|
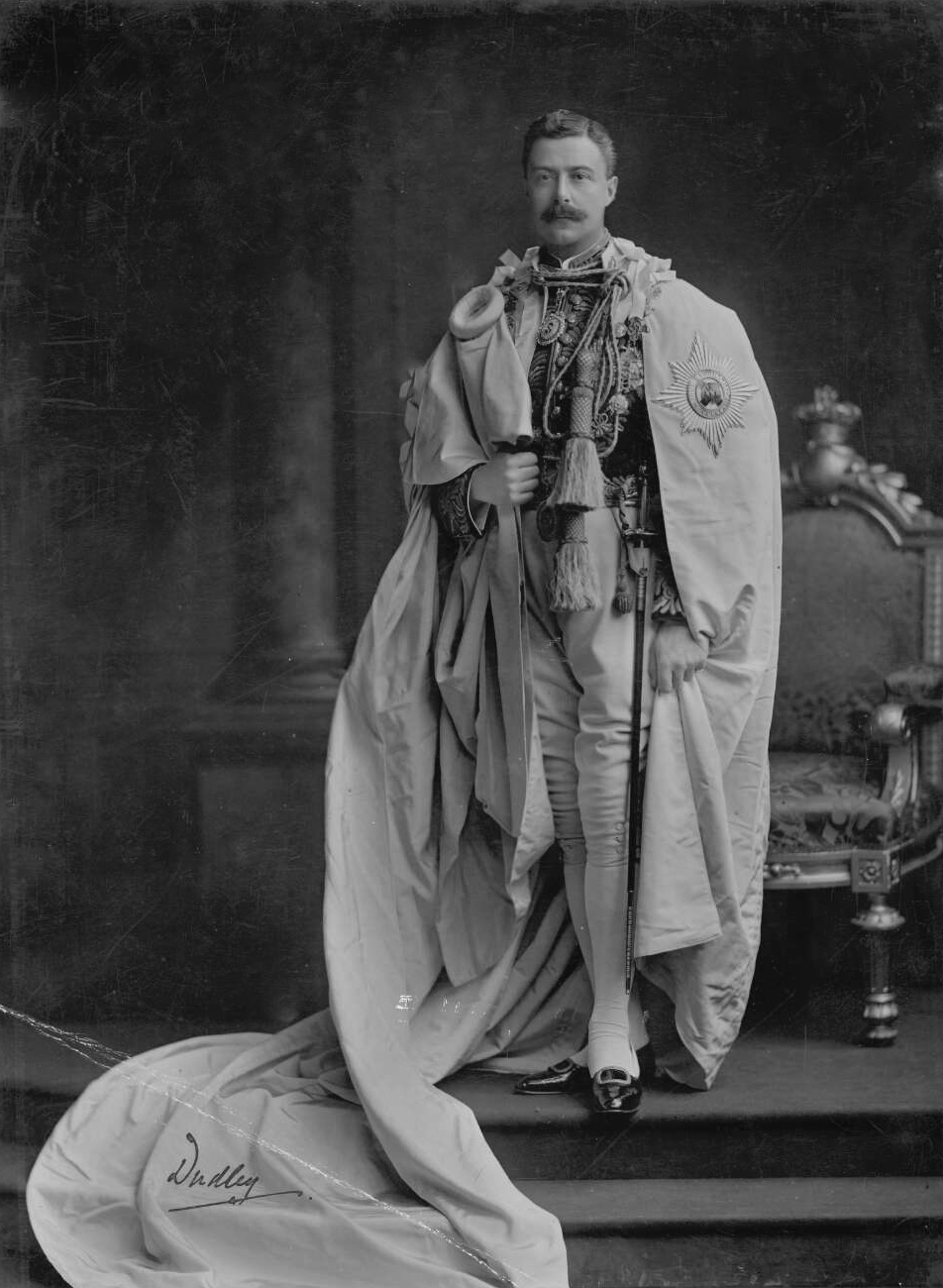
Thomas Kirk (sculptor)
Thomas Kirk (1781 – 19 April 1845) was an Irish sculptor. Born in Cork, Kirk studied at the Dublin Society's School where he won prizes in 1797 and 1800. He later worked for Henry Darley, a skillful builder and stone-cutter from Meath, based in Abbey Street, Dublin. Kirk was acclaimed for his fine relief work on mantle-pieces and monuments. Much of his work can be seen in the Royal College of Surgeons, the Royal Dublin Society and in the library of Trinity College, Dublin. He worked on committees in the Royal Dublin Society and he was a member of the Royal Hibernian Academy. He executed numerous church memorials throughout the country. His favourite relief was one of the Good Samaritan, which was well suited for memorials to either doctors or clergymen. One of his earliest commissions, which appeared in 1809, was the statue of Nelson for Nelson's Pillar in O'Connell Street, Dublin. This monument was destroyed by an explosion on 8 March 1966. Another of Kirk’s commis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cork (city)
Cork ( , from , meaning 'marsh') is the second largest city in Ireland and third largest city by population on the island of Ireland. It is located in the south-west of Ireland, in the province of Munster. Following an extension to the city's boundary in 2019, its population is over 222,000. The city centre is an island positioned between two channels of the River Lee which meet downstream at the eastern end of the city centre, where the quays and docks along the river lead outwards towards Lough Mahon and Cork Harbour, one of the largest natural harbours in the world. Originally a monastic settlement, Cork was expanded by Viking invaders around 915. Its charter was granted by Prince John in 1185. Cork city was once fully walled, and the remnants of the old medieval town centre can be found around South and North Main streets. The city's cognomen of "the rebel city" originates in its support for the Yorkist cause in the Wars of the Roses. Corkonians sometimes refer to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
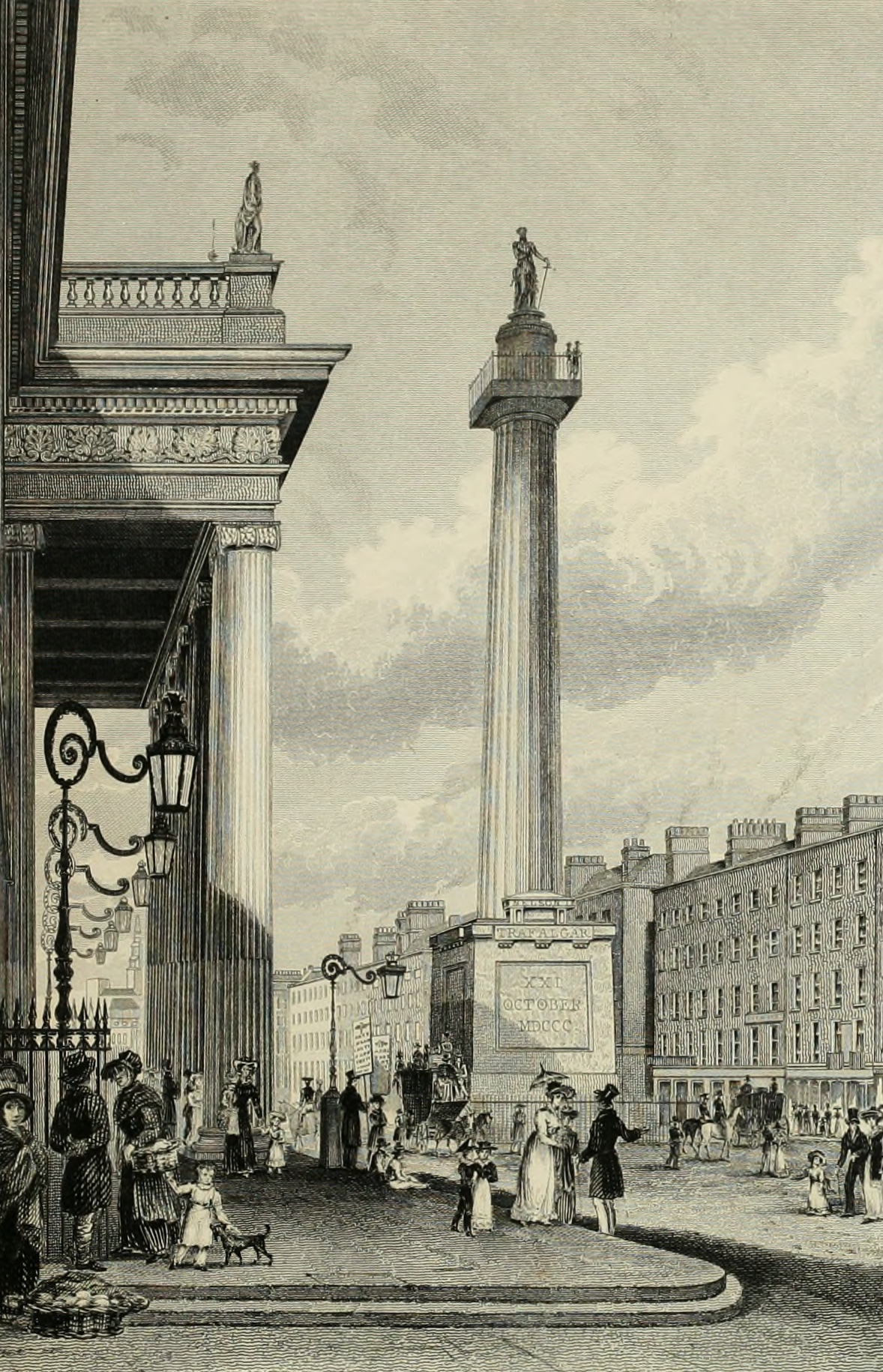
O'Connell Street
O'Connell Street () is a street in the centre of Dublin, Ireland, running north from the River Liffey. It connects the O'Connell Bridge to the south with Parnell Street to the north and is roughly split into two sections bisected by Henry Street. The Luas tram system runs along the street. During the 17th century, it was a narrow street known as Drogheda Street, named after Henry Moore, Earl of Drogheda. It was widened in the late 18th century by the Wide Streets Commission and renamed Sackville Street (''Sráid Saicfil'') after Lionel Sackville, 1st Duke of Dorset. In 1924, it was renamed in honour of nationalist leader Daniel O'Connell, whose statue by John Henry Foley stands at the lower end of the street facing O'Connell Bridge. The street has played an important part in Irish history and features several important monuments, including statues of O'Connell and trade union leader James Larkin, as well as the Spire of Dublin. It formed the backdrop to one of the 1913 D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cavan
Cavan ( ; ) is the county town of County Cavan in Ireland. The town lies in Ulster, near the border with County Fermanagh in Northern Ireland. The town is bypassed by the main N3 road that links Dublin (to the south) with Enniskillen, Ballyshannon and Donegal Town (to the north). History Gaelic Cavan 1300–1607 Cavan was founded by the Irish clan chief and Lord of East Breifne, Giolla Íosa Ruadh O’Reilly, between 1300 and his death in 1330. During his lordship, a friary run by the Dominican Order was established close to the O’Reilly stronghold at Tullymongan and was at the centre of the settlement close to a crossing over the river and to the town's marketplace. It is recorded that the (Cavan) Dominicans were expelled in 1393, replaced by an Order of Conventual Franciscan friars. The friary's location is marked by an eighteenth-century tower in the graveyard at Abbey Street which appears to incorporate remains of the original medieval friary tower. The imprint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nathaniel Sneyd
Nathaniel Sneyd (c. 1767 – 31 July 1833) was an Irish politician, landowner and businessman He was a Member of the Parliament of Ireland representing the Carrick constituency from 1794 to 1800 and was High Sheriff of Cavan in 1795. He briefly represented the Cavan County Parliament of Ireland constituency which was succeeded after the Union with Great Britain in 1800 by the Cavan Westminster constituency, which he represented from 1801 until 1826. In general election of 1806 he contested two constituencies for Parliament, winning both and choosing to represent Cavan over Enniskillen. In Cavan, Sneyd lived in Ballyconnell and owned plantation lands around Bawnboy. From 1800, he was president of the Bawnboy Farming Society, the first founded in County Cavan. In 1801 he was appointed Custos Rotulorum of Cavan. On 29 July 1833, in Westmoreland Street, Dublin, Nathaniel Sneyd was shot in the head by a madman, John Mason, who had a grudge against the firm of wine merchants S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
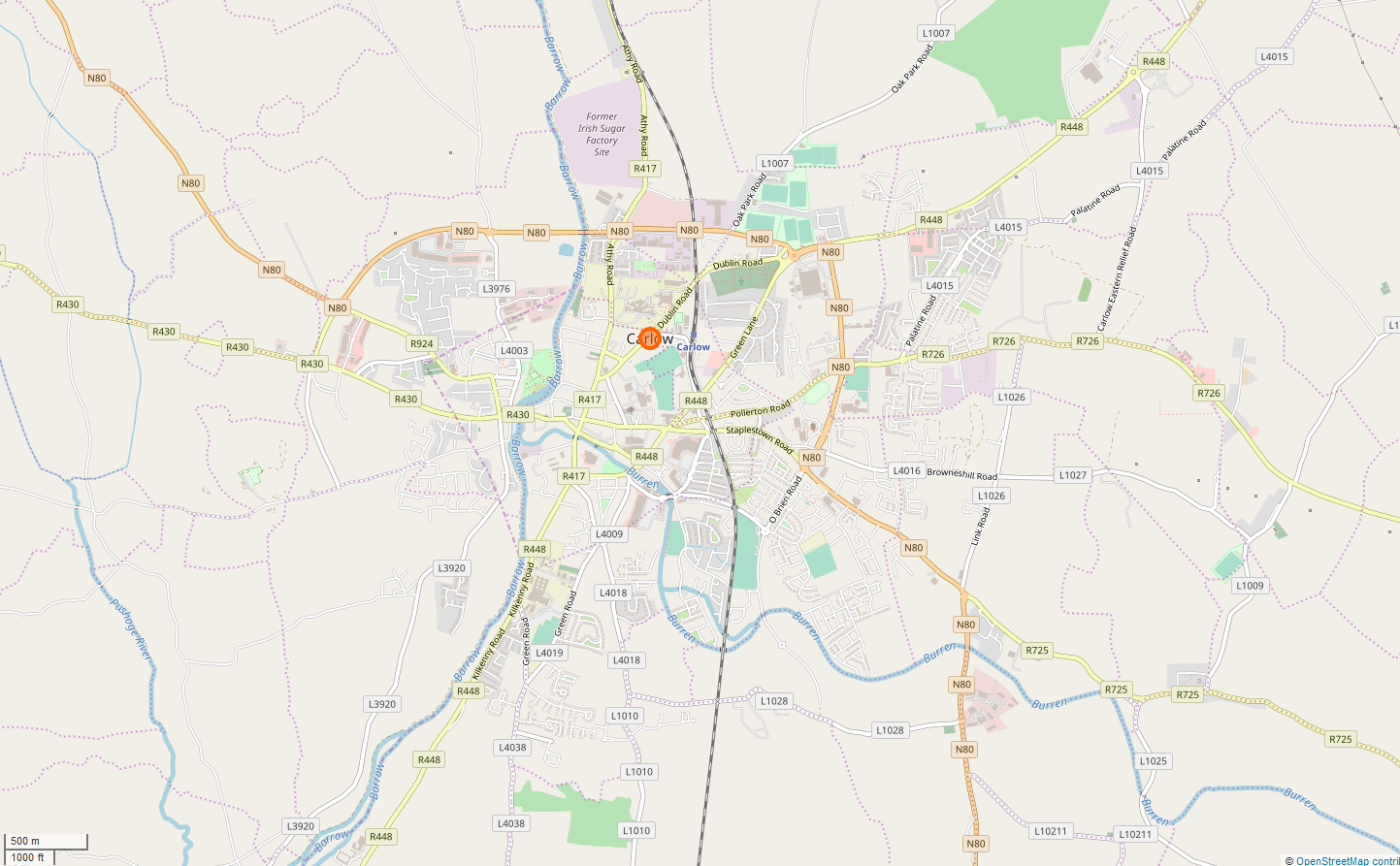
Carlow
Carlow ( ; ) is the county town of County Carlow, in the south-east of Ireland, from Dublin. At the 2016 census, it had a combined urban and rural population of 24,272. The River Barrow flows through the town and forms the historic boundary between counties Laois and Carlow. However, the Local Government (Ireland) Act 1898 included the town entirely in County Carlow. The settlement of Carlow is thousands of years old and pre-dates written Irish history. The town has played a major role in Irish history, serving as the capital of the country in the 14th century. Etymology The name is an anglicisation of the Irish ''Ceatharlach''. Historically, it was anglicised as ''Caherlagh'', ''Caterlagh'' and ''Catherlagh'', which are closer to the Irish spelling. According to logainm.ie, the first part of the name derives from the Old Irish word ''cethrae'' ("animals, cattle, herds, flocks"), which is related to ''ceathar'' ("four") and therefore signified "four-legged". The second pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Industrial Exhibition
The Irish Industrial Exhibition was a world's fair held in Cork in 1852, Frank Leslie's Illustrated Historical Register of the Centennial Exposition, 1876. Edited by Frank Norton. Frank Leslie's Publishing House, New York, 1877. Pg. 4 the first to be held in Ireland (then part of the ). It was opened on 10 June by the Lord Lieutenant, the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Irish Academy
The Royal Irish Academy (RIA; ga, Acadamh Ríoga na hÉireann), based in Dublin, is an academic body that promotes study in the sciences, humanities and social sciences. It is Ireland's premier learned society and one its leading cultural institutions. The Academy was established in 1785 and granted a royal charter in 1786. the RIA has around 600 members, regular members being Irish residents elected in recognition of their academic achievements, and Honorary Members similarly qualified but based abroad; a small number of members are elected in recognition of non-academic contributions to society. Until the late 19th century the Royal Irish Academy was the owner of the main national collection of Irish antiquities. It presented its collection of archaeological artefacts and similar items, which included such famous pieces as the Tara Brooch, the Cross of Cong and the Ardagh Chalice to what is now the National Museum of Ireland, but retains its very significant collec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knole
Knole () is a country house and former archbishop's palace owned by the National Trust. It is situated within Knole Park, a park located immediately to the south-east of Sevenoaks in west Kent. The house ranks in the top five of England's largest houses, under any measure used, occupying a total of four acres. The current house dates back to the mid-15th century, with major additions in the 16th and, particularly, the early 17th centuries. Its grade I listing reflects its mix of late-medieval to Stuart structures and particularly its central façade and state rooms. In 2019 an extensive conservation project, "Inspired by Knole", was completed to restore and develop the structures of the buildings and thus help to conserve its important collections. The surrounding deer park has also survived with varying degrees of management in the 400 years since 1600. History Location Knole is located at the southern end of Sevenoaks, in the Weald of west Kent. To the north, the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Smyth (sculptor)
John Smyth (1776 – 1840) was an Irish sculptor. The son of sculptor Edward Smyth (1749–1812), John Smyth was trained at the Dublin Society's school, and worked with his father at Montgomery Street (now Foley Street) in Dublin. One of his first public works was a monument to John Ball in St Patrick's Cathedral, Dublin. He assisted his father, Edward, with a number of sculptures at Parliament House (now Bank of Ireland), the King's Inns, and with decorative plaster and stonework at the Chapel Royal of Dublin Castle. He also sculpted the statues of Mercury, Fidelity, and Hibernia for the pediment of the General Post Office, Dublin (c.1814). He repaired the equestrian statue of William III (William of Orange) in College Green after it was blown up in 1836. Other pieces by John Smyth were sculpted for Dublin's Richmond Bridge (c.1816; now O'Donovan Rossa Bridge), and several public buildings and churches in the capital. In 1818, Smyth was commissioned to produce a bus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Lieutenant Of Ireland
Lord Lieutenant of Ireland (), or more formally Lieutenant General and General Governor of Ireland, was the title of the chief governor of Ireland from the Williamite Wars of 1690 until the Partition of Ireland in 1922. This spanned the Kingdom of Ireland (1541–1800) and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801–1922). The office, under its various names, was often more generally known as the Viceroy, and his wife was known as the vicereine. The government of Ireland in practice was usually in the hands of the Lord Deputy up to the 17th century, and later of the Chief Secretary for Ireland. Role The Lord Lieutenant possessed a number of overlapping roles. He was * the representative of the King (the "viceroy"); * the head of the executive in Ireland; * (on occasion) a member of the English or British Cabinet; * the fount of mercy, justice and patronage; * (on occasion) commander-in-chief in Ireland. * Grand Master of the Order of St. Patrick Prior to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Whitworth, 1st Earl Whitworth
Charles Whitworth, 1st Earl Whitworth, GCB, PC (29 May 1752 – 13 May 1825), known as The Lord Whitworth between 1800 and 1813 and as The Viscount Whitworth between 1813 and 1815, was a British diplomat and politician. Early years Whitworth, the eldest of the three sons (there were also four daughters) and heir of Sir Charles Whitworth, MP (a nephew of The 1st Baron Whitworth), was born at Leybourne Grange, Kent, on 19 May 1752 and baptised there on 29 May 1752. He was educated at Tonbridge School, his preceptors there including James Cawthorn and "Mr. Towers". He entered the first regiment of footguards in April 1772 as ensign, became captain in May 1781, and was eventually on 8 April 1783 appointed lieutenant-colonel of the 104th regiment. His transference from military life to diplomacy is not easy to explain, but in the account given by Wraxall, disfigured though it is by malicious or purely fanciful embroidery, there is perhaps a nucleus of truth. Whitworth was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabella Cope
''Arabella'', Op. 79, is a lyric comedy, or opera, in three acts by Richard Strauss to a German libretto by Hugo von Hofmannsthal, their sixth and last operatic collaboration. Performance history It was first performed on 1 July 1933 at the Dresden Sächsisches Staatstheater. The opera received its premiere in the UK on 17 May 1934 at London's Royal Opera House. Two decades later, on 10 February 1955, it was performed at the Metropolitan Opera in New York with Eleanor Steber in the title role. The Met has given numerous performances of the work since that date. At the 2008 Helpmann Awards, the production by Opera Australia won the Award for Best Opera. Helpmann Awards Roles [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)

