|
Thioacetic Acid
Thioacetic acid is an organosulfur compound with the molecular formula . It is the sulfur analogue of acetic acid (), as implied by the ''thio-'' prefix. It is a yellow liquid with a strong thiol-like odor. It is used in organic synthesis for the introduction of thiol groups () in molecules. Synthesis and properties Thioacetic acid is prepared by the reaction of acetic anhydride with hydrogen sulfide: :(CH3C(O))2O + H2S -> CH3C(O)SH + CH3C(O)OH It has also been produced by the action of phosphorus pentasulfide on glacial acetic acid, followed by distillation. :CH3C(O)OH + P2S5 -> CH3C(O)SH + P2OS4 Thioacetic acid is typically contaminated by acetic acid. The compound exists exclusively as the thiol tautomer, consistent with the strength of the double bond. Reflecting the influence of hydrogen-bonding, the boiling point (93 °C) and melting points are 20 and 75 K lower than those for acetic acid. Reactivity Acidity With a p''K''a near 3.4, thioacetic acid is about 15 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Union Of Pure And Applied Chemistry
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC ) is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations working for the advancement of the chemical sciences, especially by developing nomenclature and terminology. It is a member of the International Science Council (ISC). IUPAC is registered in Zürich, Switzerland, and the administrative office, known as the "IUPAC Secretariat", is in Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, United States. This administrative office is headed by IUPAC's executive director, currently Lynn Soby. IUPAC was established in 1919 as the successor of the International Congress of Applied Chemistry for the advancement of chemistry. Its members, the National Adhering Organizations, can be national chemistry societies, national academies of sciences, or other bodies representing chemists. There are fifty-four National Adhering Organizations and three Associate National Adhering Organizations. IUPAC's Inter-divisional Committee on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
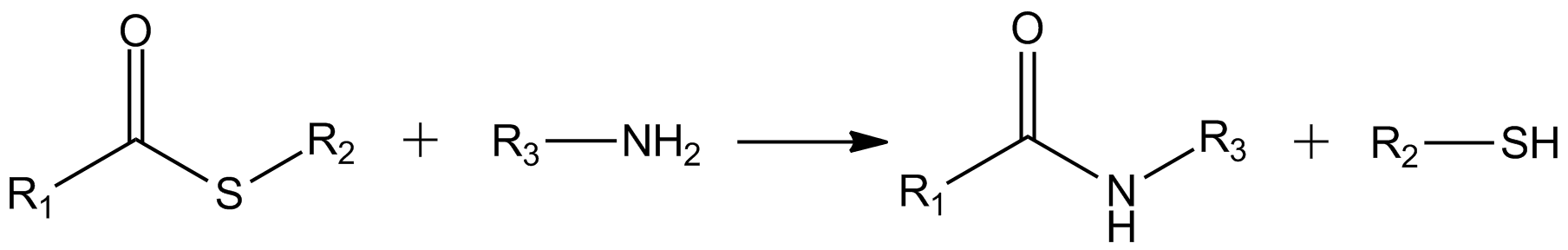
Potassium Thioacetate
Potassium thioacetate is an organosulfur compound and a salt with the formula . This white, water-soluble solid is used as a reagent for preparing thioacetate esters and other derivatives. Synthesis and reactions Potassium thioacetate, which is commercially available, can be prepared by combining acetyl chloride and potassium hydrogen sulfide: :CH3COCl + 2 KSH -> KCl + CH3COSK + H2S It arises also by the neutralization of thioacetic acid with potassium hydroxide. Use in preparation of thiols In a common application, potassium thioacetate is combined with alkylating agents to give thioacetate esters (X = halide): :CH3COSK + RX -> CH3COSR + KX Hydrolysis of these esters affords thiol In organic chemistry, a thiol (; ), or thiol derivative, is any organosulfur compound of the form , where R represents an alkyl or other organic substituent. The functional group itself is referred to as either a thiol group or a sulfhydryl gro ...s: :CH3COSR + H2O -> CH3CO2H + RSH The thioace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reagents For Organic Chemistry
In chemistry, a reagent ( ) or analytical reagent is a substance or compound added to a system to cause a chemical reaction, or test if one occurs. The terms ''reactant'' and ''reagent'' are often used interchangeably, but reactant specifies a substance ''consumed'' in the course of a chemical reaction. ''Solvents'', though involved in the reaction mechanism, are usually not called reactants. Similarly, ''catalysts'' are not consumed by the reaction, so they are not reactants. In biochemistry, especially in connection with enzyme-catalyzed reactions, the reactants are commonly called substrates. Definitions Organic chemistry In organic chemistry, the term "reagent" denotes a chemical ingredient (a compound or mixture, typically of inorganic or small organic molecules) introduced to cause the desired transformation of an organic substance. Examples include the Collins reagent, Fenton's reagent, and Grignard reagents. Analytical chemistry In analytical chemistry, a reagent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Acids
An organic acid is an organic compound with acidic properties. The most common organic acids are the carboxylic acids, whose acidity is associated with their carboxyl group –COOH. Sulfonic acids, containing the group –SO2OH, are relatively stronger acids. Alcohols, with –OH, can act as acids but they are usually very weak. The relative stability of the conjugate base of the acid determines its acidity. Other groups can lsoconfer acidity, usually weakly: the thiol group –SH, the enol group, and the phenol group. In biological systems, organic compounds containing these groups are generally referred to as organic acids. A few common examples include: * lactic acid * acetic acid * formic acid * citric acid * oxalic acid * uric acid * malic acid * tartaric acid Characteristics In general, organic acids are weak acids and do not dissociate completely in water, whereas the strong mineral acids do. Lower molecular mass organic acids such as formic and lactic ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paracetamol
Paracetamol, also known as acetaminophen, is a medication used to treat fever and mild to moderate pain. Common brand names include Tylenol and Panadol. At a standard dose, paracetamol only slightly decreases body temperature; it is inferior to ibuprofen in that respect, and the benefits of its use for fever are unclear. Paracetamol may relieve pain in acute mild migraine but only slightly in episodic tension headache. However, the aspirin/paracetamol/caffeine combination helps with both conditions where the pain is mild and is recommended as a first-line treatment for them. Paracetamol is effective for post-surgical pain, but it is inferior to ibuprofen. The paracetamol/ibuprofen combination provides further increase in potency and is superior to either drug alone. The pain relief paracetamol provides in osteoarthritis is small and clinically insignificant. The evidence in its favor for the use in low back pain, cancer pain, and neuropathic pain is insufficient. In the sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arkivoc
''Arkivoc'' (''Archive for Organic Chemistry'') is a peer-reviewed open access scientific journal covering all aspects of organic chemistry. It is published by the non-profit organization Arkat USA, which was established in 2000 through a personal donation from Alan R. Katritzky and Linde Katritzky. ''Arkivoc'' is the primary publication of Arkat USA. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2014 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as i ... of 1.165, ranking it 37th out of 57 journals in the category "Chemistry, Organic". Abstracting and Indexing According to the Journal Citation Reports, the journal has a 2018 impact factor of 1.253. The journal is indexed in Web of Science: Science Citation Index Expanded. References External link ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thioester
In organic chemistry, thioesters are organosulfur compounds with the functional group . They are analogous to carboxylate esters () with the sulfur in the thioester playing the role of the linking oxygen in the carboxylate ester, as implied by the ''thio-'' prefix. They are the product of esterification between a carboxylic acid () and a thiol (). In biochemistry, the best-known thioesters are derivatives of coenzyme A, e.g., acetyl-CoA.Matthys J. Janssen "Carboxylic Acids and Esters" in PATAI's Chemistry of Functional Groups: Carboxylic Acids and Esters, Saul Patai, Ed. John Wiley, 1969, New York: pp. 705–764. Synthesis The most typical route to thioester involves the reaction of an acid chloride with an alkali metal salt of a thiol: :RSNa + R'COCl -> R'COSR + NaCl Another common route entails the displacement of halides by the alkali metal salt of a thiocarboxylic acid. For example, thioacetate esters are commonly prepared by alkylation of potassium thioacetate: :CH3COSK + ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene is often used as synonym of olefin, that is, any hydrocarbon containing one or more double bonds.H. Stephen Stoker (2015): General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry'. 1232 pages. Two general types of monoalkenes are distinguished: terminal and internal. Also called α-olefins, terminal alkenes are more useful. However, the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) recommends using the name "alkene" only for acyclic hydrocarbons with just one double bond; alkadiene, alkatriene, etc., or polyene for acyclic hydrocarbons with two or more double bonds; cycloalkene, cycloalkadiene, etc. for cyclic ones; and "olefin" for the general class – cyclic or acyclic, with one or more double bonds. Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups (also known as mono-enes) form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula with '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exocyclic
In organic chemistry, an alicyclic compound contains one or more all-carbon rings which may be either saturated or unsaturated, but do not have aromatic character. Alicyclic compounds may have one or more aliphatic side chains attached. The simplest alicyclic compounds are the monocyclic cycloalkanes: cyclopropane, cyclobutane, cyclopentane, cyclohexane, cycloheptane, cyclooctane, and so on. Bicyclic alkanes include bicycloundecane, decalin, and housane. Polycyclic alkanes include cubane, basketane, and tetrahedrane. Spiro compounds have two or more rings that are connected through only one carbon atom. The mode of ring-closing in the formation of many alicyclic compounds can be predicted by Baldwin's rules. Otto Wallach, a German chemist, received the 1910 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his work on alicyclic compounds. Cycloalkenes Monocyclic cycloalkenes are cyclopropene, cyclobutene, cyclopentene, cyclohexene, cycloheptene, cyclooctene, and so on. Bicyclic alkenes incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleophilic Addition
In organic chemistry, a nucleophilic addition reaction is an addition reaction where a chemical compound with an electrophilic double or triple bond reacts with a nucleophile, such that the double or triple bond is broken. Nucleophilic additions differ from electrophilic additions in that the former reactions involve the group to which atoms are added accepting electron pairs, whereas the latter reactions involve the group donating electron pairs. Addition to carbon–heteroatom double bonds Nucleophilic addition reactions of nucleophiles with electrophilic double or triple bond (π bonds) create a new carbon center with two additional single, or σ, bonds.March Jerry; (1985). Advanced Organic Chemistry reactions, mechanisms and structure (3rd ed.). New York: John Wiley & Sons, inc. Addition of a nucleophile to carbon–heteroatom double or triple bonds such as >C=O or -C≡N show great variety. These types of bonds are polar (have a large difference in electronegativity betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Radical
A daughter category of ''Ageing'', this category deals only with the biological aspects of ageing. Ageing Ailments of unknown cause Biogerontology Biological processes Causes of death Cellular processes Gerontology Life extension Metabolic disorders Metabolism Old age Time in life Wikipedia categories named after diseases and disorders {{CatAutoTOC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |