ''repertoire'' was in 1847. It is a loanword from the French language, as (), with a similar meaning in the arts. This word, in turn, has its origin in the Late Latin word ''repertorium''. The concept of a basic repertoire has been extended to refer to groups which focus mainly on performing standard works, as in repertory theater or repertoire ballet. See also * setlist – a list of works for a specific performance * playlist – a list of works available to play * signature song A signature (; from la, signare, "to sign") is a Handwriting, handwritten (and often Stylization, stylized) depiction of someone's name, nickname, or even a simple "X" or other mark that a person writes on documents as a proof of identity and ... – a musical composition most associ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berlin State Library
The Berlin State Library (german: Staatsbibliothek zu Berlin; officially abbreviated as ''SBB'', colloquially ''Stabi'') is a universal library in Berlin, Germany and a property of the Prussian Cultural Heritage Foundation. It is one of the largest libraries in Europe, and one of the most important academic research libraries in the German-speaking world. It collects texts, media and cultural works from all fields in all languages, from all time periods and all countries of the world, which are of interest for academic and research purposes. Some famous items in its collection include the oldest biblical illustrations in the fifth-century Quedlinburg Itala fragment, a Gutenberg Bible, the main autograph collection of Goethe, the world's largest collection of Johann Sebastian Bach's and Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart's manuscripts, and the original score of Ludwig van Beethoven's Symphony No. 9. Central functions and cooperation with other libraries The SBB is one of six libraries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zehnder 2011 (score)
Zehnder is a German-language surname, mostly Swiss in origin: * Zehnder (surname) It may also refer to the following: *Conley–Zehnder theorem, a mathematical theorem named after Charles C. Conley and Eduard Zehnder * Mach–Zehnder interferometer, a device used in physics * Egon Zehnder, a global executive search firm based in Switzerland *Zehnder Confair Zehnder Harry "Dick" Confair (January 11, 1906 – January 26, 1982) was an American politician from Pennsylvania who served as a Republican member of the Pennsylvania State Senate for the 24th district from 1959 to 1968 and the 23rd district f ..., American politician * Zehnder's, a large restaurant in Frankenmuth, Michigan {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |