|
Thomas Brattle
Thomas Brattle (June 20, 1658 – May 18, 1713) was an American merchant who served as treasurer of Harvard College and member of the Royal Society. He is known for his involvement in the Salem Witch Trials and the formation of the Brattle Street Church. Brattle was also a mathematician, astronomer, and an experienced traveler. Early life Thomas Brattle was born on June 20, 1658, in Boston, Massachusetts to Elizabeth Brattle née Tyng and Captain Thomas Brattle. He was the couple's second child and the first son to survive past infancy. He had eight siblings, including William Brattle and Catherine Winthrop. Brattle's date of birth is often confused with the first-born son of the Brattle family (also named Thomas Brattle) – who was born on, and died on, September 5, 1657. As a child, Thomas Brattle was exposed to radical forms of the Puritan faith, primarily through his father's participation in the controversial founding of the Third (South) Church, which advocated for e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
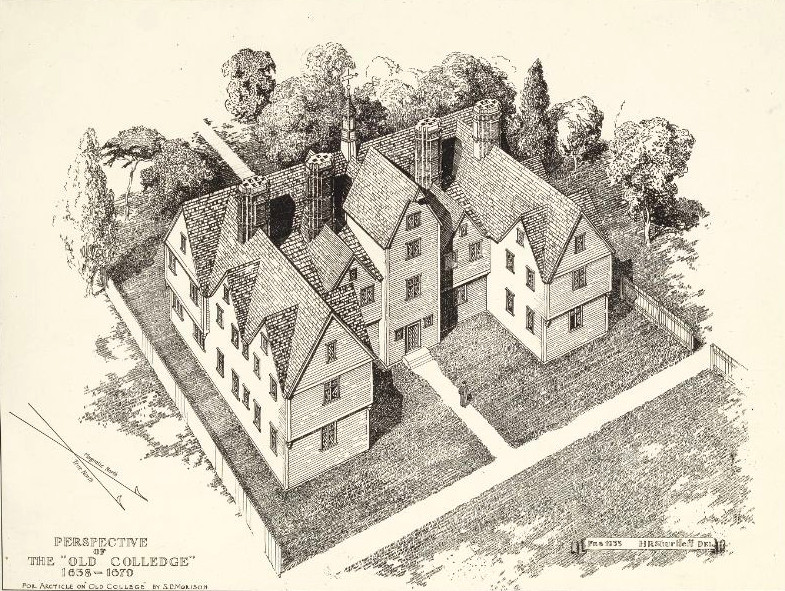
Harvard College
Harvard College is the undergraduate college of Harvard University, an Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636, Harvard College is the original school of Harvard University, the oldest institution of higher learning in the United States and among the most prestigious in the world. Part of the Faculty of Arts and Sciences, Harvard College is Harvard University's traditional undergraduate program, offering AB and SB degrees. It is highly selective, with fewer than five percent of applicants being offered admission in recent years. Harvard College students participate in more than 450 extracurricular organizations and nearly all live on campus—first-year students in or near Harvard Yard, and upperclass students in community-oriented "houses". History The school came into existence in 1636 by vote of the Great and General Court of the Massachusetts Bay Colony—though without a single building, instructor, or student. In 1638, the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Boyle
Robert Boyle (; 25 January 1627 – 31 December 1691) was an Anglo-Irish natural philosopher, chemist, physicist, alchemist and inventor. Boyle is largely regarded today as the first modern chemist, and therefore one of the founders of modern chemistry, and one of the pioneers of modern experimental scientific method. He is best known for Boyle's law, which describes the inversely proportional relationship between the absolute pressure and volume of a gas, if the temperature is kept constant within a closed system. Among his works, '' The Sceptical Chymist'' is seen as a cornerstone book in the field of chemistry. He was a devout and pious Anglican and is noted for his writings in theology. Biography Early years Boyle was born at Lismore Castle, in County Waterford, Ireland, the seventh son and fourteenth child of The 1st Earl of Cork ('the Great Earl of Cork') and Catherine Fenton. Lord Cork, then known simply as Richard Boyle, had arrived in Dublin from England ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Critics Of Witch Hunting
A critic is a person who communicates an assessment and an opinion of various forms of creative works such as art, literature, music, cinema, theater, fashion, architecture, and food. Critics may also take as their subject social or government policy. Critical judgments, whether derived from critical thinking or not, weigh up a range of factors, including an assessment of the extent to which the item under review achieves its purpose and its creator's intention and a knowledge of its context. They may also include a positive or negative personal response. Characteristics of a good critic are articulateness, preferably having the ability to use language with a high level of appeal and skill. Sympathy, sensitivity and insight are important too. Form, style and medium are all considered by the critic. In architecture and food criticism, the item's function, value and cost may be added components. Critics are publicly accepted and, to a significant degree, followed because of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18th-century American Businesspeople
The 18th century lasted from January 1, 1701 ( MDCCI) to December 31, 1800 ( MDCCC). During the 18th century, elements of Enlightenment thinking culminated in the American, French, and Haitian Revolutions. During the century, slave trading and human trafficking expanded across the shores of the Atlantic, while declining in Russia, China, and Korea. Revolutions began to challenge the legitimacy of monarchical and aristocratic power structures, including the structures and beliefs that supported slavery. The Industrial Revolution began during mid-century, leading to radical changes in human society and the environment. Western historians have occasionally defined the 18th century otherwise for the purposes of their work. For example, the "short" 18th century may be defined as 1715–1789, denoting the period of time between the death of Louis XIV of France and the start of the French Revolution, with an emphasis on directly interconnected events. To historians who expand the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
17th-century American Businesspeople
The 17th century lasted from January 1, 1601 ( MDCI), to December 31, 1700 ( MDCC). It falls into the early modern period of Europe and in that continent (whose impact on the world was increasing) was characterized by the Baroque cultural movement, the latter part of the Spanish Golden Age, the Dutch Golden Age, the French ''Grand Siècle'' dominated by Louis XIV, the Scientific Revolution, the world's first public company and megacorporation known as the Dutch East India Company, and according to some historians, the General Crisis. From the mid-17th century, European politics were increasingly dominated by the Kingdom of France of Louis XIV, where royal power was solidified domestically in the civil war of the Fronde. The semi-feudal territorial French nobility was weakened and subjugated to the power of an absolute monarchy through the reinvention of the Palace of Versailles from a hunting lodge to a gilded prison, in which a greatly expanded royal court could be more easily ke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1713 Deaths
Events January–March * January 17 – Tuscarora War: Colonel James Moore leads the Carolina militia out of Albemarle County, North Carolina, in a second offensive against the Tuscarora. Heavy snows force the troops to take refuge in Fort Reading, on the Pamlico River. * February 1 – Skirmish at Bender, Moldova: Charles XII of Sweden is defeated by the Ottoman Empire. * February 4 – Tuscarora War: The Carolina militia under Colonel James Moore leaves Fort Reading, to continue the campaign against the Tuscarora. * February 25 – Frederick William I of Prussia begins his reign. * March 1 – Tuscarora War: Colonel James Moore's Carolina militia lays siege to the Tuscaroran stronghold of Fort Neoheroka, located a few miles up Contentnea Creek from Fort Hancock. * March 20 – Tuscarora War: Colonel James Moore's Carolina militia launches a major offensive against Fort Neoheroka. * March 23 – Tuscarora War: Fort Neoheroka falls to the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1658 Births
Events January–March * January 13 – Edward Sexby, who had plotted against Oliver Cromwell, dies in the Tower of London. * January 30 – The " March Across the Belts" (''Tåget över Bält''), Sweden's use of winter weather to send troops across the waters of the Danish straits at a time when winter has turned them to ice, begins. Within 17 days, Sweden's King Karl X Gustav leads troops across the ice belts to capture six of Denmark's islands as Swedish territory. * February 5 – Prince Muhi al-Din Muhammad, one of the sons of India's Mughal, Emperor Shah Jahan, proclaims himself Emperor after Jahan names Muhi's older brother, Dara Shikoh, as regent, and departs from Aurangabad with troops. * February 6 – Swedish troops of Charles X Gustav of Sweden cross The Great Belt in Denmark, over frozen sea. * March 8 (February 26 OS) – The peace between Sweden and Denmark is concluded in Roskilde by the Treaty of Roskilde, under which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Date Of Birth Unknown
Date or dates may refer to: * Date (fruit), the fruit of the date palm (''Phoenix dactylifera'') Social activity * Dating, a form of courtship involving social activity, with the aim of assessing a potential partner ** Group dating *Play date, an appointment for children to get together for a few hours *Meeting, when two or more people come together Chronology * Calendar date, a day on a calendar ** Old Style and New Style dates, from before and after the change from the Julian calendar to the Gregorian calendar ** ISO 8601, an international standard covering date formats * Date (metadata), a representation term to specify a calendar date **DATE command, a system time command for displaying the current date * Chronological dating, attributing to an object or event a date in the past ** Radiometric dating, dating materials such as rocks in which trace radioactive impurities were incorporated when they were formed Arts, entertainment and media Music * Date (band), a Swedi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oyer And Terminer
In English law, oyer and terminer (; a partial translation of the Anglo-French ''oyer et terminer'', which literally means "to hear and to determine") was one of the commissions by which a judge of assize sat. Apart from its Law French name, the commission was also known by the Law Latin name ''audiendo et terminando'', and the Old English-derived term soc and sac. By the commission of oyer and terminer the commissioners (in practice the judges of assize, though other persons were named with them in the commission) were commanded to make diligent inquiry into all treasons, felonies and misdemeanours whatever committed in the counties specified in the commission, and to hear and determine the same according to law. The inquiry was by means of the grand jury; after the grand jury had found the bills of indictment submitted to it, the commissioners proceeded to hear and determine by means of the petit jury. The words ''oyer and terminer'' were also used to denote the court th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perry Miller
Perry Gilbert Eddy Miller (February 25, 1905 – December 9, 1963) was an American intellectual historian and a co-founder of the field of American Studies. Miller specialized in the history of early America, and took an active role in a revisionist view of the colonial Puritan theocracy that was cultivated at Harvard University beginning in the 1920s. Heavy drinking led to his premature death at the age of 58. "Perry Miller was a great historian of Puritanism but the dark conflicts of the Puritan mind eroded his own mental stability." Life Miller was born in 1905 Chicago, Illinois, to Eben Perry Sturges Miller, M.D., from Mansfield, Ohio, and Sarah Gertrude Miller (née Eddy) from Bellows Falls, Vermont. Eben Perry Sturges Miller appeared in 1895 and 1898 deacon's candidacy lists for Seabury-Western Theological Seminary. Eben Perry Sturges received an 1898 "notice of discipline" for "abandonment or forfeiture of the Holy Orders" and "deposition" from the ministry, seven year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Maule (Quaker)
Thomas Maule (May 3, 1645 – July 2, 1724), was a prominent Quaker in colonial Salem, Massachusetts. Maule was born in Berkswell Parish, Warwickshire, England. He originally emigrated to Barbados around 1658 and later relocated to Boston in 1668 before permanently settling in Salem about 1679. He remained in Salem until his death in 1724 at the age of 79. Maule was a tailor in Boston, and later expanded his business to general merchandising. He also dealt in construction and real estate while in Salem. It is unknown precisely when Maule converted to Quakerism, although it is suspected his conversion happened while he lived in Barbados. Maule's son Thomas was born in 1720 in Salem, apprenticed as a carpenter, and by 1744 relocated with his mother Sarah and her second husband Henry Clifton (m. 1733) to Philadelphia. Construction of the Quaker Meeting House in Salem During the fall of 1688, Maule was instrumental in building the first known Quaker Meeting House in the United Stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Calef
Robert Calef (baptized 2 November 1648 – 13 April 1719) was a cloth merchant in colonial Boston. He was the author o''More Wonders of the Invisible World'' a book composed throughout the mid-1690s denouncing the recent Salem witch trials of 1692–1693 and particularly examining the influential role played by Cotton Mather. Life and education Robert Calef, son of Joseph Calef, was baptized in Stanstead, Suffolk, England on 2 November 1648. The Calef family of Stanstead was "one of substantial yeoman and clothiers." The majority of what is known about the character of Robert Calef is what can be gleaned from his single book, and it contains almost no details about his own life. His writing displays broad education and it is possible that following grammar school he attended one of England's clandestine dissenting academies as evidenced by Cotton Mather's use of the title "Mr." ("Mr. R.C") and Calef's pride in having no proficiency in Latin. (In contrast to Oxford and Cambridge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
