|
Thymine-DNA Glycosylase
G/T mismatch-specific thymine DNA glycosylase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the TDG gene. Several bacterial proteins have strong sequence homology with this protein. Function The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the TDG/mug DNA glycosylase family. Thymine-DNA glycosylase (TDG) removes thymine moieties from G/T mismatches by hydrolyzing the carbon-nitrogen bond between the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA and the mispaired thymine. With lower activity, this enzyme also removes thymine from C/T and T/T mispairings. TDG can also remove uracil and 5-bromouracil from mispairings with guanine. TDG knockout mouse models showed no increase in mispairing frequency suggesting that other enzymes, like the functional homologue MBD4, may provide functional redundancy. This gene may have a pseudogene in the p arm of chromosome 12. Additionally, in 2011, the human thymine DNA glycosylase (hTDG) was reported to efficiently excise 5-formylcytosine (5fC) and 5-carboxylcytosine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' Chemical specificity, specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequence Homology
Sequence homology is the biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences, defined in terms of shared ancestry in the evolutionary history of life. Two segments of DNA can have shared ancestry because of three phenomena: either a speciation event (orthologs), or a duplication event (paralogs), or else a horizontal (or lateral) gene transfer event (xenologs). Homology among DNA, RNA, or proteins is typically inferred from their nucleotide or amino acid sequence similarity. Significant similarity is strong evidence that two sequences are related by evolutionary changes from a common ancestral sequence. Alignments of multiple sequences are used to indicate which regions of each sequence are homologous. Identity, similarity, and conservation The term "percent homology" is often used to mean "sequence similarity”, that is the percentage of identical residues (''percent identity''), or the percentage of residues conserved with similar physicochemical properties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Glycosylase
DNA glycosylases are a family of enzymes involved in base excision repair, classified under EC number EC 3.2.2. Base excision repair is the mechanism by which damaged bases in DNA are removed and replaced. DNA glycosylases catalyze the first step of this process. They remove the damaged nitrogenous base while leaving the sugar-phosphate backbone intact, creating an apurinic/apyrimidinic site, commonly referred to as an AP site. This is accomplished by flipping the damaged base out of the double helix followed by cleavage of the N-glycosidic bond. Glycosylases were first discovered in bacteria, and have since been found in all kingdoms of life. In addition to their role in base excision repair, DNA glycosylase enzymes have been implicated in the repression of gene silencing in ''A. thaliana'', ''N. tabacum'' and other plants by active demethylation. 5-methylcytosine residues are excised and replaced with unmethylated cytosines allowing access to the chromatin structure of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudogene
Pseudogenes are nonfunctional segments of DNA that resemble functional genes. Most arise as superfluous copies of functional genes, either directly by DNA duplication or indirectly by reverse transcription of an mRNA transcript. Pseudogenes are usually identified when genome sequence analysis finds gene-like sequences that lack regulatory sequences needed for transcription or translation, or whose coding sequences are obviously defective due to frameshifts or premature stop codons. Most non-bacterial genomes contain many pseudogenes, often as many as functional genes. This is not surprising, since various biological processes are expected to accidentally create pseudogenes, and there are no specialized mechanisms to remove them from genomes. Eventually pseudogenes may be deleted from their genomes by chance DNA replication or DNA repair errors, or they may accumulate so many mutational changes that they are no longer recognizable as former genes. Analysis of these degeneration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
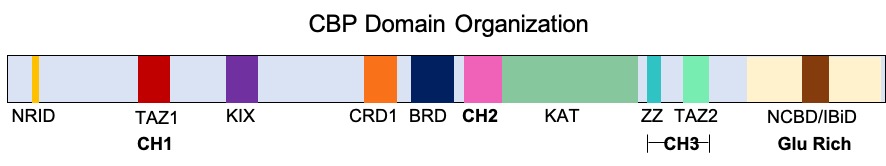
CREB-binding Protein
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate Response Element Binding protein Binding Protein (CREB-binding protein), also known as CREBBP or CBP or KAT3A, is a coactivator encoded by the ''CREBBP'' gene in humans, located on chromosome 16p13.3. CBP has intrinsic acetyltransferase functions; it is able to add acetyl groups to both transcription factors as well as histone lysines, the latter of which has been shown to alter chromatin structure making genes more accessible for transcription. This relatively unique acetyltransferase activity is also seen in another transcription enzyme, EP300 (p300). Together, they are known as the p300-CBP coactivator family and are known to associate with more than 16,000 genes in humans; however, while these proteins share many structural features, emerging evidence suggests that these two co-activators may promote transcription of genes with different biological functions. For example, CBP alone has been implicated in a wide variety of pathophysiologies in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estrogen Receptor Alpha
Estrogen receptor alpha (ERα), also known as NR3A1 (nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group A, member 1), is one of two main types of estrogen receptor, a nuclear receptor (mainly found as a chromatin-binding protein) that is activated by the sex hormone estrogen. In humans, ERα is encoded by the gene ''ESR1'' (EStrogen Receptor 1). Structure The estrogen receptor (ER) is a ligand-activated transcription factor composed of several domains important for hormone binding, DNA binding, and activation of transcription. Alternative splicing results in several ESR1 mRNA transcripts, which differ primarily in their 5-prime untranslated regions. The translated receptors show less variability. Ligands Agonists Non-selective * Endogenous estrogens (e.g., estradiol, estrone, estriol, estetrol) * Natural estrogens (e.g., conjugated equine estrogens) * Synthetic estrogens (e.g., ethinylestradiol, diethylstilbestrol) Selective Agonists of ERα selective over ERβ include: * Prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Promyelocytic Leukemia Protein
Promyelocytic leukemia protein (PML) (also known as MYL, RNF71, PP8675 or TRIM19) is the protein product of the PML gene. PML protein is a tumor suppressor protein required for the assembly of a number of nuclear structures, called PML-nuclear bodies, which form amongst the chromatin of the cell nucleus. These nuclear bodies are present in mammalian nuclei, at about 1 to 30 per cell nucleus. PML-NBs are known to have a number of regulatory cellular functions, including involvement in programmed cell death, genome stability, antiviral effects and controlling cell division. PML mutation or loss, and the subsequent dysregulation of these processes, has been implicated in a variety of cancers. History PML was poorly understood until described in the findings of Grignani ''et al'' in their 1996 study of patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL). It was found that the karyotype of 90% of APL patients included a reciprocal translocation, resulting in the fusion of the Retinoic A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SUMO3
Small ubiquitin-related modifier 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SUMO3'' gene. Function SUMO proteins, such as SUMO3, and ubiquitin (see MIM 191339) posttranslationally modify numerous cellular proteins and affect their metabolism and function. However, unlike ubiquitination, which targets proteins for degradation, sumoylation participates in a number of cellular processes, such as nuclear transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, and protein stability (Su and Li, 2002). upplied by OMIMref name="entrez"/> Interactions SUMO3 has been shown to interact with ARNTL and Thymine-DNA glycosylase G/T mismatch-specific thymine DNA glycosylase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the TDG gene. Several bacterial proteins have strong sequence homology with this protein. Function The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the TDG/mug .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-21-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Ubiquitin-related Modifier 1
Small ubiquitin-related modifier 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SUMO1'' gene. Function This gene encodes a protein that is a member of the SUMO (small ubiquitin-like modifier) protein family. It is a ubiquitin-like protein and functions in a manner similar to ubiquitin in that it is bound to target proteins as part of a post-translational modification system. However, unlike ubiquitin, which is primarily associated with targeting proteins for proteasomal degradation, SUMO1 is involved in a variety of cellular processes, such as nuclear transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, and protein stability. It is not active until the last four amino acids of the carboxy-terminus have been cleaved off. Several pseudogenes have been reported for this gene. Alternate transcriptional splice variants encoding different isoforms have been characterized. Most cleft genes have a sumoylation component. Analysis of chromosomal anomalies in patients has led to the ide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |