|
Timeline Of Therizinosaur Research
The timeline of therizinosaur research is a chronological listing of events in the history of paleontology focused on therizinosaurs. They were unusually long-necked, pot-bellied, and large-clawed herbivorous theropods most closely related to birds. The early history of therizinosaur research occurred in three phases. The first phase was the discovery of scanty and puzzling fossils in Asia by the Central Asiatic Expeditions of the 1920s and Soviet-backed research in the 1950s. This phase resulted in the discovery of the ''Therizinosaurus cheloniformis'' type specimen. Soviet paleontologist Evgeny Maleev interpreted these unusual remains as belonging to some kind of gigantic turtle. The second major phase of therizinosaur research followed the discovery of better preserved remains in the 1970s by collaborative research between the Soviets and Mongolians. These finds revealed the true nature of therizinosaurs as bizarre dinosaurs. However, the exact nature and classification of ther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nothronychus Graffami And Falcarius Utahensis - Natural History Museum Of Utah - DSC07207
''Nothronychus'' (meaning "slothful claw") is a genus of therizinosaurid theropod dinosaurs that lived in North America during the Late Cretaceous period. The type species, ''Nothronychus mckinleyi'', was described by James Kirkland and Douglas G. Wolfe in 2001. It was recovered near New Mexico's border with Arizona, in an area known as the Zuni Basin, from rocks assigned to the Moreno Hill Formation, dating to the late Cretaceous period (mid-Turonian stage), around 91 million years ago. A second specimen, described in 2009 as a second species, ''Nothronychus graffami'', was found in the Tropic Shale of Utah, dating to the early Turonian, between one million and a half million years older than ''N. mckinleyi''. ''Nothronychus'' were bulky herbivorous theropods with wide, sloth-like hip (resembling that of the non-related ornithischians), four-toed feet with all four toes facing forward, elongated necks and prominent arms with sharp claws. Both species were similar in dimensions, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family of Mongolic peoples. The Oirats in Western Mongolia as well as the Buryats and Kalmyks of Russia are classified either as distinct ethno-linguistic groups or subgroups of Mongols. The Mongols are bound together by a common heritage and ethnic identity. Their indigenous dialects are collectively known as the Mongolian language. The ancestors of the modern-day Mongols are referred to as Proto-Mongols. Definition Broadly defined, the term includes the Mongols proper (also known as the Khalkha Mongols), Buryats, Oirats, the Kalmyk people and the Southern Mongols. The latter comprises the Abaga Mongols, Abaganar, Aohans, Baarins, Chahars, Eastern Dorbets, Gorlos Mongols, Jalaids, Jaruud, Kharchins, Khishig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
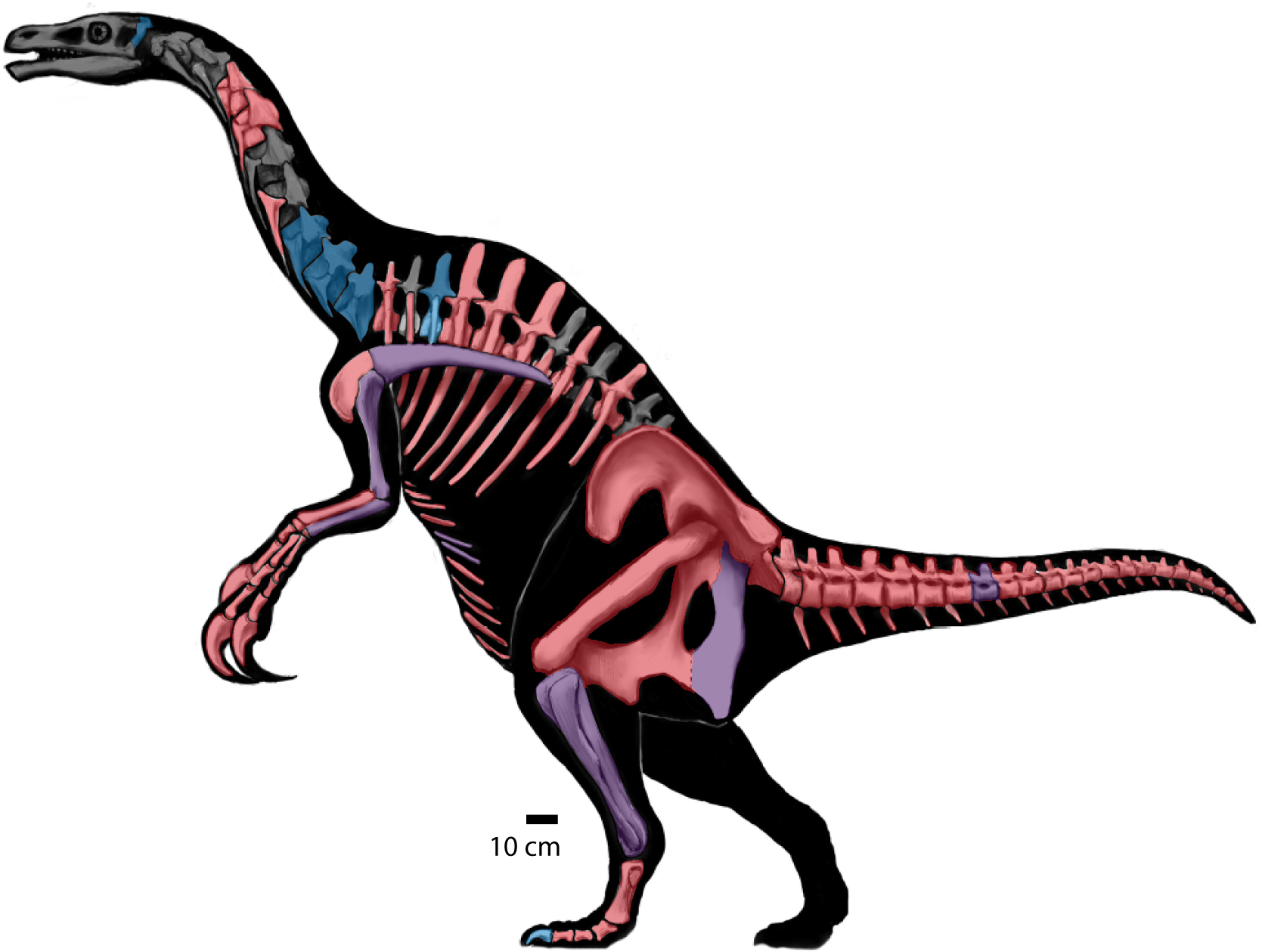
Alxasaurus Elsitaiensis
''Alxasaurus'' (; meaning " Alxa lizard") is a genus of therizinosauroid theropod dinosaurs from the Early Cretaceous (Albian age) Bayin-Gobi Formation of Inner Mongolia. History of discovery The fossil remains were first discovered in 1988 and described by the Canadian paleontologist Dale Russell and his Chinese colleague Dong Zhiming in 1993. However, although the paper is technically included in the last issue of the 1993 volume of the Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, this issue was actually released in the early weeks of 1994. ''Alxasaurus'' is named after the Alxa Desert of Inner Mongolia, also known as the "Alashan" desert, and the name also includes the Greek word ''sauros'' ("lizard"). Alxa (or Alashan) is also the name of the league, or administrative division, of the Inner Mongolia (Nei Mongol Zizhiqu) region of the People's Republic of China. The single known species, ''elesitaiensis'', is named after Elesitai, a village found in this region, near which the fossil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teresa Maryańska
Teresa Maryańska (1937 – 3 October 2019) was a Polish paleontologist who specialized in Mongolian dinosaurs, particularly pachycephalosaurians and ankylosaurians. Peter Dodson (1998 p. 9) states that in 1974 Maryanska together with Halszka Osmólska were among the first "women to describe new kinds of dinosaurs". She is considered not only as one of Poland's but also one of the world's leading experts on dinosaurs. A member of the 1964, 1965, 1970, and 1971 Polish–Mongolian expeditions to the Gobi Desert, she has described many finds from these rocks, often with Halszka Osmólska. Among the dinosaurs she has described are: * ''Saichania'' and ''Tarchia'' (1977) * with Osmólska, ''Homalocephale'', ''Prenocephale'', and ''Tylocephale'' (and Pachycephalosauria) (1974), ''Bagaceratops'' (1975), and ''Barsboldia'' (1981) * and with Osmόlska and Altangerel Perle, ''Goyocephale'' (1982). Alan Feduccia notes that Maryanska and her colleagues (Osmólska and Wolsan) produced i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rinchen Barsbold
, Rinchyengiin Barsbold, born December 21, 1935 in Ulaanbaatar) is a Mongolian paleontologist and geologist. He works with the Institute of Geology, at Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia. He is an expert in vertebrate paleontology and Mesozoic stratigraphy. Barsbold has been instrumental in the discovery and recovery of one of the largest dinosaur collections in the world. His work has helped to form a more modern understanding of the later stages of dinosaur evolution in Eurasia. Barsbold has had considerable influence on dinosaur paleontology in the Communist world. His scientific work has made him a leading authority on theropods of the Gobi Desert, starting with his doctoral dissertation on these dinosaurs. As early as 1983, he noted that in different lineages of theropods, many features previously only known from birds had evolved in various combinations (Barsbold 1983). He postulated that as a result of this "ornithization", one or several lineages of theropods that happened to acquire th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Segnosauria
Therizinosaurs (once called segnosaurs) were large herbivorous theropod dinosaurs whose fossils have been found across the Early to Late Cretaceous deposits in Asia and North America. Various features of the forelimbs, skull and pelvis unite these finds as both theropods and maniraptorans, close relatives to birds. The name of the representative genus, ''Therizinosaurus'', is derived from the Greek (, 'to reap' or 'scythe')Translated paper and (, 'lizard'). The older representative, ''Segnosaurus'', is derived from the ('slow') and the Greek . History of research [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Segnosauridae
Therizinosauridae (meaning 'scythe lizards')Translated paper is a family of derived (advanced) whose fossil remains have been found in mostly boundary. Even though representative fossils have only been found throughout and |
Segnosaurus Galbinensis
''Segnosaurus'' is a genus of therizinosaurid dinosaur that lived in what is now southeastern Mongolia during the Late Cretaceous, about 102–86 million years ago. Multiple incomplete but well-preserved specimens were discovered in the Gobi Desert in the 1970s, and in 1979 the genus and species ''Segnosaurus galbinensis'' were named. The generic name ''Segnosaurus'' means "slow lizard" and the specific name ''galbinensis'' refers to the Galbin region. The known material of this dinosaur includes the lower jaw, neck and tail vertebrae, the pelvis, shoulder girdle, and limb bones. Parts of the specimens have gone missing or become damaged since they were collected. ''Segnosaurus'' was a large-bodied therizinosaur that is estimated to have been about long and to have weighed about . It would have been bipedal, with the trunk of its body tilted upwards. The head was small with a beak at the tip of the jaws, and the neck was long and slender. The lower jaw was down-turned at t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altangerel Perle
Altangerel Perle (born 1945) is a Mongolian palaeontologist. He is employed at the National University of Mongolia. He has described species such as ''Goyocephale lattimorei'', '' Achillobator giganticus'' and '' Erlikosaurus andrewsi''. He has been honored by Polish palaeontologist Halszka Osmólska Halszka Osmólska (September 15, 1930 – March 31, 2008) was a Polish paleontologist who had specialized in Mongolian dinosaurs. Biography She was born in 1930 in Poznań. In 1949, she began to study biology at Faculty of Biology and Earth Scie ..., who named the species '' Hulsanpes perlei'' after him. References 1945 births Living people Mongolian paleontologists National University of Mongolia faculty {{Mongolia-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1979 In Paleontology
Paleontology Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossi ... Paleontology 9 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |