|
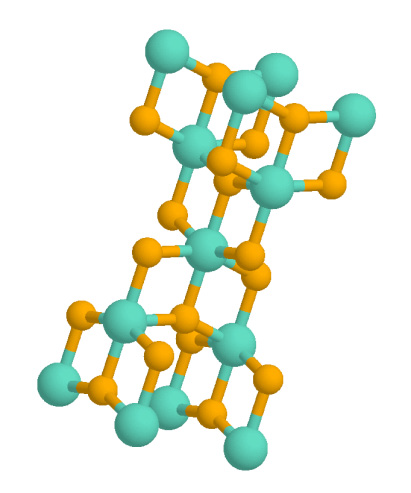
Titanium(II) Oxide
Titanium(II) oxide ( Ti O) is an inorganic chemical compound of titanium and oxygen. It can be prepared from titanium dioxide and titanium metal at 1500 °C. It is non-stoichiometric in a range TiO0.7 to TiO1.3 and this is caused by vacancies of either Ti or O in the defect rock salt structure. In pure TiO 15% of both Ti and O sites are vacant, as the vacancies allow metal-metal bonding between adjacent Ti centres. Careful annealing can cause ordering of the vacancies producing a monoclinic form which has 5 TiO units in the primitive cell that exhibits lower resistivity. A high temperature form with titanium atoms with trigonal prismatic coordination is also known. Acid solutions of TiO are stable for a short time then decompose to give hydrogen: :2 Ti2+(aq) + 2 H+(aq) → 2 Ti3+(aq) + H2(g) Gas-phase TiO shows strong bands in the optical spectra of cool ( M-type) stars. In 2017, TiO was claimed to be detected in an exoplanet An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a plan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanium(III) Oxide
Titanium(III) oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Titanium, Ti2oxide, O3. A black semiconducting solid, it is prepared by reducing titanium dioxide with Titanium, titanium metal at 1600 °C. Ti2O3 adopts the alumina, Al2O3 (corundum) structure. It is reactive with oxidising agents. At around 200 °C there is a transition from semiconducting to metallic conducting. Titanium(III) oxide occurs naturally as the extremely rare mineral tistarite. Other titanium(III) oxides include LiTi2O4 and LiTiO2. References Titanium(III) compounds Sesquioxides Transition metal oxides Semiconductor materials {{inorganic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-stoichiometric
In chemistry, non-stoichiometric compounds are chemical compounds, almost always solid inorganic compounds, having elemental composition whose proportions cannot be represented by a ratio of small natural numbers (i.e. an empirical formula); most often, in such materials, some small percentage of atoms are missing or too many atoms are packed into an otherwise perfect lattice work. Contrary to earlier definitions, modern understanding of non-stoichiometric compounds view them as homogeneous, and not mixtures of stoichiometric chemical compounds. Since the solids are overall electrically neutral, the defect is compensated by a change in the charge of other atoms in the solid, either by changing their oxidation state, or by replacing them with atoms of different elements with a different charge. Many metal oxides and sulfides have non-stoichiometric examples; for example, stoichiometric iron(II) oxide, which is rare, has the formula , whereas the more common material is nonstoichi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-stoichiometric Compounds
In chemistry, non-stoichiometric compounds are chemical compounds, almost always solid inorganic compounds, having elemental composition whose proportions cannot be represented by a ratio of small natural numbers (i.e. an empirical formula); most often, in such materials, some small percentage of atoms are missing or too many atoms are packed into an otherwise perfect lattice work. Contrary to earlier definitions, modern understanding of non-stoichiometric compounds view them as homogeneous, and not mixtures of stoichiometric chemical compounds. Since the solids are overall electrically neutral, the defect is compensated by a change in the charge of other atoms in the solid, either by changing their oxidation state, or by replacing them with atoms of different elements with a different charge. Many metal oxides and sulfides have non-stoichiometric examples; for example, stoichiometric iron(II) oxide, which is rare, has the formula , whereas the more common material is nonstoichi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanium(II) Compounds
Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in sea water, aqua regia, and chlorine. Titanium was discovered in Cornwall, Great Britain, by William Gregor in 1791 and was named by Martin Heinrich Klaproth after the Titans of Greek mythology. The element occurs within a number of minerals, principally rutile and ilmenite, which are widely distributed in the Earth's crust and lithosphere; it is found in almost all living things, as well as bodies of water, rocks, and soils. The metal is extracted from its principal mineral ores by the Kroll and Hunter processes. The most common compound, titanium dioxide, is a popular photocatalyst and is used in the manufacture of white pigments. Other compounds include titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4), a component of smoke screens and catalysts; and titan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature (journal)
''Nature'' is a British weekly scientific journal founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, ''Nature'' features peer-reviewed research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. It has core editorial offices across the United States, continental Europe, and Asia under the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature. ''Nature'' was one of the world's most cited scientific journals by the Science Edition of the 2019 ''Journal Citation Reports'' (with an ascribed impact factor of 42.778), making it one of the world's most-read and most prestigious academic journals. , it claimed an online readership of about three million unique readers per month. Founded in autumn 1869, ''Nature'' was first circulated by Norman Lockyer and Alexander Macmillan as a public forum for scientific innovations. The mid-20th century facilitated an editorial expansion for the journal; ''Nature'' redoubled its efforts in exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monthly Notices Of The Royal Astronomical Society
''Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society'' (MNRAS) is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research in astronomy and astrophysics. It has been in continuous existence since 1827 and publishes letters and papers reporting original research in relevant fields. Despite the name, the journal is no longer monthly, nor does it carry the notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. History The first issue of MNRAS was published on 9 February 1827 as ''Monthly Notices of the Astronomical Society of London'' and it has been in continuous publication ever since. It took its current name from the second volume, after the Astronomical Society of London became the Royal Astronomical Society (RAS). Until 1960 it carried the monthly notices of the RAS, at which time these were transferred to the newly established ''Quarterly Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society'' (1960–1996) and then to its successor journal ''Astronomy & Geophysics'' (since 1997). Until 1965, MNRAS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exoplanet
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first possible evidence of an exoplanet was noted in 1917 but was not recognized as such. The first confirmation of detection occurred in 1992. A different planet, initially detected in 1988, was confirmed in 2003. There are many methods of detecting exoplanets. Transit photometry and Doppler spectroscopy have found the most, but these methods suffer from a clear observational bias favoring the detection of planets near the star; thus, 85% of the exoplanets detected are inside the tidal locking zone. In several cases, multiple planets have been observed around a star. About 1 in 5 Sun-like starsFor the purpose of this 1 in 5 statistic, "Sun-like" means G-type star. Data for Sun-like stars was not available so this statistic is an extrapolation from data about K-type stars. have an "Earth-sized"For the purpose of this 1 in 5 statistic, Earth-sized means 1–2 Earth radii. planet in the habitable zone. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stellar Classification
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their stellar spectrum, spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a Prism (optics), prism or diffraction grating into a spectrum exhibiting the Continuum (spectrum), rainbow of colors interspersed with spectral lines. Each line indicates a particular chemical element or molecule, with the line strength indicating the abundance of that element. The strengths of the different spectral lines vary mainly due to the temperature of the photosphere, although in some cases there are true abundance differences. The ''spectral class'' of a star is a short code primarily summarizing the ionization state, giving an objective measure of the photosphere's temperature. Most stars are currently classified under the Morgan–Keenan (MK) system using the letters ''O'', ''B'', ''A'', ''F'', ''G'', ''K'', and ''M'', a sequence from the hottest (''O'' type) to the coo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanium Dioxide
Titanium dioxide, also known as titanium(IV) oxide or titania , is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula . When used as a pigment, it is called titanium white, Pigment White 6 (PW6), or CI 77891. It is a white solid that is insoluble to water, although mineral forms can appear black. As a pigment, it has a wide range of applications, including paint, sunscreen, and food coloring. When used as a food coloring, it has E number E171. World production in 2014 exceeded 9 million tonnes. It has been estimated that titanium dioxide is used in two-thirds of all pigments, and pigments based on the oxide have been valued at a price of $13.2 billion. Structure In all three of its main dioxides, titanium exhibits octahedral geometry, being bonded to six oxide anions. The oxides in turn are bonded to three Ti centers. The overall crystal structure of rutile is tetragonal in symmetry whereas anatase and brookite are orthorhombic. The oxygen substructures are all slight distort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanium(III,IV) Oxide
Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in sea water, aqua regia, and chlorine. Titanium was discovered in Cornwall, Great Britain, by William Gregor in 1791 and was named by Martin Heinrich Klaproth after the Titans of Greek mythology. The element occurs within a number of minerals, principally rutile and ilmenite, which are widely distributed in the Earth's crust and lithosphere; it is found in almost all living things, as well as bodies of water, rocks, and soils. The metal is extracted from its principal mineral ores by the Kroll and Hunter processes. The most common compound, titanium dioxide, is a popular photocatalyst and is used in the manufacture of white pigments. Other compounds include titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4), a component of smoke screens and catalysts; and tita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element is therefore not a compound. A compound can be transformed into a different substance by a chemical reaction, which may involve interactions with other substances. In this process, bonds between atoms may be broken and/or new bonds formed. There are four major types of compounds, distinguished by how the constituent atoms are bonded together. Molecular compounds are held together by covalent bonds; ionic compounds are held together by ionic bonds; intermetallic compounds are held together by metallic bonds; coordination complexes are held together by coordinate covalent bonds. Non-stoichiometric compounds form a disputed marginal case. A chemical formula specifies the number of atoms of each element in a compound molecule, using the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganic
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as '' inorganic chemistry''. Inorganic compounds comprise most of the Earth's crust, although the compositions of the deep mantle remain active areas of investigation. Some simple carbon compounds are often considered inorganic. Examples include the allotropes of carbon (graphite, diamond, buckminsterfullerene, etc.), carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, carbides, and the following salts of inorganic anions: carbonates, cyanides, cyanates, and thiocyanates. Many of these are normal parts of mostly organic systems, including organisms; describing a chemical as inorganic does not necessarily mean that it does not occur within living things. History Friedrich Wöhler's conversion of ammonium cyanate into urea in 1828 is often cited as the starting point of modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |