|
Thyroiditis
Thyroiditis is the inflammation of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is located on the front of the neck below the laryngeal prominence, and makes hormones that control metabolism. Thyroiditis is a group of disorders that all cause thyroidal inflammation. Symptoms, diagnosis and treatment depend on the cause of thyroiditis. Forms of thyroiditis are Hashimoto's thyroiditis, postpartum thyroiditis, subacute (de Quervain's) thyroiditis, silent thyroiditis, drug-induced thyroiditis, radiation-induced thyroiditis and acute thyroiditis. Types Hashimoto's thyroiditis is an autoimmune disease where the body creates thyroid antibodies. It presents with hypothyroidism due to the destruction of thyroid cells. In Hashimoto's thyroiditis, the hypothyroidism is most often permanent, with symptoms are fatigue, weight gain, depression, dry skin, and constipation. Thyroid hormone replacement is the treatment of hypothyroidism. Silent thyroiditis or painless thyroiditis, also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
Hashimoto's thyroiditis, also known as chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis, Hashimoto's disease and autoimmune thyroiditis, is an autoimmune disease in which the thyroid gland is gradually destroyed. Early on, symptoms may not be noticed. Over time, the thyroid may enlarge, forming a painless goiter. Most people eventually develop hypothyroidism with accompanying weight gain, fatigue, constipation, hair loss, and general pains. After many years the thyroid typically shrinks in size. Potential complications include thyroid lymphoma. Further complications of hypothyroidism can include high cholesterol, heart disease, heart failure, high blood pressure, myxedema, and potential problems in pregnancy. Hashimoto's thyroiditis is thought to be due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Risk factors include a family history of the condition and having another autoimmune disease. Diagnosis is confirmed with blood tests for TSH, thyroxine ( T4), antithyroid autoant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subacute Thyroiditis
Subacute thyroiditis refers to a temporal classification of the different forms of thyroiditis based on onset of symptoms. The temporal classification of thyroiditis includes presentation of symptoms in an acute, subacute, or chronic manner. There are also other classification systems for thyroiditis based on factors such as clinical symptoms and underlying etiology. Broadly, there are three categories of thyroiditis that can present in a subacute fashion, including subacute granulomatous thyroiditis, subacute lymphocytic thyroiditis, and drug-induced thyroiditis. In all three categories, there is inflammation of the thyroid gland causing damage to the thyroid follicular cells which produce and secrete thyroid hormone. This often results in three phases of thyroid dysfunction beginning with initial thyrotoxicosis followed by hypothyroidism before resolution back to normal thyroid function. In the thyrotoxic stage, individuals usually complain of fever, myalgia, and may have a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Quervain's Thyroiditis
De Quervain's thyroiditis, also known as subacute granulomatous thyroiditis or giant cell thyroiditis, is a self-limiting inflammatory illness of the thyroid gland. De Quervain thyroiditis is characterized by fever, Influenza-like illness, flu-like symptoms, a painful Goitre, goiter, and neck pain. The disease has a natural history of four phases: thyroid pain, thyrotoxicosis, euthyroid phase, Hypothyroidism, hypothyroid phase, and recovery euthyroid phase. De Quervain's thyroiditis has been linked to various diseases, including mumps, Adenoviridae, adenovirus, and enterovirus. It may have a hereditary component, with two-thirds of patients having positive HLA-B35, histocompatibility antigen (HLA) B35 results. Atypical cases have HLA-B15, HLA B15/62 positivity, and it is more common in summer or fall months in people who test positive for HLA-B67, HLA B67. De Quervain thyroiditis is diagnosed through clinical and test results, with laboratory features including elevated C-reactiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Thyroiditis
Acute infectious thyroiditis (AIT) also known as suppurative thyroiditis, microbial inflammatory thyroiditis, pyrogenic thyroiditis and bacterial thyroiditis. The thyroid is normally very resistant to infection. Due to a relatively high amount of iodine in the tissue, as well as high vascularity and lymphatic drainage to the region, it is difficult for pathogens to infect the thyroid tissue. Despite all this, a persistent fistula from the piriform sinus may make the left lobe of the thyroid susceptible to infection and abscess formation. AIT is most often caused by a bacterial infection but can also be caused by a fungal or parasitic infection, most commonly in an immunocompromised host. Signs and symptoms In most cases AIT is characterized by onset of pain, firmness, tenderness, redness or swelling in the anterior aspect of the neck. Patients will also present with a sudden fever, dysphagia, difficulty swallowing and dysphonia, difficulty controlling the voice. Symptoms may be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid Gland
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, it is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck below the Adam's apple. It consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the isthmus (: isthmi). Microscopically, the functional unit of the thyroid gland is the spherical thyroid follicle, lined with follicular cells (thyrocytes), and occasional parafollicular cells that surround a lumen containing colloid. The thyroid gland secretes three hormones: the two thyroid hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4)and a peptide hormone, calcitonin. The thyroid hormones influence the metabolic rate and protein synthesis and growth and development in children. Calcitonin plays a role in calcium homeostasis. Secretion of the two thyroid hormones is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is secreted from the anterior pituitary gland. TSH is regulated by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postpartum Thyroiditis
Postpartum thyroiditis is a type of thyroiditis, inflammation of the thyroid, occurring in the first 12 months after pregnancy and typically involves hyperthyroidism followed by hypothyroidism which is most often temporary. Postpartum thyroiditis is believed to result from the modifications to the immune system necessary in pregnancy, and histologically is the same as subacute lymphocytic thyroiditis also called silent thyroiditis or painless thyroiditis, a form of subacute thyroiditis. The process is normally self-limiting, but when thyroid antibodies are found there is a high chance of this proceeding to permanent hypothyroidism. Signs and symptoms The initial phase of hyperthyroid symptoms occurs transiently about two to six months postpartum. Typical symptoms include irritability, nervousness, palpitations, and heat intolerance. Hormonal disturbances during this phase tend to occur with lower intensity compared with the hypothyroid phase. As a result, the hyperthyroid phas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
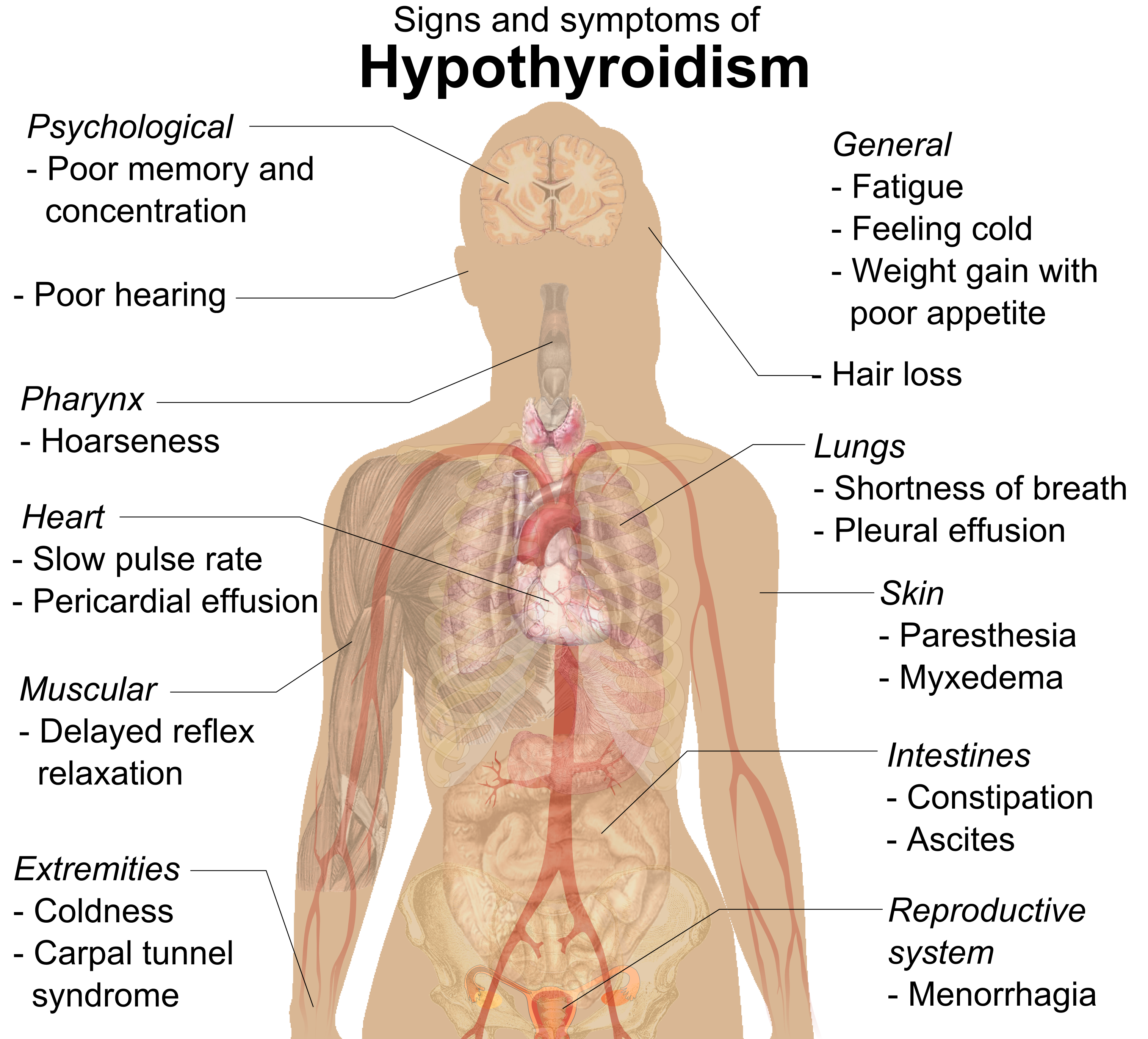
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is an endocrine disease in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as cold intolerance, poor ability to tolerate cold, fatigue, extreme fatigue, muscle aches, constipation, slow heart rate, Depression (mood), depression, and weight gain. Occasionally there may be swelling of the front part of the neck due to goiter. Untreated cases of hypothyroidism during pregnancy can lead to delays in child development, growth and intellectual development in the baby or congenital iodine deficiency syndrome. Worldwide, iodine deficiency, too little iodine in the diet is the most common cause of hypothyroidism. Hashimoto's thyroiditis, an autoimmune disease where the body's immune system reacts to the thyroid gland, is the most common cause of hypothyroidism in countries with sufficient dietary iodine. Less common causes include previous treatment with iodine-131, radioactive iodine, injury to the hypothalamus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postpartum Thyroiditis
Postpartum thyroiditis is a type of thyroiditis, inflammation of the thyroid, occurring in the first 12 months after pregnancy and typically involves hyperthyroidism followed by hypothyroidism which is most often temporary. Postpartum thyroiditis is believed to result from the modifications to the immune system necessary in pregnancy, and histologically is the same as subacute lymphocytic thyroiditis also called silent thyroiditis or painless thyroiditis, a form of subacute thyroiditis. The process is normally self-limiting, but when thyroid antibodies are found there is a high chance of this proceeding to permanent hypothyroidism. Signs and symptoms The initial phase of hyperthyroid symptoms occurs transiently about two to six months postpartum. Typical symptoms include irritability, nervousness, palpitations, and heat intolerance. Hormonal disturbances during this phase tend to occur with lower intensity compared with the hypothyroid phase. As a result, the hyperthyroid phas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silent Thyroiditis
Silent thyroiditis is a form of thyroiditis. It may occur at any age and is more common in females. When silent thyroiditis occurs postpartum it is called postpartum thyroiditis. Both of these entities can be considered subtypes of Hashimoto's thyroiditis and have an autoimmune basis. Anti-thyroid antibodies are common in all three and the underlying histology is similar. This disorder should not be confused with de Quervain's thyroiditis which is another form of subacute thyroiditis. Symptoms and signs Silent thyroiditis features a small goiter without tenderness. This condition tends to have a phase of hyperthyroidism followed by a return to a euthyroid state, and then a phase of hypothyroidism, followed again by a return to the euthyroid state. The time span of each phase can vary; however, each phase usually lasts 2–3 months. Diagnosis Silent thyroiditis can only be diagnosed definitively by taking a radioactive iodine uptake test (RAIU) test. During both the hyperthyroid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riedel's Thyroiditis
Riedel's thyroiditis (also known as invasive fibrous thyroiditis), is a chronic form of thyroiditis. It is now believed that Riedel's thyroiditis is one manifestation of a systemic disease that can affect many organ systems called IgG4-related disease. It is often a multi-organ disease affecting pancreas, liver, kidney, salivary and orbital tissues and retroperitoneal space. The hallmarks of the disease are fibrosis and infiltration by IgG4 secreting plasma cells. Signs and symptoms IgG4-related autoimmune diseases are characterized by excessive fibrosis. In case of Riedel's thyroiditis, fibrosis extends beyond the capsule and involves contiguous neck structures, clinically simulating thyroid carcinoma. There is a rapid thyroid enlargement. Compression of trachea, dysphagia are probable outcomes. Marked thyroid follicular cell atrophy confirms hypothyroidism. Signs of hypothyroidism include myxedema, lethargy, cold-intolerance, apathy, slowed intellectual functions, dysthymia or s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |