|
Thomas Sydney Beckwith
Lieutenant-General Sir Thomas Sydney Beckwith (17 February 177015 January 1831) was an English officer of the British Army who served as quartermaster general of the British forces in Canada during the War of 1812, and a commander-in-chief of the Bombay Army during the British Raj.Stephens, H. M. (2004)Beckwith, Sir Thomas Sydney (1772–1831) rev. Roger T. Stearn, ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'', Oxford University Press. He is most notable for his distinguished service during the Peninsular War and for his contributions to the development and command of the 95th Rifles. Family His father was Major General John Beckwith, who commanded the 20th Regiment of Foot. His brothers were Captain John Beckwith, Sir George Beckwith and Brigadier General Ferdinand Beckwith. He was also the uncle of Major-General John Charles Beckwith. He entered the Army himself in 1791, joining the 71st (Highland) Regiment of Foot, and served with them in India. In 1817, he married Lady ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
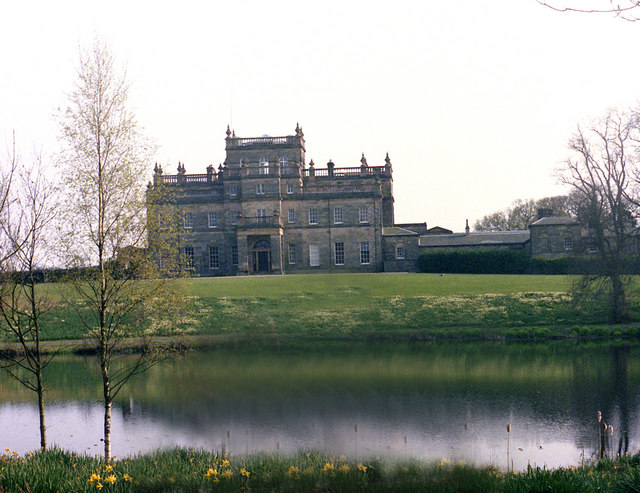
Ford, Northumberland
Ford is a small village and civil parish in Northumberland, England, about from Berwick-upon-Tweed. The parish also includes Etal. History before 1513 Very little is known of the history of the area before the Norman Conquest in the 11th century, but Bronze Age rock carvings in the area suggest that there might have been some settlement at that time. It is thought the shallow crossing of the River Till (a ford) which gave the village its name, was probably a crossing place for monks and nuns travelling between the monasteries at Iona and Lindisfarne during the Anglo-Saxon period. Written records for Ford begin after the Norman Conquest in 1066 and the introduction of the manorial system when the manor of Ford was held by the Heron family. A substantial stone castle was built at Ford in 1287, to protect the manor from the constant border warfare waged between the Scots and the English during the medieval period. South-west of the castle are the remains of the Parson's Tower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Beckwith (British Army Officer)
General Sir George Beckwith GCB (1753 – 20 March 1823) was a British Army officer. Military career Beckwith was commissioned into the 37th Regiment of Foot in 1771. He distinguished himself as a regimental officer in the American Revolutionary War, where he was assistant to Major Oliver Delancey responsible for British Intelligence. In July 1782, he replaced Delancey and after the war he worked for Sir Guy Carleton in Canada. His efforts were aimed at stirring up trouble in Vermont, Florida, Kentucky and Tennessee. At the time Britain thought the weak American government might ask for British help. He was then appointed Governor and Commander-in-Chief of Bermuda in 1797, when a colonel. His baggage and furniture left England on 23 September 1797, aboard the ''Caledonia'', travelling in a convoy bound for Halifax, Nova Scotia, but was lost when the ''Caledonia'' was captured by the French. Beckwith was to follow aboard a Royal Navy frigate and so escaped the fate of his ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copenhagen Expedition
The Second Battle of Copenhagen (or the Bombardment of Copenhagen) (16 August – 7 September 1807) was a British bombardment of the Danish capital, Copenhagen, in order to capture or destroy the Dano-Norwegian fleet during the Napoleonic Wars. The incident led to the outbreak of the Anglo-Russian War of 1807, which ended with the Treaty of Örebro in 1812. Britain's first response to Napoleon's Continental System was to launch a major naval attack on Denmark. Although ostensibly neutral, Denmark was under heavy French pressure to pledge its fleet to Napoleon. In September 1807, the Royal Navy bombarded Copenhagen, seizing the Danish fleet and assured use of the sea lanes in the North Sea and Baltic Sea for the British merchant fleet. A consequence of the attack was that Denmark did join the Continental System and the war on the side of France, but without a fleet it had little to offer. The attack gave rise to the term to ''Copenhagenize''. Background Despite the defeat a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanover Expedition
The Hanover Expedition, also known as the Weser Expedition, was a British invasion of the Electorate of Hanover during the Napoleonic Wars. Coordinated as part of an attack on France by the nations of the War of the Third Coalition, Third Coalition against Napoleon by William Pitt the Younger and Robert Stewart, Viscount Castlereagh, Lord Castlereagh, planning began for an invasion of French territories in July 1805. Hanover, previously a British possession, was chosen as the goal of the expedition, with Swedish and Russian forces under Gustav IV Adolf and Alexander Ivanovich Ostermann-Tolstoy brought in to support the endeavour. Key to the success of the invasion was the support of Prussia, a nation poised to threaten France but not as yet openly hostile to the country. George Don (British Army officer), Sir George Don commanded the British expedition and he arrived with an army of around 14,000 men at Cuxhaven in November. To bolster the expedition and to strengthen the resol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light Division
The Light Division was a light infantry division of the British Army. Its origins lay in "Light Companies" formed during the late 18th century, to move at speed over inhospitable terrain and protect a main force with skirmishing tactics. These units took advantage of then-new technology in the form of rifles, which allowed it to emphasise marksmanship, and were aimed primarily at disrupting and harassing enemy forces, in skirmishes before the main forces clashed. Formed in 1803, during the Napoleonic Wars, the Light Division was raised thrice thereafter: during the Crimean War, the First World War and from 1968 to 2007. Some light infantry units remained outside the Light Division. Origins of the Light Division The British Army's first three "Rifle Battalion" was raised by the 60th (Royal Americans) in 1797–99. The command of this first rifle battalion was given to Francis de Rottenburg, who had extensive experience with light infantry. While the 60th did not officially be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
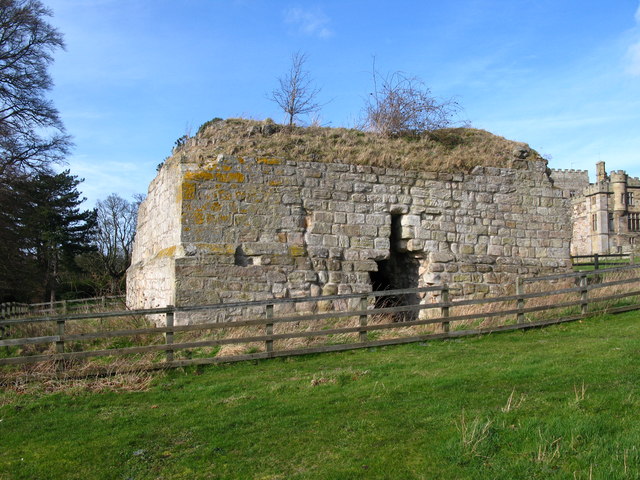
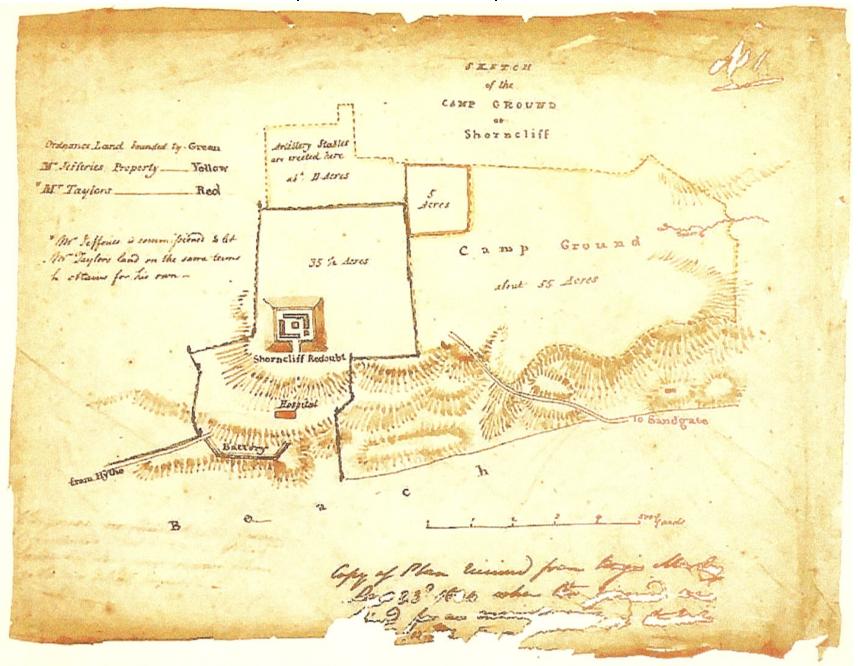
Shorncliffe Redoubt
Shorncliffe Redoubt is a British Napoleonic earthwork fort. The site is approximately 300 feet by 300 feet and is situated on the Kentish Coast in Sandgate, Kent. History In 1793, the French Revolution reached its climax when the Revolutionary Government issued orders to execute King Louis XVI and Marie Antoinette. Two weeks later, on 1 February, the French republic declared war on Great Britain, which then braced itself for invasion. At that time British land-based defences were woefully inadequate as Great Britain had always relied on the Royal Navy for its defence. To prepare for invasion in 1794 British Parliament purchased a large piece of land at Shorncliffe, the obvious place for initial fortifications to be built as it was just 20 miles away from the French coast, so close, in fact, that the locals could see the smoke from the camp fires of Napoleon's waiting army. Later further defences were added to the Kent Coast including the 28-mile-long Royal Military Canal, st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Moore (British Army Officer)
Lieutenant-General Sir John Moore, (13 November 1761 – 16 January 1809), also known as Moore of Corunna , was a senior British Army officer. He is best known for his military training reforms and for his death at the Battle of Corunna, in which he repulsed a French army under Marshal Soult during the Peninsular War. After the war General Sarrazin wrote a French history of the battle, which nonetheless may have been written in light of subsequent events, stating that "Whatever Bonaparte may assert, Soult was most certainly repulsed at Corunna; and the British gained a defensive victory, though dearly purchased with the loss of their brave general Moore, who was alike distinguished for his private virtues, and his military talents." Early years John Moore was born in Glasgow, the son of John Moore, a doctor and writer, and the older brother of Admiral Sir Graham Moore. He attended Glasgow High School, but at the age of 11 joined his father and Douglas, the young 16-year-o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rifle Brigade (Prince Consort's Own)
The Rifle Brigade (The Prince Consort's Own) was an infantry rifle regiment of the British Army formed in January 1800 as the "Experimental Corps of Riflemen" to provide sharpshooters, scouts, and skirmishers. They were soon renamed the "Rifle Corps". In January 1803, they became an established regular regiment and were titled the 95th Regiment of Foot (Rifles). In 1816, at the end of the Napoleonic Wars, they were again renamed, this time as the "Rifle Brigade". The unit was distinguished by its use of green uniforms in place of the traditional redcoat as well as by being armed with the Baker rifle, which was the first British-made rifle accepted by the British Army in place of smooth-bore muskets. The 95th was the first regular infantry corps in the British Army to be so armed. They performed distinguished service in both the First and Second World Wars. Post war, in 1958 the regiment formed part of the Green Jackets Brigade as 3rd Green Jackets and was amalgamated with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coote Manningham
Major General Coote Manningham (1765–1809) was a British army officer who played a significant role in the creation and early development of the 95th Rifles of which he was Colonel in Chief. Military career Born the second son of Charles Manningham of Surrey, Manningham began his career as a subaltern in the 39th Foot serving under his uncle, Sir Robert Boyd, at the Siege of Gibraltar. On the outbreak of the French Revolutionary Wars in 1793, he was appointed as Major to the light infantry battalion where he fought in the Caribbean. He became Lieutenant-Colonel of the 81st Foot and then adjutant-general in Santo Domingo, under the command of Lieutenant-General Forbes. In early 1800, Colonel Manningham and Lieutenant-Colonel William Stewart proposed, and were given the assignment, to use what they had learned while leading light infantry to train the Experimental Corps of Riflemen, later to become the 95th Rifles and then the Rifle Brigade. That summer the new corps was t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marquess Of Queensberry
Marquess of Queensberry is a title in the Peerage of Scotland. The title has been held since its creation in 1682 by a member of the Douglas family. The Marquesses also held the title of Duke of Queensberry from 1684 to 1810, when it was inherited by the Duke of Buccleuch. History The feudal barony of Drumlanrig was held by Sir William Douglas, illegitimate son of The 2nd Earl of Douglas and Mar, some time before 1427, when he died. His descendant William Douglas, 9th of Drumlanrig, was created the 1st Earl of Queensberry in 1633. The subsidiary titles of Lord Queensberry are: Earl of Queensberry (created 1633), Viscount Drumlanrig (1628) and Lord Douglas of Hawick and Tibbers (1628), all in the peerage of Scotland. He is also a Scottish baronet, styled "of Kelhead", created 26 February 1668, so the 6th Marquess was the 5th Baronet. The courtesy title used by Lord Queensberry's eldest son and heir is ''Viscount Drumlanrig''. There is no special courtesy title for Lord Dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Douglas, 7th Marquess Of Queensberry
John Douglas, 7th Marquess of Queensberry (1779 – 19 December 1856), styled Lord John Douglas from May to December 1837, was a Scottish Whig politician. Early life Queensberry was the son of Sir William Douglas, 4th Baronet (died 16 May 1783), and his wife, Grace (née Johnstone) who died 25 March 1836, and succeeded his elder brother, Charles (1777–1837), in the marquessate in December 1837. Career The same year he was appointed a Lord-in-waiting (government whip in the House of Lords) in the Whig administration of Lord Melbourne, a position he held until the government fell in 1841. Between 1837 and 1850 he also served as Lord-Lieutenant of Dumfriesshire.Kidd, Charles, Williamson, David (editors). ''Debrett's Peerage and Baronetage'' (1990 edition). New York: St Martin's Press, 1990, Personal life On 16 July 1817, Douglas married Sarah (died 13 November 1864), daughter of James Sholto Douglas. They had two children : * Archibald William Douglas, 8th Marquess of Q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Douglas, 6th Marquess Of Queensberry
Charles Douglas, 6th Marquess of Queensberry, (March 1777 – 3 December 1837), known as Sir Charles Douglas, 5th Baronet between 1783 and 1810, was a Scottish peer and member of Clan Douglas. Early life Douglas was the eldest son and heir of Sir William Douglas, 4th Baronet, and his wife, Grace, ''née'' Johnstone, of Lockerbie. Among his four brothers and four sisters were John Douglas, 7th Marquess of Queensberry and Lord William Douglas, MP for Dumfries Burghs. His mother was the eldest daughter and co-heiress of William Johnstone of Lockerbie. His paternal grandparents were Sir John Douglas, 3rd Baronet of Kelhead, MP for Dumfriesshire, and the former Christian Cunningham (a daughter of Sir William Cunningham, 2nd Baronet of Caprington). Career Upon his father's death in 1783, he inherited the baronetcy of Kelhead. In 1810, he succeeded his fourth cousin once removed, William Douglas, 4th Duke of Queensberry, as Marquess of Queensberry. Upon simultaneously inheriting K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |