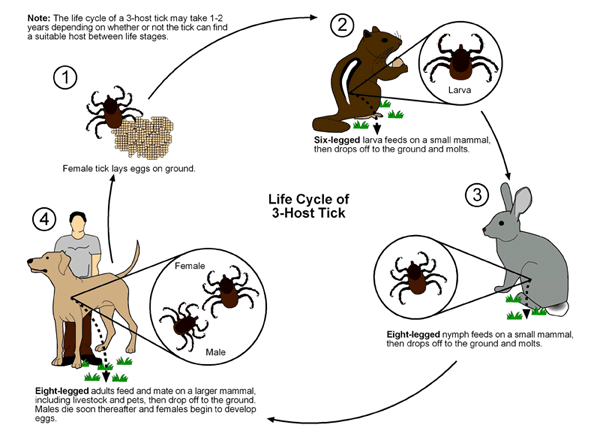
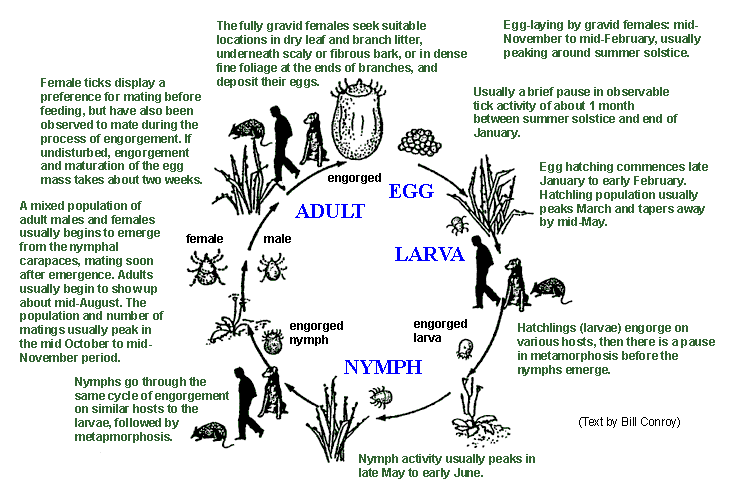
|
Ticks Of Domestic Animals
Ticks of domestic animals directly cause poor health and loss of production to their hosts. Ticks also transmit numerous kinds of viruses, bacteria, and protozoa between domestic animals. These microbes cause diseases which can be severely debilitating or fatal to domestic animals, and may also affect humans. Ticks are especially important to domestic animals in tropical and subtropical countries, where the warm climate enables many species to flourish. Also, the large populations of wild animals in warm countries provide a reservoir of ticks and infective microbes that spread to domestic animals. Farmers of livestock animals use many methods to control ticks, and related treatments are used to reduce infestation of companion animals. Variety of ticks affecting domestic animals Ticks are invertebrate animals in the phylum Arthropoda, and are related to spiders. Ticks are in the subclass Acari, which consists of many orders of mites and one tick order, the Ixodida. Some mites are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyalomma Dromedarii
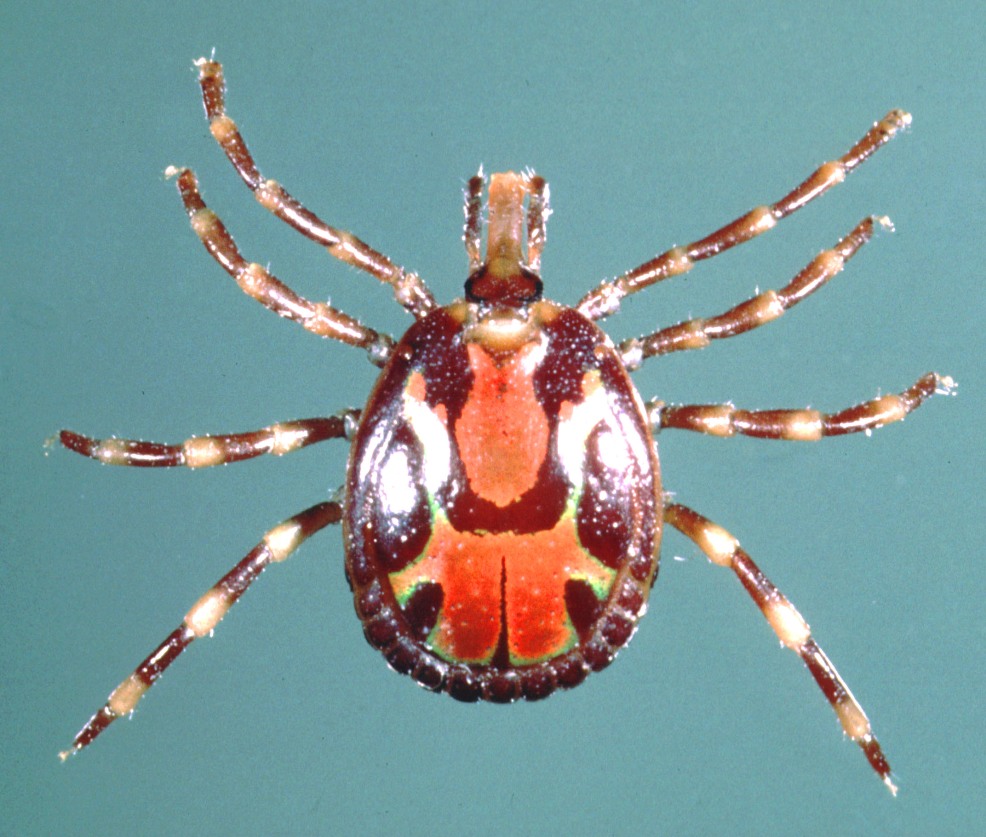
''Hyalomma dromedarii'' is a species of hard-bodied ticks belonging to the family Ixodidae. Description The dorsal shield ( conscutum) of males can reach a length of . These hard-bodied ticks are broadly oval in shape. The basic color is yellow- to red-brown. This species is closely associated with camels, that are the main hosts of the adults, which may also parasitize other domestic animals. Nymphs and larvae are associated with the same hosts, but can also parasitize rodents, hedgehogs and birds. This species is ascribed with spreading the virus that causes the life-threatening Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever. The bites cause the surrounding tissue to die and become necrotic. The dead tissue falls out of the body after a few days. The wounds look very serious, but usually heal without any intervention and do not generally become infected any further. Distribution ''Hyalomma dromedarii ''is widespread in North Africa, the northern regions of West, Central, and East Africa, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loss Of Appetite
Anorexia is a medical term for a loss of appetite. While the term in non-scientific publications is often used interchangeably with anorexia nervosa, many possible causes exist for a loss of appetite, some of which may be harmless, while others indicate a serious clinical condition or pose a significant risk. Anorexia is a symptom, not a diagnosis. Anorexia is not to be confused with the mental health disorder anorexia nervosa. Because the term 'anorexia' is often used as a short-form of anorexia nervosa, to avoid confusion a provider must clarify to a patient whether they are simply referring to a decreased appetite or the mental health disorder. Anyone can manifest anorexia as a loss of appetite, regardless of their gender, age, or weight. The symptom also occurs in other animals, such as cats, dogs, cattle, goats, and sheep. In these species, anorexia may be referred to as inappetence. As in humans, loss of appetite can be due to a range of diseases and conditions, as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermacentor Reticulatus
''Dermacentor reticulatus'', also known as the ornate cow tick, ornate dog tick, meadow tick, and marsh tick, is a species of tick from the family Ixodidae. It is the type species for the genus '' Dermacentor''. ''D. reticulatus'' is an ornate tick. The female varies in size from 3.8–4.2 mm (unfed) to 10 mm when engorged after feeding. The unfed male is 4.2–4.8 mm long. ''D. reticulatus'' is found in Europe and Western Asia, generally in wooded areas. Lifecycle ''D. reticulartus'' has a three-host development cycle. The adult female remains on a host for 9–15 days, and can lay 3000–4500 eggs, although the total number of eggs depends on the size of the female. The larva hatches from the egg in 14–21 days. Disease transmission ''D. reticulatus'' is a vector of various disease organisms, including '' Babesia canis'', ''Francisella tularensis'', '' Coxiella burnetti'', ''Theileria equi'', and several ''Rickettsia'' species, such as ''Rickettsia ''Ricke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermacentor Variabilis
''Dermacentor variabilis'', also known as the American dog tick or wood tick, is a species of tick that is known to carry bacteria responsible for several diseases in humans, including Rocky Mountain spotted fever and tularemia (''Francisella tularensis''). It is one of the best-known hard ticks. Diseases are spread when it sucks blood from the host. It may take several days for the host to experience symptoms. Though ''D. variabilis'' may be exposed to ''Borrelia burgdorferi'', the causative agent of Lyme disease, these ticks are not competent vectors for the transmission of this disease. The primary vectors for ''B. burgdorferi'' are the deer ticks '' Ixodes scapularis'' in eastern parts of the United States, '' Ixodes pacificus'' in California and Oregon, and ''Ixodes ricinus'' in Europe. ''D. variabilis'' may also carry '' Anaplasma phagocytophilum'', the causative agent of human granulocytic anaplasmosis, and '' Ehrlichia chaffeensis'', the causative agent of human mon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermacentor Andersoni
''Dermacentor andersoni'', commonly known as the Rocky Mountain wood tick, is a hard tick, or member of the Ixodidae family, with three life stages including larvae, nymph, and finally adult An adult is a human or other animal that has reached full growth. In human context, the term ''adult'' has meanings associated with social and legal concepts. In contrast to a " minor", a legal adult is a person who has attained the age of major ..., or, more entomologically, imago. This tick is generally located in the northwest United States and southwest Canada along the Rocky Mountains. This tick is generally a vector for Colorado tick fever, but can also be a vector for Rocky Mountain spotted fever and tularemia. During the larval and nymphal stages, the tick does not feed on humans, but during the adult stage, it will. Prevention of infections associated with these ticks is based on control of exposure to the vector, including wearing proper clothing when in woods/wet areas, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ixodes Holocyclus
''Ixodes holocyclus'', commonly known as the Australian paralysis tick, is one of about 75 species in the Australian tick fauna and is considered the most medically important. It can cause paralysis by injecting neurotoxins into its host. It is usually found in a 20-kilometre wide band following the eastern coastline of Australia. Within this range ''Ixodes holocyclus'' is the tick most frequently encountered by humans and their pets. As this area also contains Australia's most densely populated regions, bites on people, pets and livestock are relatively common. Paralysis ticks are found in many types of habitat particularly areas of high rainfall such as wet sclerophyll forest and temperate rainforest. The natural hosts for the paralysis tick include koalas, bandicoots, possums and kangaroos. Common names The use of common names has led to many colloquial expressions for ''Ixodes holocyclus''. The most generally accepted name used within Australia is ''Australian paralysis ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ixodes Scapularis
''Ixodes scapularis'' is commonly known as the deer tick or black-legged tick (although some people reserve the latter term for '' Ixodes pacificus'', which is found on the west coast of the US), and in some parts of the US as the bear tick. It was also named ''Ixodes dammini'' until it was shown to be the same species in 1993. It is a hard-bodied tick found in the eastern and northern Midwest of the United States as well as in southeastern Canada. It is a vector for several diseases of animals, including humans ( Lyme disease, babesiosis, anaplasmosis, Powassan virus disease, etc.) and is known as the deer tick owing to its habit of parasitizing the white-tailed deer. It is also known to parasitize mice, lizards, migratory birds, etc. especially while the tick is in the larval or nymphal stage. Description The image shown here—and in fact, most images of ''Ixodes scapularis'' that are commonly available—show an adult female that is unengorged, that is, an adult female th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ixodes Ricinus
''Ixodes ricinus'', the castor bean tick, is a chiefly European species of hard-bodied tick. It may reach a length of when engorged with a blood meal, and can transmit both bacterial and viral pathogens such as the causative agents of Lyme disease and tick-borne encephalitis. Description In common with other species of '' Ixodes'', ''I. ricinus'' has no eyes and is not ornate; it has no festoons (wrinkles along the posterior margin). The palpi are longer than they are wide, and an anal groove is above the anus. It has a hard dorsal shield which covers the entire opisthosoma (abdomen), but only part of it in females and nymphs. ''I. ricinus'' is the largest of the three common species of ''Ixodes'' in the British Isles (the other two being '' I. canisuga'', the British dog tick, and '' I. trianguliceps'', the vole tick). Adult males are long, and unfed nymphs are long; females are long before feeding and long when engorged. Distribution ''Ixodes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |