|
Thibaud, Dominica
Thibaud is a village on the northern coast of Dominica. It has a population of approximately 500. Located near Vieille Case, Thibaud's main industries are fishing and farming. Thibaud appears on the earliest detailed map of the island by Thomas Jefferys in 1768. It was named after an early French settler, Louis Thibaud, (spelt in the early British texts as Teaubaud) who obtained ten acres from the Island Caribs in the early 18th century. Thibaud is connected to two bays. Sandwich Bay, is named after John Montagu, 4th Earl of Sandwich (1718-1792). The other bay is the beaching place for the village fishing boats . The school playing field was the site of an Amerindian The Indigenous peoples of the Americas are the inhabitants of the Americas before the arrival of the European settlers in the 15th century, and the ethnic groups who now identify themselves with those peoples. Many Indigenous peoples of the Am ... village. During the period after the abolition of slavery in D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominica
Dominica ( or ; Kalinago: ; french: Dominique; Dominican Creole French: ), officially the Commonwealth of Dominica, is an island country in the Caribbean. The capital, Roseau, is located on the western side of the island. It is geographically situated as part of the Windward Islands chain in the Lesser Antilles archipelago in the Caribbean Sea. Dominica's closest neighbours are two constituent territories of the European Union, the overseas departments of France, Guadeloupe to the northwest and Martinique to the south-southeast. Dominica comprises a land area of , and the highest point is Morne Diablotins, at in elevation. The population was 71,293 at the 2011 census. The island was settled by the Arawak arriving from South America in the fifth century. The Kalinago displaced the Arawak by the 15th century. Columbus is said to have passed the island on Sunday, 3 November 1493. It was later colonised by Europeans, predominantly by the French from the 1690s to 1763. The Frenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vieille Case
Vieille Case, sometimes spelled as Vielle-Case, is a village on the north coast of Dominica. The Commonwealth of Dominica in the West Indies was first inhabited by the Kalinago tribe referred to by the Europeans as Caribs. Itassi (pronounced: e-tassy) is the Kalinago name for the area in Dominica which is now known as Vieille Case. Vieille Case has an estimated population of 726.Commonwealth of Dominica, ''Population and Housing Census — 2001''. Roseau, Dominica: Central Statistical Office, Ministry of Finance and Planning, Kennedy Avenue, 2001. The name is a local French term for "old house". When Europeans first settled in the area, they lived there together with the Caribs. The current villagers are mixed descendants of the Kalinagos, the French settlers and the African slaves that were imported to the area. The centre of the village is called "Under The Mango". There are various shops, similar to convenience stores, located here. Few restaurants can be found in this tropic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Jefferys
Thomas Jefferys (c. 1719 – 1771), "Geographer to King George III", was an English cartographer who was the leading map supplier of his day.Oxford Dictionary of National Biography, 2004. He engraved and printed maps for government and other official bodies and produced a wide range of commercial maps and atlases, especially of North America.''Buckinghamshire in the 1760s and 1820s: The County Maps of Jefferys and Bryant'', Buckinghamshire Archaeological Society, 2000, . Information for this article has been taken from the introduction by Paul Laxton. Early work As "Geographer to the Prince of Wales", he produced ''A Plan of all the Houses, destroyed & damaged by the Great Fire, which began in Exchange Alley Cornhill, on Friday March 25, 1748''. He produced ''The Small English Atlas'' with Thomas Kitchin, and he engraved plans of towns in the English Midlands. Maps of North America In 1754, Jefferys published a ''Map of the Most Inhabited Part of Virginia'' which had been surve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Island Caribs
The Kalinago, also known as the Island Caribs or simply Caribs, are an indigenous people of the Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean. They may have been related to the Mainland Caribs (Kalina) of South America, but they spoke an unrelated language known as Island Carib. They also spoke a pidgin language associated with the Mainland Caribs. At the time of Spanish contact, the Kalinago were one of the dominant groups in the Caribbean, which owes its name to them. They lived throughout northeastern South America, Trinidad and Tobago, Barbados, the Windward Islands, Dominica, and possibly the southern Leeward Islands. Historically, it was thought their ancestors were mainland peoples who had conquered the islands from their previous inhabitants, the Igneri. However, linguistic and archaeological evidence contradicts the notion of a mass emigration and conquest; the Kalinago language appears not to have been Cariban, but like that of their neighbors, the Taíno. Irving Rouse and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Montagu, 4th Earl Of Sandwich
John Montagu, 4th Earl of Sandwich, PC, FRS (13 November 1718 – 30 April 1792) was a British statesman who succeeded his grandfather Edward Montagu, 3rd Earl of Sandwich as the Earl of Sandwich in 1729, at the age of ten. During his life, he held various military and political offices, including Postmaster General, First Lord of the Admiralty, and Secretary of State for the Northern Department. He is also known for the claim that he was the eponymous inventor of the sandwich. Biography Early years John Montagu was born in 1718, the son of Edward Montagu, Viscount Hinchingbrooke. His father died when John was four, leaving him as his heir. His mother soon remarried and he had little further contact with her. He succeeded his grandfather as Earl of Sandwich in 1729, at the age of ten. He was educated at Eton and at Trinity College, Cambridge, and spent some time travelling, initially going on the Grand Tour around Continental Europe before visiting the more unusual dest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amerindian
The Indigenous peoples of the Americas are the inhabitants of the Americas before the arrival of the European settlers in the 15th century, and the ethnic groups who now identify themselves with those peoples. Many Indigenous peoples of the Americas were traditionally hunter-gatherers and many, especially in the Amazon basin, still are, but many groups practiced aquaculture and agriculture. While some societies depended heavily on agriculture, others practiced a mix of farming, hunting, and gathering. In some regions, the Indigenous peoples created monumental architecture, large-scale organized cities, city-states, chiefdoms, states, kingdoms, republics, confederacies, and empires. Some had varying degrees of knowledge of engineering, architecture, mathematics, astronomy, writing, physics, medicine, planting and irrigation, geology, mining, metallurgy, sculpture, and gold smithing. Many parts of the Americas are still populated by Indigenous peoples; some countries have s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

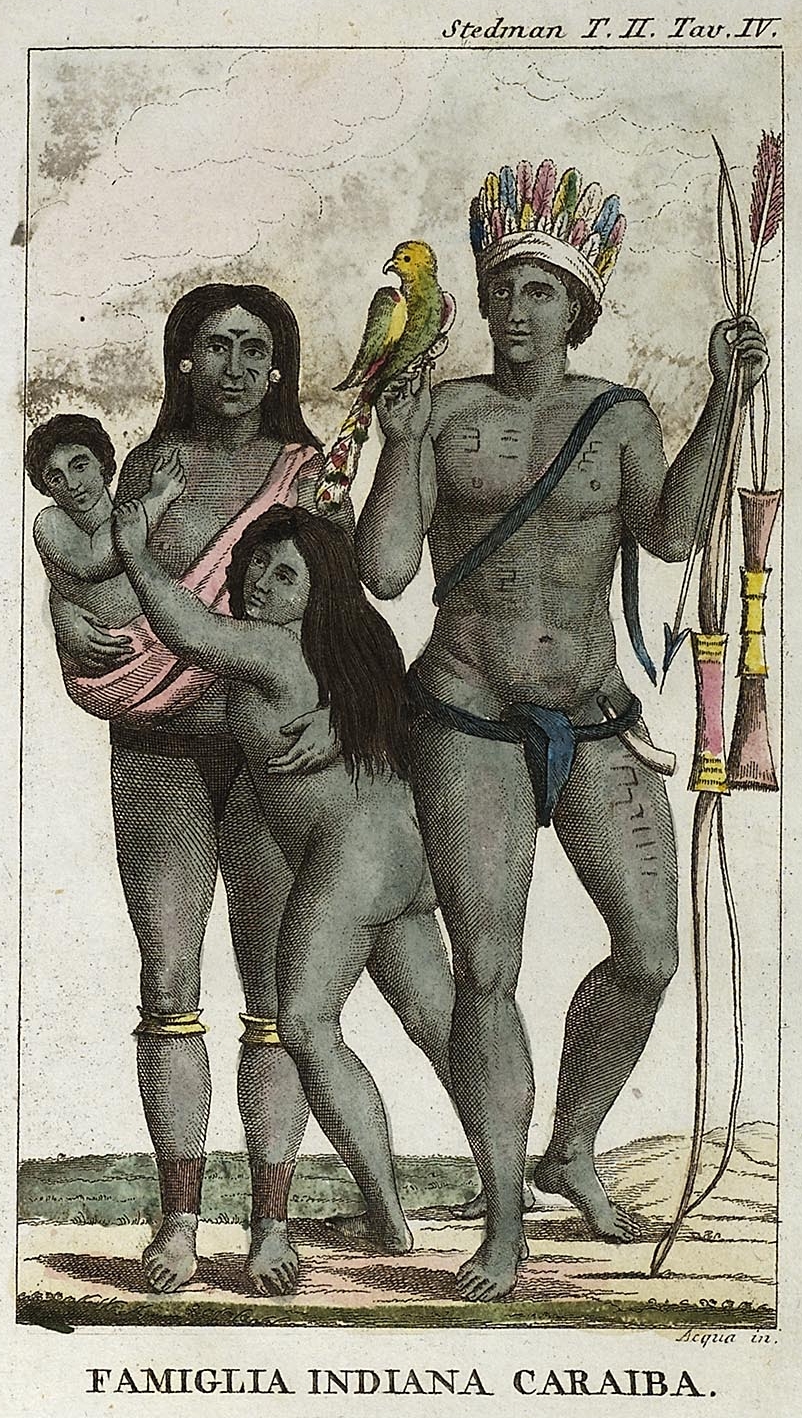

_2007.jpg)