|
Tipton Phase
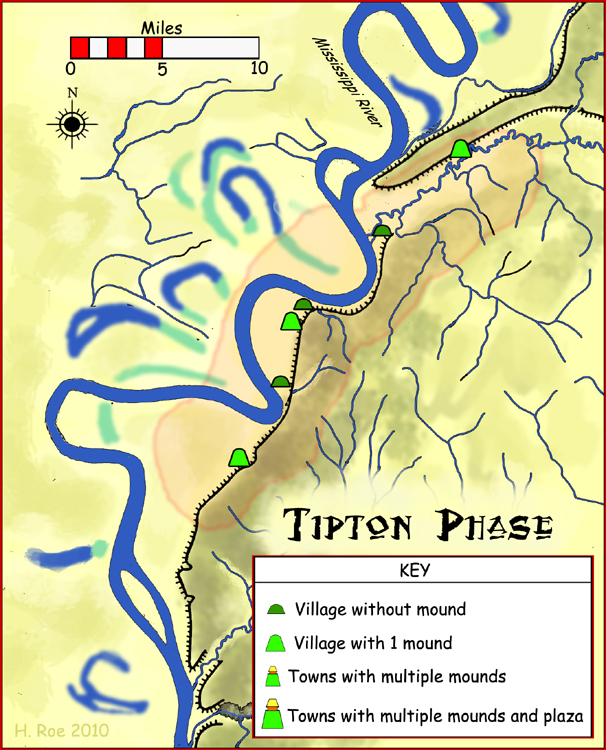
The Tipton phase is an archaeological phase in southwestern Tennessee of the Late Mississippian culture. Other contemporaneous groups in the area include the Parkin phase, Walls phase, Menard phase, and the Nodena phase. The Tipton phase is the last prehistoric people to inhabit the area before the arrival of Europeans. It is located directly across the Mississippi River from the people of the Nodena phase and directly north of the Walls phase. During the early 1540s the Hernando de Soto Expedition passed through the area, stopping at many villages in the area. The phase itself is named for Tipton County, Tennessee Tipton County is a county located on the western end of the U.S. state of Tennessee, in the Mississippi Delta region. As of the 2020 census, the population was 60,970. Its county seat is Covington. Tipton County is part of the Memphis, TN-MS .... Notes Middle Mississippian culture Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands Native American his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tipton Phase Sites HRoe 2010
Tipton is an industrial town in the West Midlands in England with a population of around 38,777 at the 2011 UK Census. It is located northwest of Birmingham. Tipton was once one of the most heavily industrialised towns in the Black Country, with thousands of people employed in the town's industries. Its factories began closing in the 1970s and it has gradually become a commuter town, home largely to people working in other parts of the region. Historically within Staffordshire, the town is now in the borough of Sandwell, It is located adjacent to the towns of Dudley, Wednesbury, Moxley, Darlaston and Bilston. It is also located between Wolverhampton and Birmingham. It also incorporates the areas of Tipton Green, Ocker Hill, Dudley Port, Horseley Heath and Great Bridge. Tipton was an urban district until 1938, when it became a municipal borough. Much of the Borough of Tipton was transferred into West Bromwich County Borough in 1966, but parts of the old borough were absorbed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Phase
In archaeology, a phase refers to the logical reduction of contexts recorded during excavation to nearly contemporary archaeological horizons that represent a distinct "phase" of previous land use. These often but not always will be a representation of a former land surface or occupation level and all associated features that were created into or from this point in time. A simplified description of phase would be that "a phase is a view of a given archaeological site as it would have been at time X". Examples of phases that would have no associated occupation surfaces are phases of a site that have been horizontally truncated by later phases and only elements surviving of the truncated phase are those that were below ground level and the subsequent truncation at that time. Subsequent or earlier phases are representations in changing occupation patterns and land use over time. Phase is an extremely important concept in archeological excavation and post-excavation work. Phasing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked state in the Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th-largest by area and the 15th-most populous of the 50 states. It is bordered by Kentucky to the north, Virginia to the northeast, North Carolina to the east, Georgia, Alabama, and Mississippi to the south, Arkansas to the southwest, and Missouri to the northwest. Tennessee is geographically, culturally, and legally divided into three Grand Divisions of East, Middle, and West Tennessee. Nashville is the state's capital and largest city, and anchors its largest metropolitan area. Other major cities include Memphis, Knoxville, Chattanooga, and Clarksville. Tennessee's population as of the 2020 United States census is approximately 6.9 million. Tennessee is rooted in the Watauga Association, a 1772 frontier pact generally regarded as the first constitutional government west of the Appalachian Mountains. Its name derives from "Tanas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mississippian Culture
The Mississippian culture was a Native Americans in the United States, Native American civilization that flourished in what is now the Midwestern United States, Midwestern, Eastern United States, Eastern, and Southeastern United States from approximately 800 CE to 1600 CE, varying regionally. It was known for building large, earthen platform mounds, and often other shaped mounds as well. It was composed of a series of urban settlements and satellite villages linked together by loose trading networks. The largest city was Cahokia, believed to be a major religious center located in what is present-day southern Illinois. The Mississippian way of life began to develop in the Mississippi River Valley (for which it is named). Cultures in the tributary Tennessee River Valley may have also begun to develop Mississippian characteristics at this point. Almost all dated Mississippian sites predate 1539–1540 (when Hernando de Soto explored the area), with notable exceptions being Natchez p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
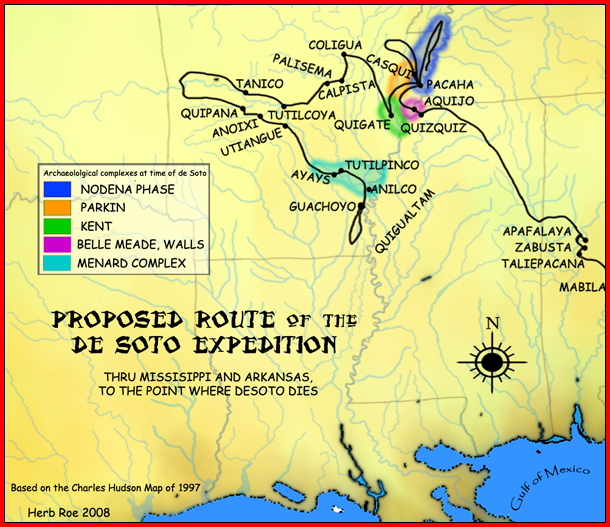
Parkin Phase
Parkin Archeological State Park, also known as Parkin Indian Mound, is an archeological site and state park in Parkin, Cross County, Arkansas. Around 1350–1650 CE an aboriginal palisaded village existed at the site, at the confluence of the St. Francis and Tyronza rivers. Artifacts from this site are on display at the site museum. The Parkin site is the type site for the Parkin phase, an expression of the Mississippian culture from the Late Mississippian period. Many archeologists believe it to be part of the province of ''Casqui'', documented as visited by Spanish explorer Hernando de Soto in 1542. Archeological artifacts from the village of the Parkin people are dated to 1400–1650 CE. The Parkin site was declared a National Historic Landmark in 1964 for its significance as a type site of the Parkin phase. In 1966, the Parkin Indian Mound was listed in the National Register of Historic Places. Parkin Archeological State Park is located at 60 Arkansas Highway 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walls Phase
The Walls phase is an archaeological phase in southwestern Tennessee and northwestern Mississippi of the Late Mississippian culture. Chucalissa is a Walls phase mound and plaza complex located on a bluff overlooking the Mississippi River. Other contemporaneous groups in the area include the Parkin phase, Tipton phase, Menard phase, and the Nodena phase. The Walls phase is the last prehistoric people to inhabit the Memphis area before the arrival of Europeans. During the early 1540s the Hernando de Soto Expedition passed through the area, stopping at many villages along the way. It is thought that the Walls phase may be the Province of Quizquiz, a Tunican people encountered by de Soto on the banks of the Mississippi River. Culture Settlement pattern The Walls phase settlements consist of one large site, located at De Soto Park in Memphis, nine single mound sites, and six smaller moundless villages scattered along the natural levees and bluffs of De Soto County, Mississippi and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menard–Hodges Site
The Menard–Hodges site ( 3AR4) (also known as Menard-Hodges Mounds and Osotouy), is an archaeological site in Arkansas County, Arkansas. It includes two large platform mounds as well as several house mounds. It is the type site for the Menard phase, a protohistoric Mississippian culture group. The Menard Mound was named for Frank Menard, on whose farm the mound was discovered. Description The site is considered as a possible candidate for the Province of Anilco encountered by the Hernando de Soto Entrada in 1540. It was contemporaneous with the Parkin site, believed by many archaeologists to be the location of the province of Casqui, and the Nodena site, believed by many archaeologists to be the location of the province of Pacaha. The site is also considered to be the location of the protohistoric Quapaw village of ''Osotouy'' (or ''Ossoteoue'') first encountered by French explorers in the late 17th century. The Quapaw at the time had four villages, Kappa, Ossoteoue, Tour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nodena Phase
The Nodena phase is an archaeological phase in eastern Arkansas and southeastern Missouri of the Late Mississippian culture which dates from about 1400–1650 CE. The Nodena phase is known from a collection of villages along the Mississippi River between the Missouri Bootheel and Wapanocca Lake. They practiced extensive maize agriculture and artificial cranial deformation and were members of a continent wide trade and religious network known as the Southeastern Ceremonial Complex, which brought chert, whelk shells, and other exotic goods to the area. The Spanish Hernando de Soto Expedition is believed to have visited several sites in the Nodena phase in the early 1540s, which is usually identified as the Province of Pacaha. Settlement pattern Nodena phase sites are found in three geographic subdistricts: the Wilson- Joiner, the Wapanocca Lake, and the Blytheville subdistricts. Wilson-Joiner subdistrict * Nodena site - The Nodena site is the type site for the Nodena ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it flows generally south for to the Mississippi River Delta in the Gulf of Mexico. With its many tributaries, the Mississippi's watershed drains all or parts of 32 U.S. states and two Canadian provinces between the Rocky and Appalachian mountains. The main stem is entirely within the United States; the total drainage basin is , of which only about one percent is in Canada. The Mississippi ranks as the thirteenth-largest river by discharge in the world. The river either borders or passes through the states of Minnesota, Wisconsin, Iowa, Illinois, Missouri, Kentucky, Tennessee, Arkansas, Mississippi, and Louisiana. Native Americans have lived along the Mississippi River and its tributaries for thousands of years. Most were hunter-ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hernando De Soto
Hernando de Soto (; ; 1500 – 21 May, 1542) was a Spanish explorer and '' conquistador'' who was involved in expeditions in Nicaragua and the Yucatan Peninsula. He played an important role in Francisco Pizarro's conquest of the Inca Empire in Peru, but is best known for leading the first European expedition deep into the territory of the modern-day United States (through Florida, Georgia, Alabama, Mississippi, and most likely Arkansas). He is the first European documented as having crossed the Mississippi River. De Soto's North American expedition was a vast undertaking. It ranged throughout what is now the southeastern United States, both searching for gold, which had been reported by various Native American tribes and earlier coastal explorers, and for a passage to China or the Pacific coast. De Soto died in 1542 on the banks of the Mississippi River; different sources disagree on the exact location, whether it was what is now Lake Village, Arkansas, or Ferriday, Louisia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Alabama Press
The University of Alabama Press is a university press founded in 1945 and is the scholarly publishing arm of the University of Alabama. An editorial board composed of representatives from all doctoral degree granting public universities within Alabama oversees the publishing program. Projects are selected that support, extend, and preserve academic research. The Press also publishes books that foster an understanding of the history and culture of this state and region. The Press strives to publish works in a wide variety of formats such as print, electronic, and on-demand technologies to ensure that the works are widely available. As the only academic publisher for the state of Alabama, The University of Alabama Press has in the past undertaken publishing partnerships with such institutions as the Birmingham Museum of Art and Samford University, and The College of Agriculture, the Jule Collins Smith Museum of Fine Art, and the Pebble Hill Center for the Humanities at Auburn Univ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tipton County, Tennessee
Tipton County is a county located on the western end of the U.S. state of Tennessee, in the Mississippi Delta region. As of the 2020 census, the population was 60,970. Its county seat is Covington. Tipton County is part of the Memphis, TN-MS-AR Metropolitan Statistical Area. History Indian cultures From about 10,000 BCE, Paleo-Indians and later Archaic-Indians lived as communities of hunter-gatherers in the area that covers the modern day southern United States. From approximately 800 CE to 1600 CE, the Mississippi Delta was populated by tribes of the Mississippian culture, a mound-building Native American people who had developed in the late Woodland Indian period. While there were chiefdoms and centers along the Mississippi and its tributaries, their major center was at Cahokia, in present-day Illinois east of St. Louis, Missouri. The Tipton phase people were a local expression of the Mississippian culture. They still inhabited the region of modern-day Tipton Count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |