|
Tick-borne Illness
Tick-borne diseases, which afflict humans and other animals, are caused by infectious agents Vector (epidemiology), transmitted by tick bites. They are caused by infection with a variety of pathogens, including rickettsia and other types of bacterium, bacteria, viruses, and protozoa. The economic impact of tick-borne diseases is considered to be substantial in humans, and tick-borne diseases are estimated to affect ~80 % of cattle worldwide. 18 tick-borne pathogens have been identified in the United States according to the Centers for Disease Control and at least 27 are known globally. New tick-borne diseases have been discovered in the 21st century, due in part to the use of Molecular diagnostics, molecular assays and next-generation sequencing. The occurrence of ticks and tick-borne illnesses in humans is increasing. Tick populations are spreading into new areas, in part Climate_change_and_infectious_diseases#Tick_borne_disease, due to climate change. Tick populations are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infectious Disease (medical Specialty)
Infectious diseases or ID, also known as infectiology, is a medical specialty dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of infections. An infectious diseases specialist's practice consists of managing nosocomial ( healthcare-acquired) infections or community-acquired infections and is historically associated with hygiene, epidemiology, clinical microbiology, travel medicine and tropical medicine. Scope Infectious diseases specialists typically serve as consultants to other physicians in cases of complex infections, and often manage patients with HIV/AIDS and other forms of immunodeficiency. Although many common infections are treated by physicians without formal expertise in infectious diseases, specialists may be consulted for cases where an infection is difficult to diagnose or manage. They may also be asked to help determine the cause of a fever of unknown origin. Specialists in infectious diseases can practice both in hospitals (inpatient) and clinics (outpatient). In hospital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatigue (medical)
Fatigue describes a state of tiredness that does not resolve with rest or sleep. In general usage, fatigue is synonymous with extreme tiredness or exhaustion that normally follows prolonged physical or mental activity. When it does not resolve after rest or sleep, or occurs independently of physical or mental exertion, it may be a symptom of a medical condition that may become severe or progressive. Fatigue can be a feature of a mental disorder such as depression; may be associated with conditions of chronic pain such as fibromyalgia; it may also feature in conditions of chronic low-level inflammation, and be a disease-related symptom in many other conditions. Fatigue often has no known cause, and is recognised as being very complex in nature. Fatigability describes a susceptibility to fatigue. Physical fatigue results from muscle fatigue brought about by intense physical activity. Mental fatigue results from prolonged periods of cognitive activity which impairs cognitive abil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borrelia Burgdorferi
''Borrelia burgdorferi'' is a bacterial species of the spirochete class in the genus ''Borrelia'', and is one of the causative agents of Lyme disease in humans. Along with a few similar genospecies, some of which also cause Lyme disease, it makes up the species complex of ''Borrelia burgdorferi'' sensu lato. The complex currently comprises 20 accepted and 3 proposed genospecies. ''B. burgdorferi'' sensu stricto exists in North America and Eurasia and until 2016 was the only known cause of Lyme disease in North America. ''Borrelia'' species are Gram-negative. Microbiology ''Borrelia burgdorferi'' is named after the researcher Willy Burgdorfer, who first isolated the bacterium in 1982. ''Borrelia burgdorferi'' is a microaerophile, requiring small amounts of oxygen in order to undergo glycolysis and survive. Like all other ''Borrelia'' sps., this bacterium is also gram-negative and a spirochete. Borrelia colonies are often smaller, rounded, and white with an elevated center. ''B. b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ixodidae
The Ixodidae are the family of hard ticks or scale ticks, one of the three families of ticks, consisting of over 700 species. They are known as 'hard ticks' because they have a scutum or hard shield, which the other major family of ticks, the 'soft ticks' (Argasidae), lack. They are ectoparasites of a wide range of host species, and some are vectors of pathogens that can cause human disease. Description They are distinguished from the Argasidae by the presence of a scutum. In both the nymph and the adult, a prominent gnathosoma (or capitulum, mouth and feeding parts) projects forward from the animal's body; in the Argasidae, conversely, the gnathosoma is concealed beneath the body. They differ, too, in their lifecycle; Ixodidae that attach to a host bite painlessly and are generally unnoticed, and they remain in place until they engorge and are ready to change their skin; this process may take days or weeks. Some species drop off the host to moult in a safe place, whereas others r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argasidae
The Argasidae are the family of soft ticks, one of the three families of ticks. The family contains 193 species, although the composition of the genera is less certain, and more study is needed before the genera can become stable. The currently accepted genera are '' Antricola'', '' Argas'', '' Nothoaspis'', ''Ornithodoros'', and '' Otobius''. The Argasidae are very common in South Asia, along with 96 other species of ticks, making South Asia the region with the highest biodiversity of ticks worldwide. Soft ticks are resistant to desiccation and can live for several years in arid conditions. Physical characteristics Soft ticks lack the hard scutum present in the hard ticks (Ixodidae). The gnathosoma (or capitulum, the mouthparts-bearing structure) is located on the underside of the animal's body and is not readily visible, while in the Ixodidae, the gnathosoma projects forward from the body. The lateral edges of the body are rounded. See also *Ticks of domestic animals Ticks of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
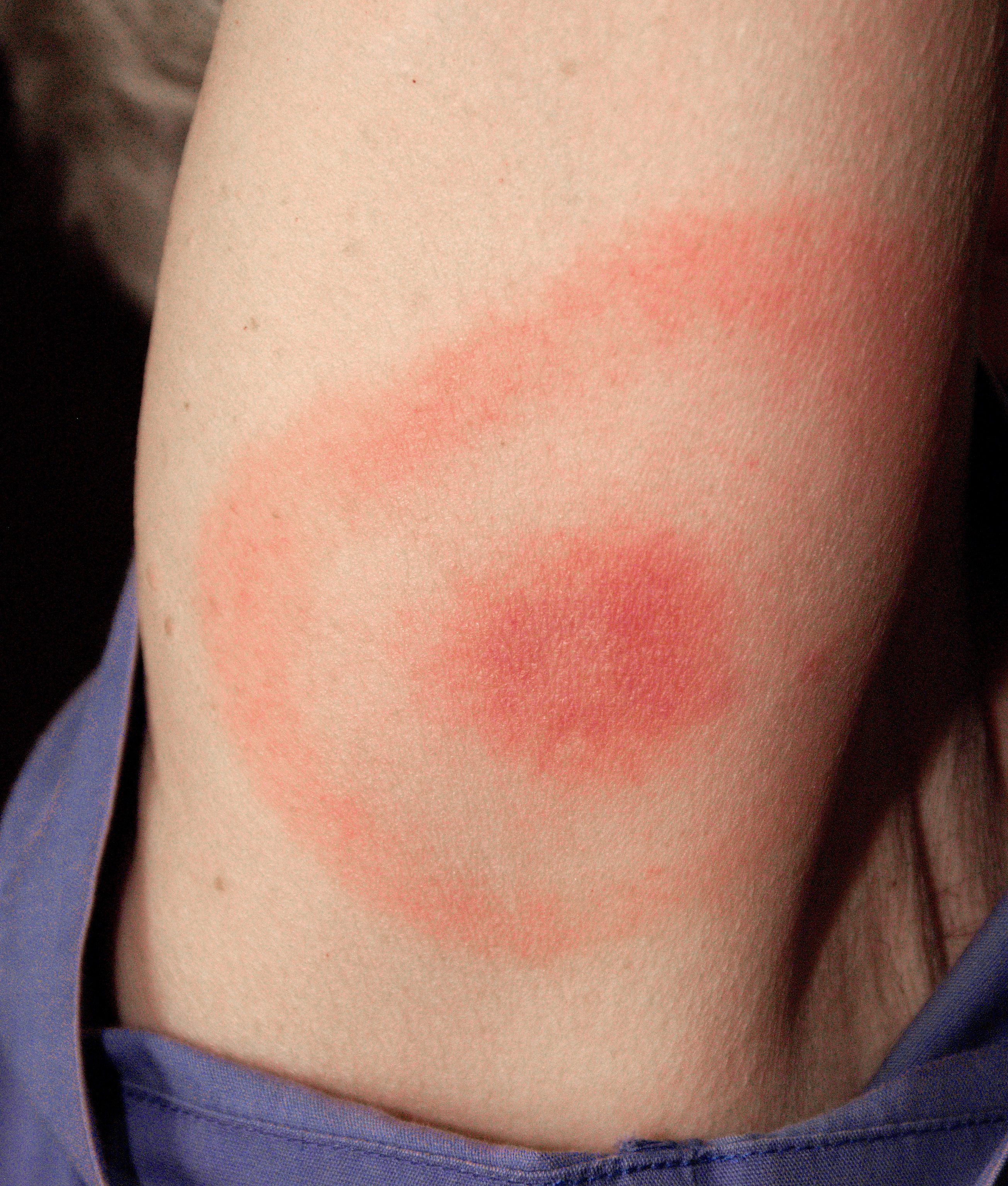
Lyme Disease
Lyme disease, also known as Lyme borreliosis, is a vector-borne disease caused by the ''Borrelia'' bacterium, which is spread by ticks in the genus ''Ixodes''. The most common sign of infection is an expanding red rash, known as erythema migrans (EM), which appears at the site of the tick bite about a week afterwards. The rash is typically neither itchy nor painful. Approximately 70–80% of infected people develop a rash. Early diagnosis can be difficult. Other early symptoms may include fever, headaches and tiredness. If untreated, symptoms may include loss of the ability to move one or both sides of the face, joint pains, severe headaches with neck stiffness or heart palpitations. Months to years later repeated episodes of joint pain and swelling may occur. Occasionally shooting pains or tingling in the arms and legs may develop. Despite appropriate treatment about 10 to 20% of those affected develop joint pains, memory problems and tiredness for at least six months. Lym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of such infections. They may either kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the common cold or influenza; drugs which inhibit viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals rather than antibiotics. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against microbes, but in the usual medical usage, antibiotics (such as penicillin) are those produced naturally (by one microorganism fighting another), whereas non-antibiotic antibacterials (such as sulfonamides and antiseptics) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
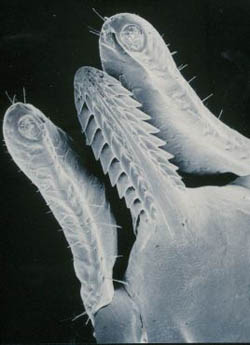
Hypostome (tick)
The hypostome (also called the maxilla, radula, or Labium (insect), labium) is a Osseous tissue, calcified harpoon-like structure near the mouth area of certain Parasitism, parasitic arthropods including ticks, that allows them to anchor themselves firmly in place on a host (biology), host vertebrate while sucking blood. The hypostome being present in almost all tick families suggests that hematophagy is the ancestral condition, as is the fact that life stages that do not feed on blood lack the organ. Some ticks of the Ixodidae family (hard ticks) secret a cement to strengthen the attachment. See also *Mandible (arthropod) References Arachnid anatomy {{Arthropod-anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of health". Headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, it has six regional offices and 150 field offices worldwide. The WHO was established on 7 April 1948. The first meeting of the World Health Assembly (WHA), the agency's governing body, took place on 24 July of that year. The WHO incorporated the assets, personnel, and duties of the League of Nations' Health Organization and the , including the International Classification of Diseases (ICD). Its work began in earnest in 1951 after a significant infusion of financial and technical resources. The WHO's mandate seeks and includes: working worldwide to promote health, keeping the world safe, and serve the vulnerable. It advocates that a billion more people should have: universal health care coverag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Institute For Occupational Safety And Health
The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH, ) is the United States federal agency responsible for conducting research and making recommendations for the prevention of work-related injury and illness. NIOSH is part of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) within the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Despite its name, it is not part of the National Institutes of Health. Its current director is John Howard. NIOSH is headquartered in Washington, D.C., with research laboratories and offices in Cincinnati, Ohio; Morgantown, West Virginia; Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania; Denver, Colorado; Anchorage, Alaska; Spokane, Washington; and Atlanta, Georgia. NIOSH is a professionally diverse organization with a staff of 1,200 people representing a wide range of disciplines including epidemiology, medicine, industrial hygiene, safety, psychology, engineering, chemistry, and statistics. The Occupational Safety and Health Act, signed by President Rich ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centers For Disease Control And Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency, under the Department of Health and Human Services, and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia. The agency's main goal is the protection of public health and safety through the control and prevention of disease, injury, and disability in the US and worldwide. The CDC focuses national attention on developing and applying disease control and prevention. It especially focuses its attention on infectious disease, food borne pathogens, environmental health, occupational safety and health, health promotion, injury prevention and educational activities designed to improve the health of United States citizens. The CDC also conducts research and provides information on non-infectious diseases, such as obesity and diabetes, and is a founding member of the International Association of National Public Health Institutes. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DEET
''N'',''N''-Diethyl-''meta''-toluamide, also called DEET () or diethyltoluamide, is the most common active ingredient in insect repellents. It is a slightly yellow oil intended to be applied to the skin or to clothing and provides protection against mosquitoes, flies, ticks, fleas, chiggers, leeches and many biting insects. History DEET was developed in 1944 by Samuel Gertler of the United States Department of Agriculture for use by the United States Army, following its experience of jungle warfare during World War II. It was originally tested as a pesticide on farm fields, and entered military use in 1946 and civilian use in 1957. It was used in Vietnam and Southeast Asia. In its original form, known as "bug juice", the application solution was composed of 75% DEET and 25% ethanol. Later, a new version of the repellent was developed by the U.S. Army and the USDA. This formulation consisted of DEET and a mixture of polymers that extended its release and reduced its evaporation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |