|
Thyristor-switched Capacitor
A thyristor-switched capacitor (TSC) is a type of equipment used for compensating reactive power in electrical power systems. It consists of a power capacitor connected in series with a bidirectional thyristor valve and, usually, a current limiting reactor (inductor). The thyristor switched capacitor is an important component of a Static VAR Compensator (SVC),Hingorani, N.G. & Gyugyi, L. Understanding FACTS - Concepts and Technology of Flexible AC Transmission Systems. IEEE. . where it is often used in conjunction with a thyristor controlled reactor (TCR). Static VAR compensators are a member of the Flexible AC transmission system (FACTS) family. Circuit diagram A TSC is usually a three-phase assembly, connected either in a delta or a star arrangement. Unlike the TCR, a TSC generates no harmonics and so requires no filtering. For this reason, some SVCs have been built with only TSCs .[Horwill, C., Young, D.J., Wong, K.T.G. A design for a relocatable tertiary connected SVC. IEE C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reactive Power
Reactive may refer to: *Generally, capable of having a reaction (other) *An adjective abbreviation denoting a bowling ball coverstock made of reactive resin *Reactivity (chemistry) *Reactive mind *Reactive programming See also *Reactance (other) Reactance may refer to: * Electrical reactance In electrical circuits, reactance is the opposition presented to alternating current by inductance or capacitance. Greater reactance gives smaller current for the same applied voltage. Reactance is ... * Reactivity (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyristor Switched Capacitor Waveforms 2
A thyristor () is a solid-state semiconductor device with four layers of alternating P- and N-type materials used for high-power applications. It acts exclusively as a bistable switch (or a latch), conducting when the gate receives a current trigger, and continuing to conduct until the voltage across the device is reversed biased, or until the voltage is removed (by some other means). There are two designs, differing in what triggers the conducting state. In a three-lead thyristor, a small current on its Gate lead controls the larger current of the Anode to Cathode path. In a two-lead thyristor, conduction begins when the potential difference between the Anode and Cathode themselves is sufficiently large (breakdown voltage). Some sources define silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR) and thyristor as synonymous. Other sources define thyristors as more complex devices that incorporate at least four layers of alternating N-type and P-type substrate. The first thyristor devices were r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Switched Capacitor
A switched capacitor (SC) is an electronic circuit that implements a function by moving charges into and out of capacitors when electronic switches are opened and closed. Usually, non-overlapping clock signals are used to control the switches, so that not all switches are closed simultaneously. Filters implemented with these elements are termed ''switched-capacitor filters'', which depend only on the ratios between capacitances and the switching frequency, and not on precise resistors. This makes them much more suitable for use within integrated circuits, where accurately specified resistors and capacitors are not economical to construct. SC circuits are typically implemented using metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) technology, with MOS capacitors and MOS field-effect transistor (MOSFET) switches, and they are commonly fabricated using the complementary MOS (CMOS) process. Common applications of MOS SC circuits include mixed-signal integrated circuits, digital-to-analog converte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Grid (Great Britain)
In the electricity sector in the United Kingdom, the National Grid is the high-voltage electric power transmission network serving Great Britain, connecting power stations and major substations and ensuring that electricity generated anywhere on it can be used to satisfy demand elsewhere. The network covers the great majority of Great Britain and several of the surrounding islands. It does not cover Northern Ireland, which is part of a single electricity market with the Republic of Ireland. The GB grid is connected as a wide area synchronous grid nominally running at 50 hertz. There are also undersea interconnections to other grids in the Isle of Man, Northern Ireland, the Republic of Ireland, France, Belgium, the Netherlands and Norway. On the breakup of the Central Electricity Generating Board in 1990, the ownership and operation of the National Grid in England and Wales passed to National Grid Company plc, later to become National Grid Transco, and now National Grid plc. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resonance
Resonance describes the phenomenon of increased amplitude that occurs when the frequency of an applied periodic force (or a Fourier component of it) is equal or close to a natural frequency of the system on which it acts. When an oscillating force is applied at a resonant frequency of a dynamic system, the system will oscillate at a higher amplitude than when the same force is applied at other, non-resonant frequencies. Frequencies at which the response amplitude is a relative maximum are also known as resonant frequencies or resonance frequencies of the system. Small periodic forces that are near a resonant frequency of the system have the ability to produce large amplitude oscillations in the system due to the storage of vibrational energy. Resonance phenomena occur with all types of vibrations or waves: there is mechanical resonance, orbital resonance, acoustic resonance, electromagnetic resonance, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), electron spin resonance (ESR) and reso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deionised Water
Purified water is water that has been mechanically filtered or processed to remove impurities and make it suitable for use. Distilled water was, formerly, the most common form of purified water, but, in recent years, water is more frequently purified by other processes including capacitive deionization, reverse osmosis, carbon filtering, microfiltration, ultrafiltration, ultraviolet oxidation, or electrodeionization. Combinations of a number of these processes have come into use to produce ultrapure water of such high purity that its trace contaminants are measured in parts per billion (ppb) or parts per trillion (ppt). Purified water has many uses, largely in the production of medications, in science and engineering laboratories and industries, and is produced in a range of purities. It is also used in the commercial beverage industry as the primary ingredient of any given trademarked bottling formula, in order to maintain product consistency. It can be produced on-site for imme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snubber Resistor
A snubber is a device used to suppress ("snub") a phenomenon such as voltage transients in electrical systems, pressure transients in fluid systems (caused by for example water hammer) or excess force or rapid movement in mechanical systems. Electrical systems Snubbers are frequently used in electrical systems with an inductive load where the sudden interruption of current flow leads to a large counter-electromotive force: a rise in voltage across the current switching device that opposes the change in current, in accordance with Faraday's law. This transient can be a source of electromagnetic interference (EMI) in other circuits. Additionally, if the voltage generated across the device is beyond what the device is intended to tolerate, it may damage or destroy it. The snubber provides a short-term alternative current path around the current switching device so that the inductive element may be safely discharged. Inductive elements are often unintentional, arising from the curren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snubber
A snubber is a device used to suppress ("snub") a phenomenon such as voltage transients in electrical systems, pressure transients in fluid systems (caused by for example water hammer) or excess force or rapid movement in mechanical systems. Electrical systems Snubbers are frequently used in electrical systems with an inductive load where the sudden interruption of current flow leads to a large counter-electromotive force: a rise in voltage across the current switching device that opposes the change in current, in accordance with Faraday's law. This transient can be a source of electromagnetic interference (EMI) in other circuits. Additionally, if the voltage generated across the device is beyond what the device is intended to tolerate, it may damage or destroy it. The snubber provides a short-term alternative current path around the current switching device so that the inductive element may be safely discharged. Inductive elements are often unintentional, arising from the curr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
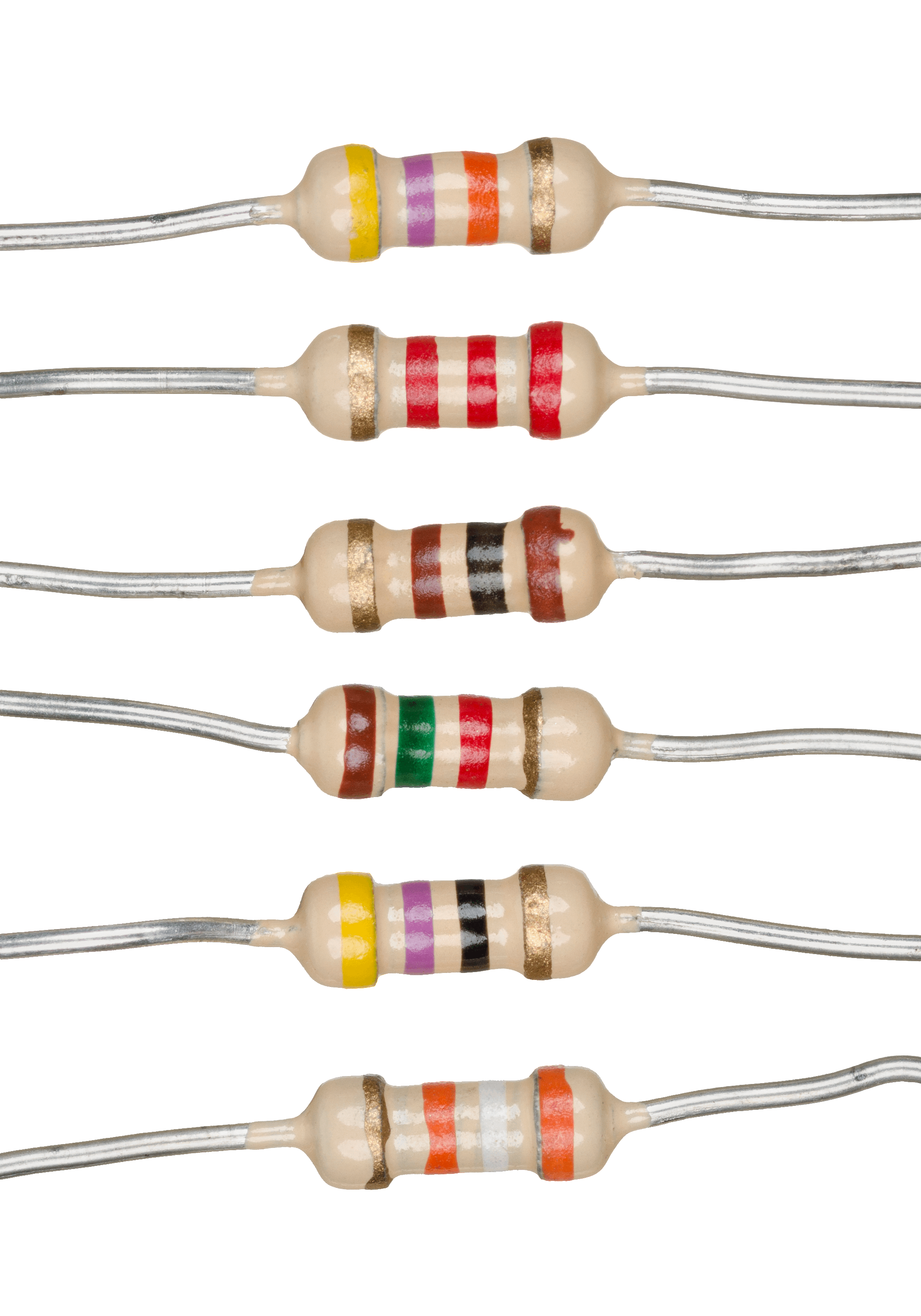
Resistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active elements, and terminate transmission lines, among other uses. High-power resistors that can dissipate many watts of electrical power as heat may be used as part of motor controls, in power distribution systems, or as test loads for generators. Fixed resistors have resistances that only change slightly with temperature, time or operating voltage. Variable resistors can be used to adjust circuit elements (such as a volume control or a lamp dimmer), or as sensing devices for heat, light, humidity, force, or chemical activity. Resistors are common elements of electrical networks and electronic circuits and are ubiquitous in electronic equipment. Practical resistors as discrete components can be composed of various compounds and forms. Resisto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyristor Switched Capacitor Valve
A thyristor () is a solid-state semiconductor device with four layers of alternating P- and N-type materials used for high-power applications. It acts exclusively as a bistable switch (or a latch), conducting when the gate receives a current trigger, and continuing to conduct until the voltage across the device is reversed biased, or until the voltage is removed (by some other means). There are two designs, differing in what triggers the conducting state. In a three-lead thyristor, a small current on its Gate lead controls the larger current of the Anode to Cathode path. In a two-lead thyristor, conduction begins when the potential difference between the Anode and Cathode themselves is sufficiently large (breakdown voltage). Some sources define silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR) and thyristor as synonymous. Other sources define thyristors as more complex devices that incorporate at least four layers of alternating N-type and P-type substrate. The first thyristor devices were r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyristor Switched Capacitor Waveforms 3
A thyristor () is a solid-state semiconductor device with four layers of alternating P- and N-type materials used for high-power applications. It acts exclusively as a bistable switch (or a latch), conducting when the gate receives a current trigger, and continuing to conduct until the voltage across the device is reversed biased, or until the voltage is removed (by some other means). There are two designs, differing in what triggers the conducting state. In a three-lead thyristor, a small current on its Gate lead controls the larger current of the Anode to Cathode path. In a two-lead thyristor, conduction begins when the potential difference between the Anode and Cathode themselves is sufficiently large (breakdown voltage). Some sources define silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR) and thyristor as synonymous. Other sources define thyristors as more complex devices that incorporate at least four layers of alternating N-type and P-type substrate. The first thyristor devices were r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyristor Switched Capacitor Waveforms 1
A thyristor () is a solid-state semiconductor device with four layers of alternating P- and N-type materials used for high-power applications. It acts exclusively as a bistable switch (or a latch), conducting when the gate receives a current trigger, and continuing to conduct until the voltage across the device is reversed biased, or until the voltage is removed (by some other means). There are two designs, differing in what triggers the conducting state. In a three-lead thyristor, a small current on its Gate lead controls the larger current of the Anode to Cathode path. In a two-lead thyristor, conduction begins when the potential difference between the Anode and Cathode themselves is sufficiently large (breakdown voltage). Some sources define silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR) and thyristor as synonymous. Other sources define thyristors as more complex devices that incorporate at least four layers of alternating N-type and P-type substrate. The first thyristor devices were r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |