|
Thryptomene Costata
''Thryptomene costata'' is a species of flowering plant in the family Myrtaceae and is endemic to Western Australia. It is an erect shrub with upward pointing, egg-shaped leaves with the narrower end towards the base, and white or pink flowers with five petals and ten stamens. Description ''Thryptomene costata'' is an erect shrub that typically grows to a height of and has many branches from just above ground level. Its leaves are pointed upwards and egg-shaped with the narrower end towards the base, long and wide on a petiole long. The flowers are arranged in pairs in up to four adjacent leaf axils, on peduncles long with egg-shaped bracteoles long that fall from the flower buds. The flowers are in diameter with egg-shaped, white or pale pink sepals long. The petals are white to deep pink, long and there are ten stamens opposite the sepals and petals. Flowering occurs from May to November. Taxonomy ''Thryptomene costata'' was first formally described in 2001 by B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbara Lynette Rye
Barbara Lynette Rye is an Australian botanist born in 1952. Barbara Rye has been associated with the Western Australian Herbarium, where her work as a taxonomist has been the source of many new descriptions of plants. The number of taxa recorded as described by women authors is historically very low, of the terrestrial plant species this amount is around three percent, yet in analysis published in 2019 Rye is amongst the ten most prolific women taxonomists. Born in Perth, Western Australia, she spent her childhood investigating the local flora and fauna of the Southwest Australia region, a biodiversity hotspot, and later began studies at the University of Western Australia. Barbara Rye entered the fields of zoology and botany, taking a special interest in genetics and evolutionary biology. The first description of a new species was a ''Darwinia'', a genus of the family Myrtaceae that Rye investigated for her doctoral thesis, separating '' Darwinia capitellata'' from a more wid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menzies, Western Australia
Menzies is a town in the Goldfields-Esperance region of Western Australia, east-northeast of the state capital, Perth, and north-northwest of the city of Kalgoorlie. At the 2016 census, Menzies had a population of 108. Aboriginal people have lived in this area since time immemorial, and the local group are the Kaburn Bardu. History Gold was discovered in the area in 1894, and Leslie Robert Menzies, a Canadian-born prospector, and John McDonald were the first to take up a lease here in October 1894, naming it the "Lady Shenton". It was a rich gold find, and the Mining Warden for the area recommended a townsite be declared in 1895, named in Menzies' honour. The townsite was gazetted in August 1895. Land around the town was sold in 1895 and by 1896 it had become a municipality. A railway line was constructed from Kalgoorlie to Menzies and opened on 22 March 1898. By 1900, Menzies had a population of approximately 10,000 with thirteen hotels and two breweries. There were appli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plants Described In 2001
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclude the fungi and some algae, as well as the prokaryotes (the archaea and bacteria). By one definition, plants form the clade Viridiplantae (Latin name for "green plants") which is sister of the Glaucophyta, and consists of the green algae and Embryophyta (land plants). The latter includes the flowering plants, conifers and other gymnosperms, ferns and their allies, hornworts, liverworts, and mosses. Most plants are multicellular organisms. Green plants obtain most of their energy from sunlight via photosynthesis by primary chloroplasts that are derived from endosymbiosis with cyanobacteria. Their chloroplasts contain chlorophylls a and b, which gives them their green color. Some plants are parasitic or mycotrophic and have los ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosids Of Western Australia
The rosids are members of a large clade (monophyletic group) of flowering plants, containing about 70,000 species, more than a quarter of all angiosperms. The clade is divided into 16 to 20 orders, depending upon circumscription and classification. These orders, in turn, together comprise about 140 families. Fossil rosids are known from the Cretaceous period. Molecular clock estimates indicate that the rosids originated in the Aptian or Albian stages of the Cretaceous, between 125 and 99.6 million years ago. Today's forests are highly dominated by rosid species, which in turn helped with diversification in many other living lineages. Additionally, rosid herbs and shrubs are also a significant part of arctic/alpine, temperate floras, aquatics, desert plants, and parasites. Name The name is based upon the name "Rosidae", which had usually been understood to be a subclass. In 1967, Armen Takhtajan showed that the correct basis for the name "Rosidae" is a description of a gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic Flora Of Western Australia
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can be also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or in scientific literature as an ''endemite''. For example ''Cytisus aeolicus'' is an endemite of the Italian flora. ''Adzharia renschi'' was once believed to be an endemite of the Caucasus, but it was later discovered to be a non-indigenous species from South America belonging to a different genus. The extreme opposite of an endemic species is one with a cosmopolitan distribution, having a global or widespread range. A rare alternative term for a species that is endemic is "precinctive", which applies to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thryptomene
''Thryptomene'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Myrtaceae and is endemic to Australia. Plants in the genus ''Thryptomene'' are shrubs with small leaves arranged in opposite pairs and white or pink flowers. About forty-seven species of ''Thryptomene'', occurring in all Australian states and the Northern Territory, have been formally described. Description Plants in the genus ''Thryptomene'' are erect, slender shrubs typically growing to a height of with small leaves arranged in opposite pairs with oil glands especially visible on the lower surface. The flowers are usually arranged singly or in pairs in leaf axils, and usually have five sepals, five white or pink petals and five, rarely ten or fifteen stamens. The fruit is a nut usually containing a single seed. Taxonomy The genus ''Thryptomene'' was first formally described in 1838 by Stephan Ladislaus Endlicher in ''Stirpium Australasicarum Herbarii Hugeliani Decades Tres'', published in the journal ''Annalen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Department Of Parks And Wildlife (Western Australia)
The Department of Parks and Wildlife (DPaW) was the department of the Government of Western Australia responsible for managing lands described in the ''Conservation and Land Management Act 1984'' and implementing the state's conservation and environment legislation and regulations. The minister responsible for the department was the Minister for the Environment (Western Australia), Minister for the Environment. History The Department of Environment and Conservation (Western Australia), Department of Environment and Conservation (DEC) was separated on 30 June 2013, forming the Department of Parks and Wildlife (DPaW) and the Department of Environment Regulation (DER), both of which commenced operations on 1 July 2013. DPaW focused on managing multiple use state forests, national parks, marine parks and reserves. DER focused on environmental regulation, approvals and appeals processes, and pollution prevention. It was announced on 28 April 2017 that the Department of Parks and Wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBRA
The Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA) is a biogeographic regionalisation of Australia developed by the Australian government's Department of Sustainability, Environment, Water, Population, and Communities. It was developed for use as a planning tool, for example for the establishment of a national reserve system. The first version of IBRA was developed in 1993–94 and published in 1995. Within the broadest scale, Australia is a major part of the Australasia biogeographic realm, as developed by the World Wide Fund for Nature The World Wide Fund for Nature Inc. (WWF) is an international non-governmental organization founded in 1961 that works in the field of wilderness preservation and the reduction of human impact on the environment. It was formerly named the Wor .... Based on this system, the world is also split into 14 terrestrial habitats, of which eight are shared by Australia. The Australian land mass is divided into 89 bioregions and 4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yalgoo (biogeographic Region)
Yalgoo is an interim Australian bioregion located in Western Australia. It has an area of . The bioregion, together with the Avon Wheatbelt and Geraldton Sandplains bioregions, is part of the larger Southwest Australia savanna ecoregion as classified by the World Wildlife Fund. Geography The Yalgoo bioregion extends southeastwards from the southern end of Shark Bay on Australia's west coast nearly to Lake Barlee in the interior of Western Australia. The western portion, known as the Edel subregion, includes the Edel Land peninsula and Dirk Hartog, Bernier, and Dorre islands, which enclose Shark Bay on the west. It also includes the coastal plain south of Shark Bay nearly to Kalbarri, where it transitions to the Geraldton Sandplains bioregion. The Edel subregion rests on the Carnarvon and Perth sedimentary basins. The Zuytdorp Cliffs line the coast from the northern end of Edel Land to the mouth of the Murchison River. Soils are generally white sands along the coast, and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murchison (biogeographic Region)
The Murchison is an interim Australian bioregion located within the Mid West of Western Australia. The bioregion is loosely related to the catchment area of the Murchison River and has an area of . Traditionally the region is known as ''The Murchison''. Geography The landscape is characterised by low hills and mesas, separated by colluvium flats and alluvial plains. The western portion of the bioregion is drained by the upper Murchison and Wooramel rivers, which drain westwards towards the coast.Anthony Desmond, Mark Cowan and Alanna Chant (2001). "Murchison 2 (MUR2 – Western Murchison subregion)", in ''A Biodiversity Audit of Western Australia’s 53 Biogeographical Subregions in 2002''. The Department of Conservation and Land Management, Government of Western Australia, November 2001/ref> Together with Gascoyne bioregion, it constitutes the Western Australian mulga shrublands ecoregion. Population is scattered; the largest population centres are Meekatharra, Mou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
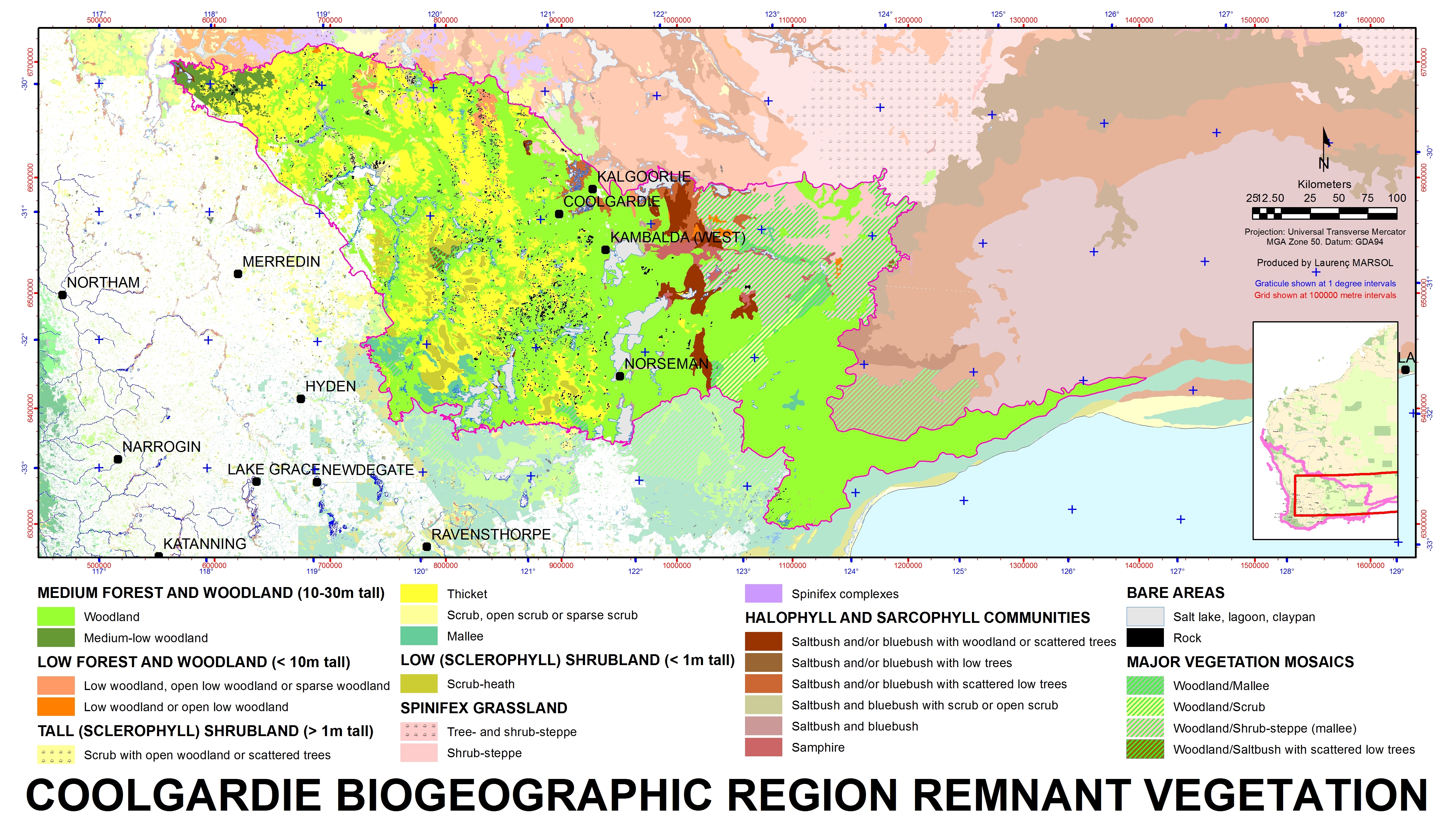
Coolgardie (biogeographic Region)
Coolgardie is an Australian bioregion consisting of an area of low hills and plains of infertile sandy soil in Western Australia. It has an area of . It includes much of the Great Western Woodlands. Location and description This is a transition zone between the Mediterranean climate of Australia's south-west coast and the country's dry interior. The poor soil makes it unsuitable for agriculture but Coolgardie has been a gold and nickel mining area. It is bounded on the north by the arid Murchison bioregion, characterised by open Mulga woodlands and steppe. The low shrublands of the arid Nullarbor Plain lie to the east. The Mallee bioregion adjoins Coolgardie on the south. The Avon Wheatbelt bioregion is to the west. The Coolgardie bioregion, together with the coastal Hampton bioregion to the southeast, constitute the Coolgardie woodlands ecoregion defined by the World Wildlife Fund. Flora and fauna The low hills are home to woodland of endemic species of eucalyptus whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avon Wheatbelt
The Avon Wheatbelt is a bioregion in Western Australia. It has an area of . It is considered part of the larger Southwest Australia savanna ecoregion. Geography The Avon Wheatbelt bioregion is mostly a gently undulating landscape with low relief. It lies on the Yilgarn Craton, an ancient block of crystalline rock, which was uplifted in the Tertiary and dissected by rivers. The craton is overlain by laterite deposits, which in places have decomposed into yellow sandplains, particularly on low hills. Steep-sided erosional gullies, known as breakaways, are common. Beecham, Brett (2001). "Avon Wheatbelt 2 (AW2 - Re-juvenated Drainage subregion)" in ''A Biodiversity Audit of Western Australia’s 53 Biogeographical Subregions in 2002''. Department of Conservation and Land Management, Government of Western Australia, November 2001. Accessed 15 May 2022/ref> In the south and west (the Katanning subregion), streams are mostly perennial, and feed rivers which drain westwards to empty i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)