|
Time-Place Learning
Time-place learning (TPL) is the process by which animals link events (e.g. finding food, encountering a predator) with both the location and time of occurrence. It enables them to decide which locations to visit or to avoid based on previous experience and knowledge of the current time of day. TPL presumably allows animals to maximize their chances of finding resources (food, mates) and avoiding predators, increasing survival chances. TPL requires spatial memory and a sense of time. The latter may be based on external time-cues (Zeitgebers), or internally generated circadian rhythms ("biological clock"). TPL may fundamentally underlie episodic memory. Insects The first evidence for time-place learning in animals came from studies in the 1930s on honeybees, which could be trained to visit two different feeders, one in the morning and the other in the afternoon. Subsequent work in the 1980s showed that only a few individuals in the colony were able to learn that task, and did so with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spatial Memory
In cognitive psychology and neuroscience, spatial memory is a form of memory responsible for the recording and recovery of information needed to plan a course to a location and to recall the location of an object or the occurrence of an event. Spatial memory is necessary for orientation in space. Spatial memory can also be divided into egocentric and allocentric spatial memory. A person's spatial memory is required to navigate around a familiar city. A rat's spatial memory is needed to learn the location of food at the end of a maze. In both humans and animals, spatial memories are summarized as a cognitive map. Spatial memory has representations within working, short-term memory and long-term memory. Research indicates that there are specific areas of the brain associated with spatial memory. Many methods are used for measuring spatial memory in children, adults, and animals. Short-term spatial memory Short-term memory (STM) can be described as a system allowing one to tempor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Starlings
Starlings are small to medium-sized passerine birds in the family Sturnidae. The Sturnidae are named for the genus '' Sturnus'', which in turn comes from the Latin word for starling, ''sturnus''. Many Asian species, particularly the larger ones, are called mynas, and many African species are known as glossy starlings because of their iridescent plumage. Starlings are native to Europe, Asia, and Africa, as well as northern Australia and the islands of the tropical Pacific. Several European and Asian species have been introduced to these areas, as well as North America, Hawaii, and New Zealand, where they generally compete for habitats with native birds and are considered to be invasive species. The starling species familiar to most people in Europe and North America is the common starling, and throughout much of Asia and the Pacific, the common myna is indeed common. Starlings have strong feet, their flight is strong and direct, and they are very gregarious. Their preferred hab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
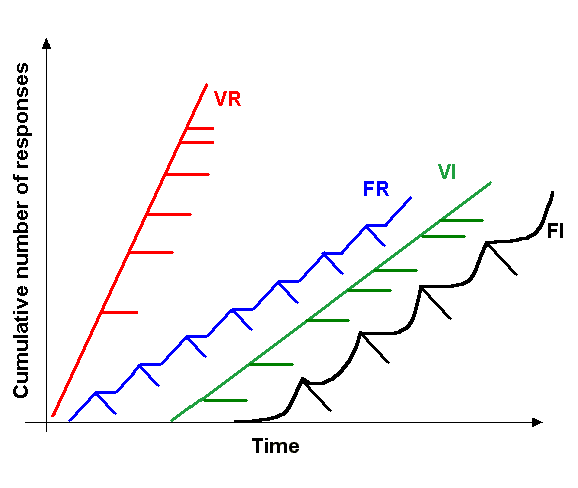
Positive Reinforcement
In behavioral psychology, reinforcement is a consequence applied that will strengthen an organism's future behavior whenever that behavior is preceded by a specific antecedent stimulus. This strengthening effect may be measured as a higher frequency of behavior (e.g., pulling a lever more frequently), longer duration (e.g., pulling a lever for longer periods of time), greater magnitude (e.g., pulling a lever with greater force), or shorter latency (e.g., pulling a lever more quickly following the antecedent stimulus). The model of self-regulation has three main aspects of human behavior, which are self-awareness, self-reflection, and self-regulation. Reinforcements traditionally align with self-regulation. The behavior can be influenced by the consequence but behavior also needs antecedents. There are four types of reinforcement: positive reinforcement, negative reinforcement, extinction, and punishment. Positive reinforcement is the application of a positive reinforcer. Nega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laboratory Mice
The laboratory mouse or lab mouse is a small mammal of the order Rodentia which is bred and used for scientific research or feeders for certain pets. Laboratory mice are usually of the species ''Mus musculus''. They are the most commonly used mammalian research model and are used for research in genetics, physiology, psychology, medicine and other scientific disciplines. Mice belong to the Euarchontoglires clade, which includes humans. This close relationship, the associated high homology with humans, their ease of maintenance and handling, and their high reproduction rate, make mice particularly suitable models for human-oriented research. The laboratory mouse genome has been sequenced and many mouse genes have human homologues. Other mouse species sometimes used in laboratory research include two American species, the white-footed mouse (''Peromyscus leucopus'') and the North American deer mouse ('' Peromyscus maniculatus''). History as a biological model Mice have be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laboratory Rat
A laboratory rat or lab rat is a brown rat of the subspecies '' Rattus norvegicus domestica'' which is bred and kept for scientific research. While less commonly used for research than mice (see laboratory mouse), rats have served as an important animal model for research in psychology and biomedical science. Origins In 18th century Europe, wild brown rats ran rampant and this infestation fueled the industry of rat-catching. Rat-catchers would not only make money by trapping the rodents, but also by selling them for food or, more commonly, for rat-baiting. Rat-baiting was a popular sport, which involved filling a pit with rats and timing how long it took for a terrier to kill them all. Over time, breeding the rats for these contests may have produced variations in color, notably the albino and hooded varieties. The first time one of these albino mutants was brought into a laboratory for a study was in 1828 for an experiment on fasting. Over the next 30 years, rats we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pigeon
Columbidae () is a bird family consisting of doves and pigeons. It is the only family in the order Columbiformes. These are stout-bodied birds with short necks and short slender bills that in some species feature fleshy ceres. They primarily feed on seeds, fruits, and plants. The family occurs worldwide, but the greatest variety is in the Indomalayan and Australasian realms. The family contains 344 species divided into 50 genera. Thirteen of the species are extinct. In English, the smaller species tend to be called "doves" and the larger ones "pigeons". However, the distinction is not consistent, and does not exist in most other languages. Historically, the common names for these birds involve a great deal of variation between the terms. The bird most commonly referred to as just "pigeon" is the domestic pigeon, which is common in many cities as the feral pigeon. Doves and pigeons build relatively flimsy nests, often using sticks and other debris, which may be placed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euplectes Hordaceus
The black-winged red bishop (''Euplectes hordeaceus''), formerly known in southern Africa as the fire-crowned bishop, is a resident breeding bird species in tropical Africa from Senegal to Sudan and south to Angola, Tanzania, Zimbabwe and Mozambique. This common weaver occurs in a range of open country, especially tall grassland and often near water. It builds a spherical woven nest in tall grass. 2-4 eggs are laid. The black-winged red bishop is a stocky 13–15 cm bird. The breeding male is scarlet apart from his black face, belly and wings and brown tail. The conical bill is thick and black. He displays prominently, singing high-pitched twitters from tall grass, puffing out his feathers or performing a slow hovering display flight. The non-breeding male is yellow-brown, streaked above and shading to whitish below. It has a whitish supercilium. It resembles non-breeding male northern red bishop, but is darker and has black wings. Females are similar, but paler. Young b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ploceus Bicolor
The dark-backed weaver (''Ploceus bicolor''), also known as the forest weaver, is a species of bird in the family Ploceidae. It is found in Angola, Burundi, Cameroon, Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Eswatini, Gabon, Kenya, Malawi, Mozambique, Nigeria, Rwanda, Somalia, South Africa, South Sudan, Tanzania, Uganda, Zambia, and Zimbabwe Zimbabwe (), officially the Republic of Zimbabwe, is a landlocked country located in Southeast Africa, between the Zambezi and Limpopo Rivers, bordered by South Africa to the south, Botswana to the south-west, Zambia to the north, and Mozam .... References External links Dark-backed weaver- Species text in Weaver Watch. * (Dark-backed weaver = ) Forest weaver Species text in The Atlas of Southern African Birds dark-backed weaver Birds of the Gulf of Guinea Birds of Sub-Saharan Africa dark-backed weaver Taxa named by Louis Pierre Vieillot Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{Plo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pigeons
Columbidae () is a bird family consisting of doves and pigeons. It is the only family in the order Columbiformes. These are stout-bodied birds with short necks and short slender bills that in some species feature fleshy ceres. They primarily feed on seeds, fruits, and plants. The family occurs worldwide, but the greatest variety is in the Indomalayan and Australasian realms. The family contains 344 species divided into 50 genera. Thirteen of the species are extinct. In English, the smaller species tend to be called "doves" and the larger ones "pigeons". However, the distinction is not consistent, and does not exist in most other languages. Historically, the common names for these birds involve a great deal of variation between the terms. The bird most commonly referred to as just "pigeon" is the domestic pigeon, which is common in many cities as the feral pigeon. Doves and pigeons build relatively flimsy nests, often using sticks and other debris, which may be placed on br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ploceidae
Ploceidae is a family of small passerine birds, many of which are called weavers, weaverbirds, weaver finches and bishops. These names come from the nests of intricately woven vegetation created by birds in this family. In most recent classifications, Ploceidae is a clade, which excludes some birds that have historically been placed in the family, such as some of the sparrows, but which includes the monotypic subfamily Amblyospizinae. The family is believed to have originated in the mid-Miocene. All birds of the Ploceidae are native to the Old World, most in Africa south of the Sahara, though a few live in tropical areas of Asia. A few species have been introduced outside their native range. Taxonomy and systematics The family Ploceidae was introduced (as Ploceïdes) by the Swedish zoologist Carl Jakob Sundevall in 1836. Phylogenetic studies have shown that the family is sister to a clade containing the families Viduidae and Estrildidae Their common ancestor lived in the mid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garden Warbler
The garden warbler (''Sylvia borin'') is a common and widespread small bird that breeds in most of Europe and in the Palearctic to western Siberia. It is a plain, long-winged and long-tailed typical warbler with brown upperparts and dull white underparts; the sexes are similar and juveniles resemble the adults. Its two subspecies differ only slightly and interbreed where their ranges overlap. Due to its lack of distinguishing features, this species can be confused with a number of other unstreaked warblers. The garden warbler's rich melodic song is similar to that of the blackcap, its closest relative, which competes with it for territory when nesting in the same woodland. The preferred breeding habitat in Eurasia is open woodland with dense low cover for nesting; despite its name, gardens are rarely occupied by this small passerine bird. The clutch of four or five blotched cream or white eggs is laid in a robust cup-shaped nest built near the ground and concealed by dense veg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeitgeber
A zeitgeber () is any external or environmental cue that entrains or synchronizes an organism's biological rhythms, usually naturally occurring and serving to entrain to the Earth's 24-hour light/dark and 12-month cycles. History The term ' (; ) was first used by Jürgen Aschoff, one of the founders of the field of chronobiology. His work demonstrated the existence of endogenous (internal) biological clocks, which synchronize biological rhythms. In addition, he found that certain exogenous (external) cues, which he called zeitgeber, influence the timing of these internal clocks. Photic and nonphotic zeitgebers * Light (light is a more important zeitgeber than social interactions). * Atmospheric conditions * Medication * Temperature * Social interactions * Exercise * Eating/drinking patterns Circadian rhythms Any biological process in the body that repeats itself over a period of approximately 24 hours and maintains this rhythm in the absence of external stimuli is considered a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)