|
Thurgoland Railway Station
Thurgoland railway station was a small railway station built by the Sheffield, Ashton-Under-Lyne and Manchester Railway to serve the village of Thurgoland, South Yorkshire, England and opened on 5 December 1845. Due to cost-cutting measures involving staff and infrastructure the station was closed, along with Dog Lane, Dukinfield, Hazelhead and Oxspring Oxspring is a village and civil parish in the Metropolitan Borough of Barnsley in South Yorkshire, England. At the 2001 census it had a population of 1,048, increasing to 1,225 at the 2011 Census. The civil parish includes the hamlets of Clay ... on 1 November 1847, making this one of the shortest-lived stations anywhere, with a life span of just one year and 11 months. References * Dow, George. "Great Central Volume 1" (The Progenitors, 1813 - 1865), Locomotive Publishing Co., London, 1959. * "A Railway Chronology of the Sheffield Area" Edited by Richard V. Proctor. Sheffield City Libraries, 1975. Disused r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thurgoland
Thurgoland (, ) is a village and civil parish in the Metropolitan Borough of Barnsley in South Yorkshire, England, on the A629 road. According to the 2001 census the parish had a population of 1,801, increasing to 1,969 at the 2011 Census. Buildings The village has one primary school, and Holy Trinity Church, Thurgoland (Church of England), built in 1870. There are four public houses: The Monkey, The Horse & Jockey, The Green Dragon and The Bridge Inn. There are several listed buildings on Huthwaite Lane, including Huthwaite Hall (1748) designed by John Carr. There is a recreational ground at the centre of the village, by the village hall and the youth centre. Thurgoland Junior School is ranked second in the local league table. History The earliest known written record of Thurgoland is in the Domesday Book of 1086, in which it is referred to as ''Turgesland''. The name is of Old Norse origin and may mean 'Cultivated land of a man called Thorgeirr'. Other sources claim de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hazelhead Railway Station
Hazlehead Bridge railway station was a railway station on the Sheffield, Ashton-under-Lyne and Manchester Railway's Woodhead Line. It served villages scattered over a wide area of South Yorkshire, England, and was adjacent to the bridge over the Huddersfield Road. History The eastern section of the Sheffield, Ashton-under-Lyne and Manchester Railway, between Sheffield (Bridgehouses) and , was opened on 14 July 1845, but originally there was no station between and Dunford Bridge; it had been intended to provide one at Hazlehead Bridge, with bus connections to Huddersfield, but the approach roads were not suitable, and the buses ran to Dunford Bridge instead. Following petitions from local inhabitants, a station named ''Hazlehead'' was opened on 1 May 1846 (as was a station at Dog Lane, near Dukinfield), and the Huddersfield omnibus served Hazlehead station from August. The original station was closed in a cost-cutting measure, along with Dukinfield Dog Lane. Oxspring and T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Stations In Great Britain Opened In 1845
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer faciliti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
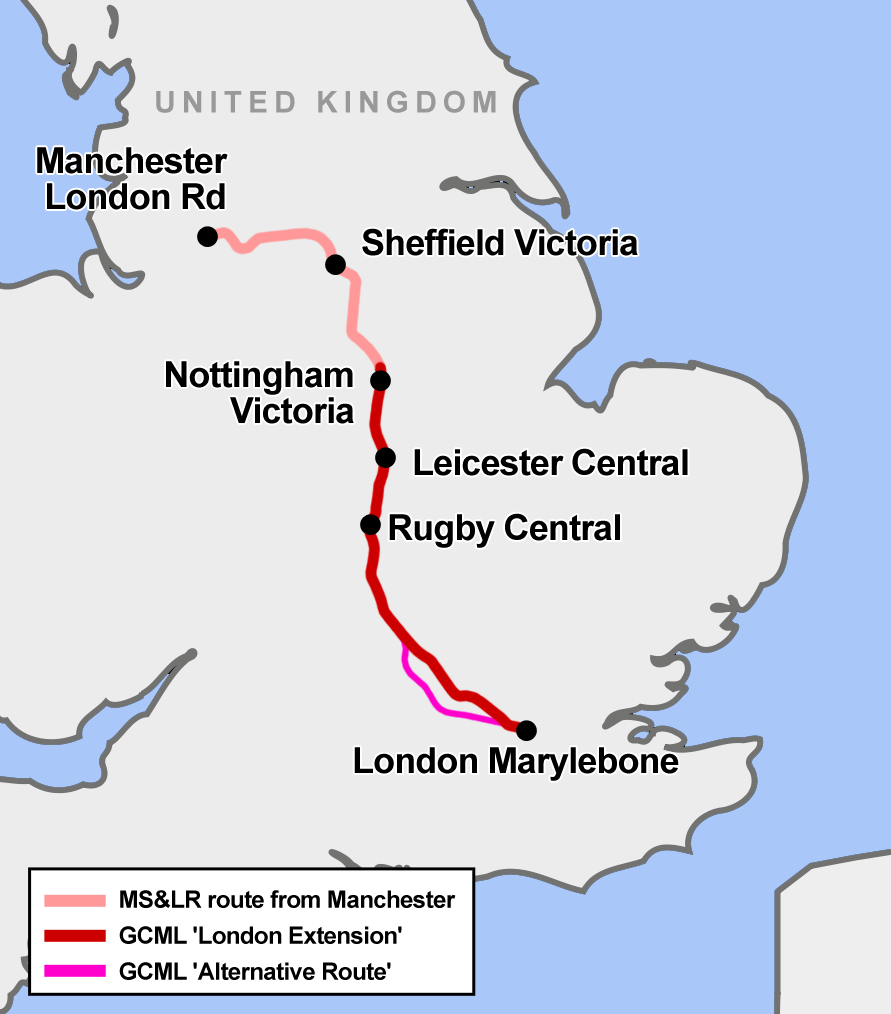
Great Central Main Line
The Great Central Main Line (GCML), also known as the London Extension of the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway (MS&LR), is a former railway line in the United Kingdom. The line was opened in 1899 and built by the Great Central Railway running from Sheffield in the North of England, southwards through Nottingham and Leicester to Marylebone in London. The GCML was the last main line railway to be built in Britain during the Victorian period. Built by the railway entrepreneur Edward Watkin with the aim to run as a fast trunk route from the North and the East Midlands to London and the south of England. Initially not a financial success, it recovered under the leadership of Sam Fay. Although initially planned for long-distance passenger services, in practice the line's most important function became to carry goods traffic, notably coal. In the 1960s, the line was considered by Dr Beeching as an unnecessary duplication of other lines that served the same places, especial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Central Railway
The Great Central Railway in England was formed when the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway changed its name in 1897, anticipating the opening in 1899 of its London Extension. On 1 January 1923, the company was grouped into the London and North Eastern Railway. History New name On assuming its new title, the Great Central Railway had a main line from Manchester London Road Station via , Sheffield Victoria, and Grimsby to . A second line left the line at Penistone and served , and Scunthorpe, before rejoining the Grimsby line at . Other lines linked Sheffield to Barnsley (via ) and Doncaster (via Rotherham) and also and Wrawby Junction. Branch lines in north Lincolnshire ran to Barton-upon-Humber and New Holland and served ironstone quarries in the Scunthorpe area. In the Manchester area, lines ran to Stalybridge and Glossop. In the 1890s, the MS&LR began constructing its Derbyshire lines, the first part of its push southwards. Leaving its east–west mai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wortley Railway Station
Wortley railway station was a railway station on the Sheffield, Ashton-under-Lyne and Manchester Railway lying between Deepcar and Penistone. It was built to serve the village of Wortley, in Barnsley, South Yorkshire, England. Wortley Hall, near the village, was the home of the Earl of Wharncliffe Earl of Wharncliffe, in the West Riding of the County of York, is a title in the Peerage of the United Kingdom. History The earldom was created in 1876 for Edward Montagu-Stuart-Wortley-Mackenzie, 3rd Baron Wharncliffe. He was a descendan ..., long time associated with railway development in the area. The station was similar to the others which opened with the line, with flanking platforms, slightly askew and linked by a footbridge, and a main, stone-built structure with canopy, on the Sheffield-bound platform. Because of its proximity to Wortley Hall the station had a private waiting room for the use of the Earl of Wharncliffe, his family and visitors. The station, opened ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxspring Railway Station
Oxspring railway station was a short lived station built by the Sheffield, Ashton-under-Lyne and Manchester Railway to serve the village of Oxspring, South Yorkshire, England. The station opened on 5 December 1845 but due to cost-cutting measures it was closed, along with Dog Lane, Hazelhead and Thurgoland Thurgoland (, ) is a village and civil parish in the Metropolitan Borough of Barnsley in South Yorkshire, England, on the A629 road. According to the 2001 census the parish had a population of 1,801, increasing to 1,969 at the 2011 Census. Bu ..., on 5 November 1847. References * Dow, George. "Geat Central Volume 1" (The Progenitors, 1813 - 1865) * "A Railway Chronology of the Sheffield Area", Edited by Richard V. Proctor, Sheffield City Libraries, 1975. Disused railway stations in Barnsley Woodhead Line Railway stations in Great Britain opened in 1845 Railway stations in Great Britain closed in 1847 {{Yorkshire-Humber-railstation-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metropolitan Borough Of Barnsley
The Metropolitan Borough of Barnsley is a metropolitan borough in South Yorkshire, England; the main settlement is Barnsley and other notable towns include Penistone, Wombwell and Hoyland. The borough is bisected by the M1 motorway; it is rural to the west, and largely urban/industrial to the east it is estimated that around 16% of the Borough is classed as Urban overall with this area being home to a vast majority of its residents. Additionally 68% of Barnsley's 32,863 hectares is green belt and 9% is national park land, the majority of which is west of the M1. In 2007 it was estimated that Barnsley had 224,600 residents, measured at the 2011 census as 231,221, nine tenths of whom live east of the M1. The borough was formed under the Local Government Act 1972, by a merger of the county borough of Barnsley with Cudworth, Darfield, Darton, Dearne, Dodworth, Hoyland Nether, Penistone, Royston, Wombwell and Worsborough urban districts, along with Penistone Rural District, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dog Lane Railway Station
The dog (''Canis familiaris'' or ''Canis lupus familiaris'') is a domesticated descendant of the wolf. Also called the domestic dog, it is derived from the extinct Pleistocene wolf, and the modern wolf is the dog's nearest living relative. Dogs were the first species to be domesticated by hunter-gatherers over 15,000 years ago before the development of agriculture. Due to their long association with humans, dogs have expanded to a large number of domestic individuals and gained the ability to thrive on a starch-rich diet that would be inadequate for other canids. The dog has been selectively bred over millennia for various behaviors, sensory capabilities, and physical attributes. Dog breeds vary widely in shape, size, and color. They perform many roles for humans, such as hunting, herding, pulling loads, protection, assisting police and the military, companionship, therapy, and aiding disabled people. Over the millennia, dogs became uniquely adapted to human behavior, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |