|
Time Point
In music a time point or ''timepoint'' ( point in time) is "an instant, analogous to a geometrical point in space". Because it has no duration, it literally cannot be heard, but it may be used to represent "the point of initiation of a single pitch, the repetition of a pitch, or a pitch simultaneity", therefore the beginning of a sound, rather than its duration. It may also designate the release of a note or the point within a note at which something changes (such as dynamic level). Other terms often used in music theory and analysis are '' attack point''Lejaren Hiller and Ramon Fuller, "Structure and Information in Webern's Symphonie, Op. 21", ''Journal of Music Theory'' 11, no. 1 (Spring 1967): 60–115. Citation on p. 94. and ''starting point''. Milton Babbitt calls the distance from one time point, attack, or starting point to the next a ''time-point interval'', independent of the durations of the sounding notes which may be either shorter than the time-point interval (r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Music
Music is generally defined as the art of arranging sound to create some combination of form, harmony, melody, rhythm or otherwise expressive content. Exact definitions of music vary considerably around the world, though it is an aspect of all human societies, a cultural universal. While scholars agree that music is defined by a few specific elements, there is no consensus on their precise definitions. The creation of music is commonly divided into musical composition, musical improvisation, and musical performance, though the topic itself extends into academic disciplines, criticism, philosophy, and psychology. Music may be performed or improvised using a vast range of instruments, including the human voice. In some musical contexts, a performance or composition may be to some extent improvised. For instance, in Hindustani classical music, the performer plays spontaneously while following a partially defined structure and using characteristic motifs. In modal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
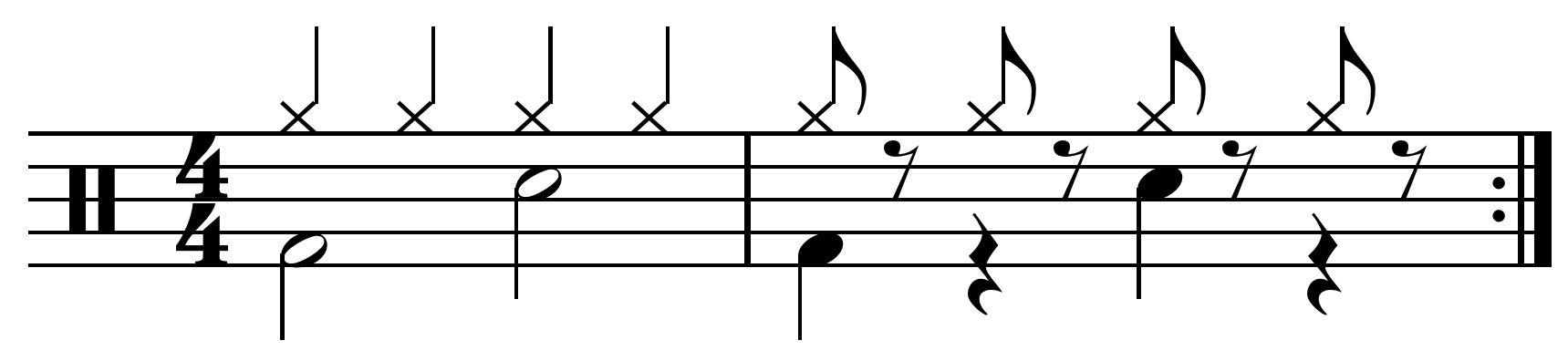
Half Time Rock Pattern
One half ( : halves) is the irreducible fraction resulting from dividing one by two or the fraction resulting from dividing any number by its double. Multiplication by one half is equivalent to division by two, or "halving"; conversely, division by one half is equivalent to multiplication by two, or "doubling". One half often appears in mathematical equations, recipes, measurements, etc. Half can also be said to be one part of something divided into two equal parts. For instance, the area ''S'' of a triangle is computed. :''S'' = × perpendicular height. One half also figures in the formula for calculating figurate numbers, such as triangular numbers and pentagonal numbers: : \frac and in the formula for computing magic constants for magic squares : M_2(n) = \frac \left(n^ + 1\right) The Riemann hypothesis states that every nontrivial complex root of the Riemann zeta function has a real part equal to . One half has two different decimal expansion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitch Class
In music, a pitch class (p.c. or pc) is a set of all pitches that are a whole number of octaves apart; for example, the pitch class C consists of the Cs in all octaves. "The pitch class C stands for all possible Cs, in whatever octave position." Important to musical set theory, a pitch class is "all pitches related to each other by octave, enharmonic equivalence, or both." Thus, using scientific pitch notation, the pitch class "C" is the set : = . Although there is no formal upper or lower limit to this sequence, only a few of these pitches are audible to humans. Pitch class is important because human pitch-perception is periodic: pitches belonging to the same pitch class are perceived as having a similar quality or color, a property called " octave equivalence". Psychologists refer to the quality of a pitch as its "chroma". A ''chroma'' is an attribute of pitches (as opposed to ''tone height''), just like hue is an attribute of color. A ''pitch class'' is a set of all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serial Music
In music, serialism is a method of composition using series of pitches, rhythms, dynamics, timbres or other musical elements. Serialism began primarily with Arnold Schoenberg's twelve-tone technique, though some of his contemporaries were also working to establish serialism as a form of post-tonal thinking. Twelve-tone technique orders the twelve notes of the chromatic scale, forming a row or series and providing a unifying basis for a composition's melody, harmony, structural progressions, and variations. Other types of serialism also work with sets, collections of objects, but not necessarily with fixed-order series, and extend the technique to other musical dimensions (often called "parameters"), such as duration, dynamics, and timbre. The idea of serialism is also applied in various ways in the visual arts, design, and architecture, and the musical concept has also been adapted in literature. Integral serialism or total serialism is the use of series for aspects such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time-point Series
In music a time point or ''timepoint'' (point in time) is "an instant, analogous to a geometrical point in space". Because it has no duration, it literally cannot be heard, but it may be used to represent "the point of initiation of a single pitch, the repetition of a pitch, or a pitch simultaneity", therefore the beginning of a sound, rather than its duration. It may also designate the release of a note or the point within a note at which something changes (such as dynamic level). Other terms often used in music theory and analysis are '' attack point''Lejaren Hiller and Ramon Fuller, "Structure and Information in Webern's Symphonie, Op. 21", ''Journal of Music Theory'' 11, no. 1 (Spring 1967): 60–115. Citation on p. 94. and ''starting point''. Milton Babbitt calls the distance from one time point, attack, or starting point to the next a ''time-point interval'', independent of the durations of the sounding notes which may be either shorter than the time-point interval (res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metre (music)
In music, metre ( Commonwealth spelling) or meter (American spelling) refers to regularly recurring patterns and accents such as bars and beats. Unlike rhythm, metric onsets are not necessarily sounded, but are nevertheless implied by the performer (or performers) and expected by the listener. A variety of systems exist throughout the world for organising and playing metrical music, such as the Indian system of '' tala'' and similar systems in Arabic and African music. Western music inherited the concept of metre from poetry, where it denotes: the number of lines in a verse; the number of syllables in each line; and the arrangement of those syllables as long or short, accented or unaccented. The first coherent system of rhythmic notation in modern Western music was based on rhythmic modes derived from the basic types of metrical unit in the quantitative metre of classical ancient Greek and Latin poetry. Later music for dances such as the pavane and galliard consisted o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhythm
Rhythm (from Greek , ''rhythmos'', "any regular recurring motion, symmetry") generally means a " movement marked by the regulated succession of strong and weak elements, or of opposite or different conditions". This general meaning of regular recurrence or pattern in time can apply to a wide variety of cyclical natural phenomena having a periodicity or frequency of anything from microseconds to several seconds (as with the riff in a rock music song); to several minutes or hours, or, at the most extreme, even over many years. Rhythm is related to and distinguished from pulse, meter, and beats: In the performance arts, rhythm is the timing of events on a human scale; of musical sounds and silences that occur over time, of the steps of a dance, or the meter of spoken language and poetry. In some performing arts, such as hip hop music, the rhythmic delivery of the lyrics is one of the most important elements of the style. Rhythm may also refer to visual presentation, as "timed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quarter Note
A quarter note (American) or crotchet ( ) (British) is a musical note played for one quarter of the duration of a whole note (or semibreve). Quarter notes are notated with a filled-in oval note head and a straight, flagless stem. The stem usually points upwards if it is below the middle line of the staff, and downwards if it is on or above the middle line. An upward stem is placed on the right side of the notehead, a downward stem is placed on the left (see image). The Unicode symbol is U+2669 (). A quarter rest (or crotchet rest) denotes a silence of the same duration as a quarter note. It typically appears as the symbol , or occasionally, as the older symbol .''Rudiments and Theory of Music'' Associated Board of the Royal Schools of Music, London 1958. I,33 and III,25. The former section shows both forms without distinction, the latter the "old" form only. The book was the Official ABRSM theory manual in the UK up until at least 1975. The "old" form was taught as a ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rest (music)
A rest is a musical notation sign that indicates the absence of a sound. Each rest symbol and name corresponds with a particular note value for length, indicating how long the silence should last. Description Rests are intervals of silence in pieces of music, marked by symbols indicating the length of the pause. Each rest symbol and name corresponds with a particular note value, indicating how long the silence should last, generally as a multiplier of a measure or whole note. * The quarter (crotchet) rest (𝄽) may also be found as a form in older music.''History of Music Notation'' (1937) by C. Gorden, p. 93. * The four-measure rest or longa rest are only used in long silent passages which are not divided into bars. * The combination of rests used to mark a pause follows the same rules as for note values.''AB guide to music theory'' by E. Taylor, chapter 13/1, One-bar rests When an entire bar is devoid of notes, a whole (semibreve) rest is used, regardless o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
