|
Time-to-live
Time to live (TTL) or hop limit is a mechanism which limits the lifespan or lifetime of data in a computer or network. TTL may be implemented as a counter or timestamp attached to or embedded in the data. Once the prescribed event count or timespan has elapsed, data is discarded or revalidated. In computer networking, TTL prevents a data packet from circulating indefinitely. In computing applications, TTL is commonly used to improve the performance and manage the caching of data. Description The original DARPA Internet Protocol's RFC document describes TTL as: IP packets Under the Internet Protocol, TTL is an 8-bit field. In the IPv4 header, TTL is the 9th octet of 20. In the IPv6 header, it is the 8th octet of 40. The maximum TTL value is 255, the maximum value of a single octet. A recommended initial value is 64. The time-to-live value can be thought of as an upper bound on the time that an IP datagram can exist in an Internet system. The TTL field is set by the sender ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domain Name System
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a hierarchical and distributed naming system for computers, services, and other resources in the Internet or other Internet Protocol (IP) networks. It associates various information with domain names assigned to each of the associated entities. Most prominently, it translates readily memorized domain names to the numerical IP addresses needed for locating and identifying computer services and devices with the underlying network protocols. The Domain Name System has been an essential component of the functionality of the Internet since 1985. The Domain Name System delegates the responsibility of assigning domain names and mapping those names to Internet resources by designating authoritative name servers for each domain. Network administrators may delegate authority over sub-domains of their allocated name space to other name servers. This mechanism provides distributed and fault-tolerant service and was designed to avoid a single large ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MX Record
A mail exchanger record (MX record) specifies the mail server responsible for accepting email messages on behalf of a domain name. It is a resource record in the Domain Name System (DNS). It is possible to configure several MX records, typically pointing to an array of mail servers for load balancing and redundancy. Overview Resource records are the basic information element of the Domain Name System (DNS). An MX record is one of these, and a domain may have one or more of these set up, as below: Domain TTL Class Type Priority Host example.com. 1936 IN MX 10 onemail.example.com. example.com. 1936 IN MX 10 twomail.example.com. The characteristic payload information of an MX record is a preference value (above labelled "Priority"), and the domain name of a mailserver ("Host" above). The priority field identifies which mailserver should be preferred - in this case the values are both 10, so mail would be expected to flow evenly to both ''onemail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
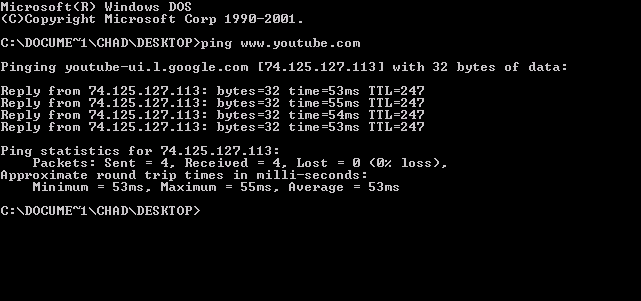
Traceroute
In computing, traceroute and tracert are computer network diagnostic commands for displaying possible routes (paths) and measuring transit delays of packets across an Internet Protocol (IP) network. The history of the route is recorded as the round-trip times of the packets received from each successive host (remote node) in the route (path); the sum of the mean times in each hop is a measure of the total time spent to establish the connection. Traceroute proceeds unless all (usually three) sent packets are lost more than twice; then the connection is lost and the route cannot be evaluated. Ping, on the other hand, only computes the final round-trip times from the destination point. For Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6) the tool sometimes has the name traceroute6 and tracert6. Implementations The command traceroute is available on many modern operating systems. On Unix-like systems such as FreeBSD, macOS, and Linux it is available as a command line tool. Traceroute is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Name Server
A name server refers to the server component of the Domain Name System (DNS), one of the two principal namespaces of the Internet. The most important function of DNS servers is the translation (resolution) of human-memorable domain names (example.com) and hostnames into the corresponding numeric Internet Protocol (IP) addresses (192.0.2.1), the second principal name space of the Internet, which is used to identify and locate computer systems and resources on the Internet. Although it is typically used in reference to DNS (Domain Name System), the term name server may also be used for any computer application that implements a network service for providing responses to queries against a directory service which translates an often humanly meaningful, text-based identifier to a system-internal, often numeric identification or addressing component. This service is performed by the server in response to a service protocol request. Domain Name Server The Internet maintains two princ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counter (digital)
In digital logic and computing, a counter is a device which stores (and sometimes displays) the number of times a particular event (philosophy), event or Process (computing), process has occurred, often in relationship to a Clock signal, clock. The most common type is a sequential logic, sequential digital logic circuit with an input line called the ''clock'' and multiple output lines. The values on the output lines represent a number in the binary number, binary or binary-coded decimal, BCD number system. Each pulse applied to the clock input :wikt:increment, increments or :wikt:decrement, decrements the number in the counter. A counter circuit is usually constructed of several flip-flop (electronics), flip-flops connected in a cascade. Counters are a very widely used component in digital circuits, and are manufactured as separate integrated circuits and also incorporated as parts of larger integrated circuits. Electronic counters An electronics, electronic counter is a sequ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TTL Of A DNS Answer Resolving Google ", a single by South Korean girl group T-ara and boy band Supernova
{{Disambiguation ...
TTL may refer to: Photography * Through-the-lens metering, a camera feature * Zenit TTL, an SLR film camera named for its TTL metering capability Technology * Time to live, a computer data lifespan-limiting mechanism * Transistor–transistor logic, a family of integrated-circuit digital logic ** Differential TTL, a serial signaling standard based on TTL * Turtle (syntax), a computer data format used in semantic web technologies Other uses * Taiwan Tobacco and Liquor, a state-owned manufacturer * "TTL (Time to Love) ''Absolute First Album'' is the first studio album and debut Korean release by South Korean girl group T-ara. It was released on November 27, 2009, through Core Contents Media. T-ara sought to showcase "two different charms" through ''Absolute Fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ping (networking Utility)
ping is a computer network administration software utility used to test the reachability of a host on an Internet Protocol (IP) network. It is available for virtually all operating systems that have networking capability, including most embedded network administration software. Ping measures the round-trip time for messages sent from the originating host to a destination computer that are echoed back to the source. The name comes from active sonar terminology that sends a pulse of sound and listens for the echo to detect objects under water. Ping operates by means of Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) packets. ''Pinging'' involves sending an ICMP echo request to the target host and waiting for an ICMP echo reply. The program reports errors, packet loss, and a statistical summary of the results, typically including the minimum, maximum, the mean round-trip times, and standard deviation of the mean. The command-line options of the ping utility and its output vary bet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hop (telecommunications)
In telecommunication, a hop is a portion of a signal's journey from source to receiver. Examples include: #The excursion of a radio wave from the Earth to the ionosphere and back to the Earth. The number of hops indicates the number of reflections from the ionosphere.Federal Standard 1037C #A similar excursion from an earth station to a communications satellite to another station, counted similarly except that if the return trip is not by satellite, then it is only a half hop. In computer network A computer network is a set of computers sharing resources located on or provided by network nodes. The computers use common communication protocols over digital interconnections to communicate with each other. These interconnections ar ...s, a hop is the step from one network segment to the next. References Telecommunications engineering Radio frequency propagation {{Telecomm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HTTP Cookie
HTTP cookies (also called web cookies, Internet cookies, browser cookies, or simply cookies) are small blocks of data created by a web server while a user is browsing a website and placed on the user's computer or other device by the user's web browser. Cookies are placed on the device used to access a website, and more than one cookie may be placed on a user's device during a session. Cookies serve useful and sometimes essential functions on the web. They enable web servers to store stateful information (such as items added in the shopping cart in an online store) on the user's device or to track the user's browsing activity (including clicking particular buttons, logging in, or recording which pages were visited in the past). They can also be used to save for subsequent use information that the user previously entered into form fields, such as names, addresses, passwords, and payment card numbers. Authentication cookies are commonly used by web servers to authentic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disaster Recovery
Disaster recovery is the process of maintaining or reestablishing vital infrastructure and systems following a natural or human-induced disaster, such as a storm or battle.It employs policies, tools, and procedures. Disaster recovery focuses on the information technology (IT) or technology systems supporting critical business functions as opposed to business continuity. This involves keeping all essential aspects of a business functioning despite significant disruptive events; it can therefore be considered a subset of business continuity. Disaster recovery assumes that the primary site is not immediately recoverable and restores data and services to a secondary site. IT service continuity IT Service Continuity (ITSC) is a subset of business continuity planning (BCP) that focuses on Recovery Point Objective (RPO) and Recovery Time Objective (RTO). It encompasses IT disaster recovery planning and wider IT resilience planning. It also incorporates IT infrastructure and servic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Web Servers
A web server is computer software and underlying hardware that accepts requests via HTTP (the network protocol created to distribute web content) or its secure variant HTTPS. A user agent, commonly a web browser or web crawler, initiates communication by making a request for a web page or other resource using HTTP, and the server responds with the content of that resource or an error message. A web server can also accept and store resources sent from the user agent if configured to do so. The hardware used to run a web server can vary according to the volume of requests that it needs to handle. At the low end of the range are embedded systems, such as a router that runs a small web server as its configuration interface. A high-traffic Internet website might handle requests with hundreds of servers that run on racks of high-speed computers. A resource sent from a web server can be a preexisting file ( static content) available to the web server, or it can be generat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |