|
Tight Gas
Tight gas is natural gas produced from reservoir rocks with such low permeability that massive hydraulic fracturing is necessary to produce the well at economic rates. This natural gas is trapped within rocks with very low permeability, in other words, they are sealed in very impermeable and hard rocks, making their formation "tight". These impermeable reservoirs which produce dry natural gas are also called "Tight Sand". Tight gas reservoirs are generally defined as having less than 0.1 milli darcy (mD) matrix permeability and less than ten percent matrix porosity. Although shales have low permeability and low effective porosity, shale gas is usually considered separate from tight gas, which is contained most commonly in sandstone, but sometimes in limestone. Tight gas is considered an unconventional source of natural gas. But they are much older than the Conventional gas. Tight gas was formed 248 million years ago in Paleozoic formations. Cementation and recrystallization chang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
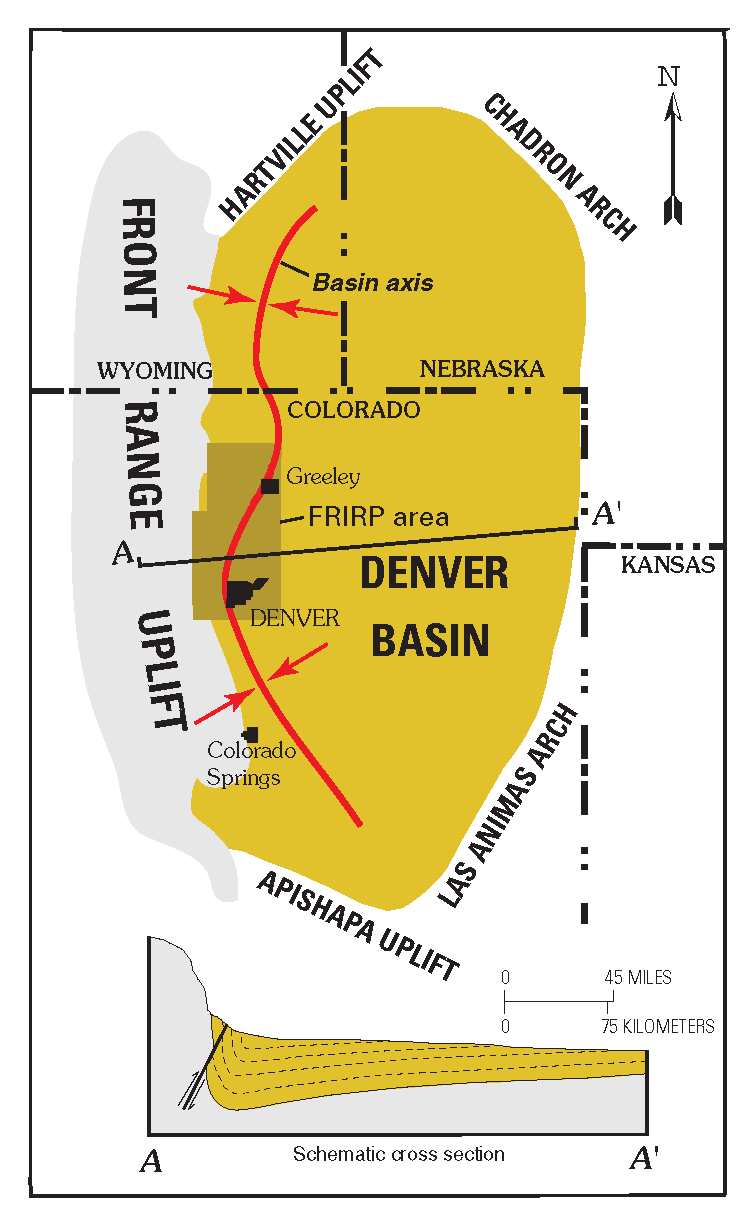
Denver Basin
The Denver Basin, variously referred to as the Julesburg Basin, Denver-Julesburg Basin (after Julesburg, Colorado), or the D-J Basin, is a geologic structural basin centered in eastern Colorado in the United States, but extending into southeast Wyoming, western Nebraska, and western Kansas. It underlies the Denver-Aurora Metropolitan Area on the eastern side of the Rocky Mountains. Geology The basin consists of a large asymmetric syncline of Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic sedimentary rock layers, trending north to south along the east side of the Front Range from the vicinity of Pueblo northward into Wyoming. The basin is deepest near Denver, where it reaches a depth of approximately 13,000 ft (3900 m) below the surface. The basin is strongly asymmetric: the Dakota Sandstone outcrops in a "hog-back" ridge near Morrison a few miles west of Denver, reaches its maximum depth beneath Denver, then ascends very gradually to its eastern outcrop in central Kansas. The Dako ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shale Gas
Shale gas is an unconventional natural gas that is found trapped within shale formations. Since the 1990s a combination of horizontal drilling and hydraulic fracturing has made large volumes of shale gas more economical to produce, and some analysts expect that shale gas will greatly expand worldwide energy supply. Shale gas has become an increasingly important source of natural gas in the United States since the start of this century, and interest has spread to potential gas shales in the rest of the world. China is estimated to have the world's largest shale gas reserves. A 2013 review by the United Kingdom Department of Energy and Climate Change noted that most studies of the subject have estimated that life-cycle greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from shale gas are similar to those of conventional natural gas, and are much less than those from coal, usually about half the greenhouse gas emissions of coal; the noted exception was a 2011 study by Howarth and others of C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of The Appalachians
The geology of the Appalachians dates back to more than 480 million years ago. A look at rocks exposed in today's Appalachian Mountains reveals elongate belts of folded and thrust faulted marine sedimentary rocks, volcanic rocks and slivers of ancient ocean floor – strong evidence that these rocks were deformed during plate collision. The birth of the Appalachian ranges marks the first of several mountain building plate collisions that culminated in the construction of the supercontinent Pangaea with the Appalachians and neighboring Anti-Atlas mountains (now in Morocco) near the center. These mountain ranges likely once reached elevations similar to those of the Alps and the Rocky Mountains before they were eroded. Geological history Paleozoic Era During the earliest part of the Paleozoic Era, the continent that would later become North America straddled the equator. The Appalachian region was a passive plate margin, not unlike today's Atlantic Coastal Plain Provinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utica Shale
The Utica Shale is a stratigraphical unit of Upper Ordovician age in the Appalachian Basin. It underlies much of the northeastern United States and adjacent parts of Canada. It takes the name from the city of Utica, New York, as it was first described as an outcrop along the Starch Factory Creek east of the city by Ebenezer Emmons in 1842. Lithology The Utica Shale is composed of calcareous, organic, and rich shale. Oil and gas The Utica shale is a major source of unconventional tight gas in Quebec, and is rapidly becoming so in Ohio. Quebec Drilling and producing from the Utica Shale began in 2006 in Quebec, focusing on an area south of the St. Lawrence River between Montreal and Quebec City. Interest has grown in the region since Denver-based Forest Oil Corp. announced a significant discovery there after testing two vertical wells. Forest Oil said its Quebec assets may hold as much as four trillion cubic feet of gas reserves, and that the Utica shale has similar rock p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotliegend
The Rotliegend, Rotliegend Group or Rotliegendes (german: the underlying red) is a lithostratigraphic unit (a sequence of rock strata) of latest Carboniferous to Guadalupian (middle Permian) age that is found in the subsurface of large areas in western and central Europe. The Rotliegend mainly consists of sandstone layers. It is usually covered by the Zechstein and lies on top of regionally different formations of late Carboniferous age. The name Rotliegend has in the past not only been used to address the rock strata themselves, but also the time span in which they were formed (in which case the Rotliegend was considered a series or subsystem of the Permian). This time span corresponds roughly with the length of the Cisuralian epoch. Facies and formation In large parts of Pangaea, the last phases of the Hercynian orogeny were still ongoing during the start of the Permian. At the same time local crustal extension formed intramontane basins such as the large Permian Basin which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
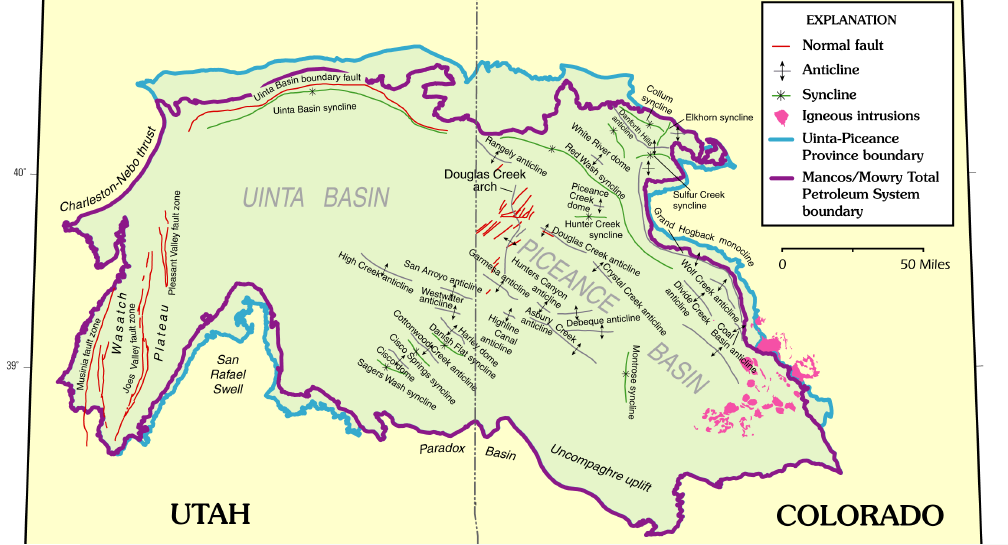
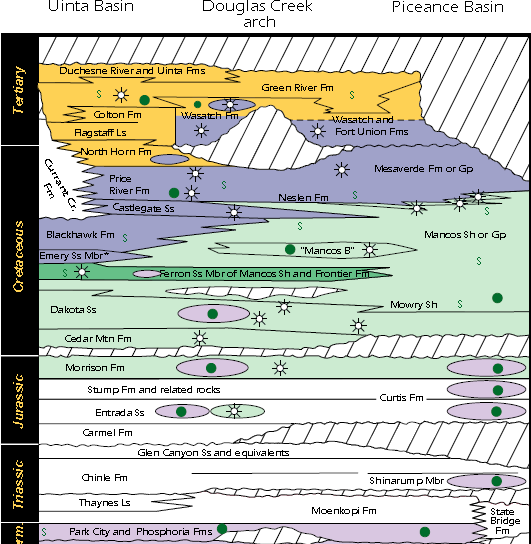
Piceance Basin
The Piceance Basin is a geologic structural basin in northwestern Colorado, in the United States. It includes geologic formations from Cambrian to Holocene in age, but the thickest section is made up of rocks from the Cretaceous Period. The basin contains reserves of coal, natural gas, and oil shale. The name likely derives from the Shoshoni word ''/piasonittsi/'' meaning “tall grass” (''/pia-/'' ‘big’ and ''/soni-/'' ‘grass’). Hydrocarbon resources In 2016 USGS released an assessment of the resources of the Mancos Shale of the Piceance Basin in Colorado and Utah, "a total of assessed technically recoverable mean resources of 74 million barrels of shale oil, 66.3 trillion cubic feet of gas, and 45 million barrels of natural gas liquids." Natural gas The basin has come to increasing public attention in recent years because of widespread drilling to extract natural gas. The primary target of gas development has been the Williams Fork Formation of the Mesaverde Group, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesaverde Formation
The Mesaverde Group is a Late Cretaceous stratigraphic group found in areas of Colorado, New Mexico, Utah, and Wyoming, in the Western United States. History The Mesaverde Formation was first described by W.H.Holmes in 1877 during the Hayden Survey. Holmes described the formation in the northern San Juan Basin as consisting of three units, which were a "Lower Escarpment" consisting of 40 m of ledge- and cliff-forming massive sandstone; a "Middle Coal Group" consisting of up to 300 m of thick slope-forming sandstone, shale, marl, and lignite; and an "Upper Escarpment" consisting of 60 m of ledge- and cliff-forming sandstone. A.J. Collier redesignated these units in 1919 as the Point Lookout Sandstone, the Menefee Formation, and the Cliff House Sandstone, and raised the Mesaverde Formation to group rank. The group was later traced to the greater Green River Basin, the Uintah and Piceance Basins, the Bighorn Basin, the Front Range, the Zuni Basin, the Wasatch Plateau, Wind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wattenberg Gas Field
The Wattenberg Gas Field is a large producing area of natural gas and condensate in the Denver Basin of central Colorado, USA. Discovered in 1970, the field was one of the first places where massive hydraulic fracturing was performed routinely and successfully on thousands of wells. The field now covers more than 2,000 square miles between the cities of Denver and Greeley, and includes more than 23,000 wells producing from a number of Cretaceous formations. The bulk of the field is in Weld County, but it extends into Adams, Boulder, Broomfield, Denver, and Larimer Counties. Geology The reservoir rocks are Cretaceous sandstones, shales, and limestones deposited under marine conditions in the Western Interior Seaway. The gas and condensate is contained within Cretaceous formations in the deepest part of the Denver Basin, where the rocks were subject to enough heat and pressure to generate oil and gas from organic material in the rock. The field is a stratigraphic trap, basin-ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbon dioxide, nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide, and helium are also usually present. Natural gas is colorless and odorless, so odorizers such as mercaptan (which smells like sulfur or rotten eggs) are commonly added to natural gas supplies for safety so that leaks can be readily detected. Natural gas is a fossil fuel and non-renewable resource that is formed when layers of organic matter (primarily marine microorganisms) decompose under anaerobic conditions and are subjected to intense heat and pressure underground over millions of years. The energy that the decayed organisms originally obtained from the sun via photosynthesis is stored as chemical energy within the molecules of methane and other hydrocarbons. Natural gas can be burned for he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Energy Technology Laboratory
The National Energy Technology Laboratory (NETL) is a U.S national laboratory under the Department of Energy Office of Fossil Energy. NETL focuses on applied research for the clean production and use of domestic energy resources. NETL performs research and development on the supply, efficiency, and environmental constraints of producing and using fossil energy resources, while maintaining their affordability. NETL has sites in Albany, Oregon; Morgantown, West Virginia; and Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. Together, these sites have 117 buildings and 242 acres of land. More than 1,400 employees work at NETL's three sites, including federal employees and contractors. NETL funds and manages contracted research in the United States and more than 40 foreign countries through arrangements with both private organizations and other government agencies. This work is augmented by onsite applied research in computational and basic sciences, energy system dynamics, geological and environmental ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanodarcy
The darcy (or darcy unit) and millidarcy (md or mD) are units of permeability, named after Henry Darcy. They are not SI units, but they are widely used in petroleum engineering and geology. The unit has also been used in biophysics and biomechanics, where the flow of fluids such as blood through capillary beds and cerebrospinal fluid through the brain interstitial space is being examined. A darcy has dimensional units of length2. Definition Permeability measures the ability of fluids to flow through rock (or other porous media). The darcy is defined using Darcy's law, which can be written as: :Q = \frac where: : The darcy is referenced to a mixture of unit systems. A medium with a permeability of 1 darcy permits a flow of 1 cm3/s of a fluid with viscosity 1 cP (1 mPa·s) under a pressure gradient of 1 atm/cm acting across an area of 1 cm2. Typical values of permeability range as high as 100,000 darcys for gravel, to less than 0.01 microdarcy for granite. Sand h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |