|
Thiosulfate
Thiosulfate ( IUPAC-recommended spelling; sometimes thiosulphate in British English) is an oxyanion of sulfur with the chemical formula . Thiosulfate also refers to the compounds containing this anion, which are the salts of thiosulfuric acid, e.g. sodium thiosulfate . Thiosulfate also refers to the esters of thiosulfuric acid, e.g. ''O'',''S''-dimethyl thiosulfate . The prefix thio- indicates that the thiosulfate is a sulfate with one oxygen replaced by sulfur. Thiosulfate is tetrahedral at the central S atom. Thiosulfate salts occur naturally. Thiosulfate ion has C3v symmetry, and is produced by certain biochemical processes. It rapidly dechlorinates water and is notable for its use to halt bleaching in the paper-making industry. Thiosulfate salts are mainly used in dying in textiles and the bleaching of natural substances. Sodium thiosulfate, commonly called ''hypo'' (from "hyposulfite"), was widely used in photography to fix black and white negatives and prints after the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Thiosulfate
Sodium thiosulfate (sodium thiosulphate) is an inorganic compound with the formula . Typically it is available as the white or colorless pentahydrate, . The solid is an efflorescent (loses water readily) crystalline substance that dissolves well in water. Sodium thiosulfate is used in gold mining, water treatment, analytical chemistry, the development of silver-based photographic film and prints, and medicine. The medical uses of sodium thiosulfate include treatment of cyanide poisoning and pityriasis. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Uses Sodium thiosulfate is used predominantly in industry. For example, it is used to convert dyes to their soluble colorless forms, which are called leuco. It is also used to bleach "wool, cotton, silk, ...soaps, glues, clay, sand, bauxite, and... edible oils, edible fats, and gelatin." Medical uses Sodium thiosulfate is used in the treatment of cyanide poisoning. Other uses include topical treatment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonium Thiosulfate
Ammonium thiosulfate (ammonium thiosulphate in British English) is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is white crystalline solid with ammonia odor, readily soluble in water, slightly soluble in acetone and insoluble in ethanol and diethyl ether. Production It is produced by treating ammonium sulfite with sulfur at temperatures between 85 and 110 °C: : Applications Ammonium thiosulfate is used in photographic fixer. It is a so-called rapid fixer, acting more quickly than sodium thiosulfate fixers. Fixation involves these chemical reactions (illustrated for silver bromide): : : Ammonium thiosulfate is also used for leaching of gold and silver. It works with presence of copper as a catalyst here. This process is a nontoxic alternative gold cyanidation. The advantage to ammonium thiosulfate is that the pyrolysis of its silver complexes leaves a residue solely of silver sulfide, in contrast to complexes derived from sodium thiosulfate. Other Ammonium thiosulfate can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
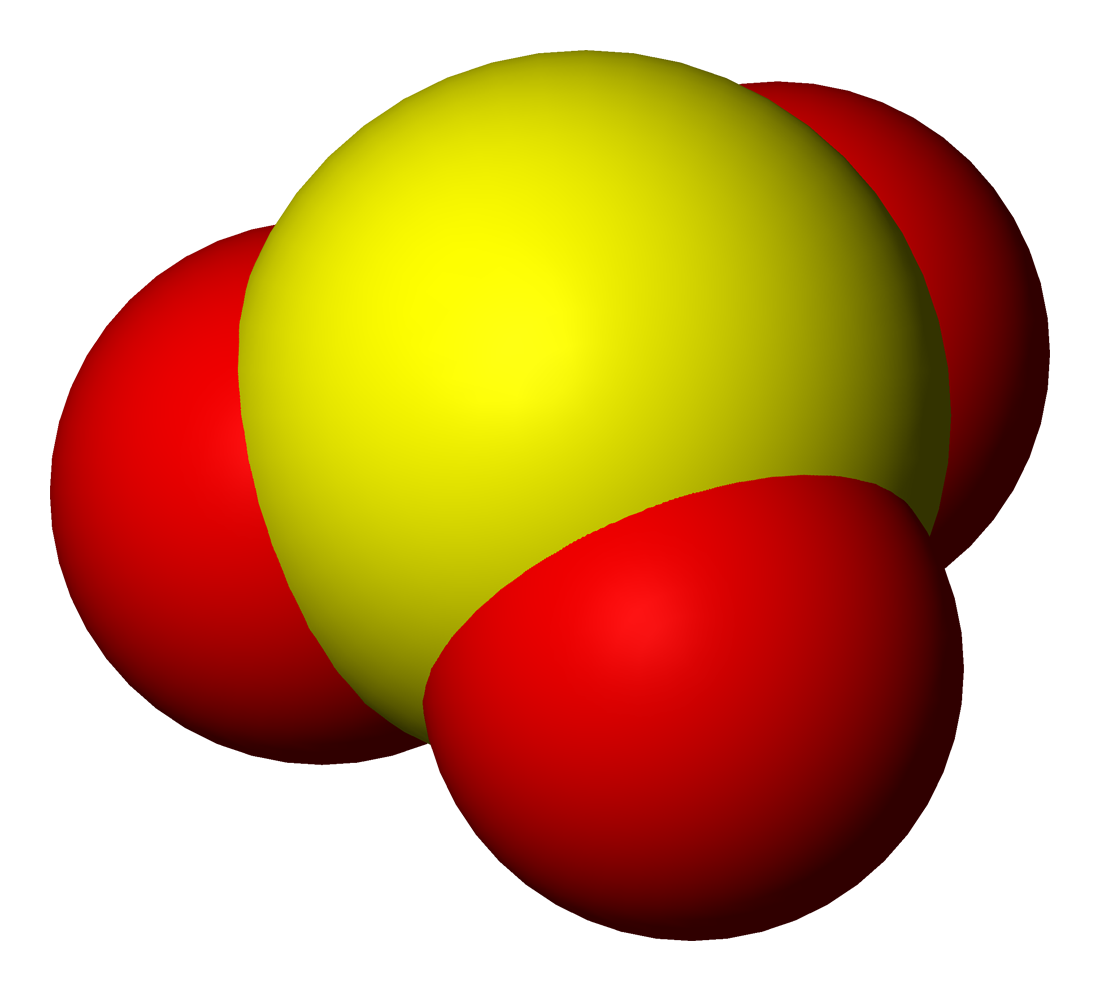
Thiosulfuric Acid
Thiosulfuric acid is the inorganic compound with the formula . It has attracted academic interest as a simple, easily accessed compound that is labile. It has few practical uses. Preparation and degradation The acid cannot be made by acidifying aqueous thiosulfate salt solutions as the acid readily decomposes in water. The decomposition products can include sulfur, sulfur dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, polysulfanes, sulfuric acid and polythionates, depending on the reaction conditions.. Anhydrous methods of producing the acid were developed by Max Schmidt: : : : The anhydrous acid also decomposes above −5 °C: : Structure The isomer is more stable than the isomer as established by Hartree–Fock/ ab initio calculations with a 6-311 G** basis set and MP2 to MP4 refinements. The theoretically predicted structure conforms with the double bond rule. An isomer of thiosulfuric acid is the adduct of hydrogen sulfide Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow, crystalline solid at room temperature. Sulfur is the tenth most abundant element by mass in the universe and the fifth most on Earth. Though sometimes found in pure, native form, sulfur on Earth usually occurs as sulfide and sulfate minerals. Being abundant in native form, sulfur was known in ancient times, being mentioned for its uses in ancient India, ancient Greece, China, and ancient Egypt. Historically and in literature sulfur is also called brimstone, which means "burning stone". Today, almost all elemental sulfur is produced as a byproduct of removing sulfur-containing contaminants from natural gas and petroleum.. Downloahere The greatest commercial use of the element is the producti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiosulfuric Acid
Thiosulfuric acid is the inorganic compound with the formula . It has attracted academic interest as a simple, easily accessed compound that is labile. It has few practical uses. Preparation and degradation The acid cannot be made by acidifying aqueous thiosulfate salt solutions as the acid readily decomposes in water. The decomposition products can include sulfur, sulfur dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, polysulfanes, sulfuric acid and polythionates, depending on the reaction conditions.. Anhydrous methods of producing the acid were developed by Max Schmidt: : : : The anhydrous acid also decomposes above −5 °C: : Structure The isomer is more stable than the isomer as established by Hartree–Fock/ ab initio calculations with a 6-311 G** basis set and MP2 to MP4 refinements. The theoretically predicted structure conforms with the double bond rule. An isomer of thiosulfuric acid is the adduct of hydrogen sulfide Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photographic Fixer
Photographic fixer is a mix of chemicals used in the final step in the photographic processing of film or paper. The fixer stabilises the image, removing the unexposed silver halide remaining on the photographic film or photographic paper, leaving behind the reduced metallic silver that forms the image. By fixation, the film or paper is insensitive to further action by light. Without fixing, the remaining silver halide would darken and cause fogging of the image. Fixation is commonly achieved by treating the film or paper with a solution of thiosulfate salt. Popular salts are sodium thiosulfate—commonly called hypo—and ammonium thiosulfate—commonly used in modern rapid fixer formulae. Fixation involves these chemical reactions (X = halide, typically Br−):Karlheinz Keller et al. "Photography" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. :AgX + 2 S2O32− → g(S2O3)2sup>3− + X− :AgX + 3 S2O32− → g(S2O3)3sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disproportionation
In chemistry, disproportionation, sometimes called dismutation, is a redox reaction in which one compound of intermediate oxidation state converts to two compounds, one of higher and one of lower oxidation states. More generally, the term can be applied to any desymmetrizing reaction of the following type, regardless of whether it is a redox or some other type of process: :2A -> A' + A'' Examples * Mercury(I) chloride disproportionates upon UV-irradiation: :Hg2Cl2 → Hg + HgCl2 * Phosphorous acid disproportionates upon heating to give phosphoric acid and phosphine: :4 → 3 H3PO4 + PH3 *Desymmetrizing reactions are sometimes referred to as disproportionation, as illustrated by the thermal degradation of bicarbonate: :2 → + H2CO3 :The oxidation numbers remain constant in this acid-base reaction. This process is also called autoionization. *Another variant on disproportionation is radical disproportionation, in which two radicals form an alkene and an alkane. : R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfide
Sulfide (British English also sulphide) is an inorganic anion of sulfur with the chemical formula S2− or a compound containing one or more S2− ions. Solutions of sulfide salts are corrosive. ''Sulfide'' also refers to chemical compounds large families of inorganic and organic compounds, e.g. lead sulfide and dimethyl sulfide. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and bisulfide (SH−) are the conjugate acids of sulfide. Chemical properties The sulfide ion, S2−, does not exist in aqueous alkaline solutions of Na2S. Instead sulfide converts to hydrosulfide: :S2− + H2O → SH− + OH− Upon treatment with an acid, sulfide salts convert to hydrogen sulfide: :S2− + H+ → SH− :SH− + H+ → H2S Oxidation of sulfide is a complicated process. Depending on the conditions, the oxidation can produce elemental sulfur, polysulfides, polythionates, sulfite, or sulfate. Metal sulfides react with halogens, forming sulfur and metal salts. :8 MgS + 8 I2 → S8 + ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfite
Sulfites or sulphites are compounds that contain the sulfite ion (or the sulfate(IV) ion, from its correct systematic name), . The sulfite ion is the conjugate base of bisulfite. Although its acid (sulfurous acid) is elusive, its salts are widely used. Sulfites are substances that naturally occur in some foods and the human body. They are also used as regulated food additives. When in food or drink, sulfites are often lumped together with sulfur dioxide.SeREGULATION (EU) No 1169/2011 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL/ref> Structure The structure of the sulfite anion can be described with three equivalent resonance structures. In each resonance structure, the sulfur atom is double-bonded to one oxygen atom with a formal charge of zero (neutral), and sulfur is singly bonded to the other two oxygen atoms, which each carry a formal charge of −1, together accounting for the −2 charge on the anion. There is also a non-bonded lone pair on the sulfur, so the structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidation
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in the oxidation state. There are two classes of redox reactions: * ''Electron-transfer'' – Only one (usually) electron flows from the reducing agent to the oxidant. This type of redox reaction is often discussed in terms of redox couples and electrode potentials. * ''Atom transfer'' – An atom transfers from one substrate to another. For example, in the rusting of iron, the oxidation state of iron atoms increases as the iron converts to an oxide, and simultaneously the oxidation state of oxygen decreases as it accepts electrons released by the iron. Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides, other chemical species can serve the same function. In hydrogenation, C=C (and other) bond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur Oxoacid
Sulfur oxoacids are chemical compounds that contain sulfur, oxygen, and hydrogen. The best known and most important industrially used is sulfuric acid. Sulfur has several oxoacids; however, some of these are known only from their salts (these are shown in italics in the table below). The acids that have been characterised contain a variety of structural features, for example: *tetrahedral sulfur when coordinated to oxygen *terminal and bridging oxygen atoms *terminal peroxo groups *terminal S=S *chains of (−S−)''n'' See also *Chlorosulfuric acid *Fluorosulfuric acid * Nitrosylsulfuric acid *Peroxydisulfuric acid Peroxydisulfuric acid is an inorganic compound with a chemical formula . Also called Marshall's acid after Professor Hugh Marshall, who discovered it in 1891. Structure and bonding This oxoacid features sulfur in its +6 oxidation state and a ... * Sulfinic acids * Sulfonic acids References External links *{{MeSH name, Sulfur+Acids Sulfur oxoacids along wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |