|
They Did Not Expect Him
''They Did Not Expect Him'' is a painting by Russian realist artist Ilya Repin made between 1884 and 1888. It depicts the return of a narodnik from exile and his family's reaction. The painting is part of Repin's "Narodniki" series, which includes four other artworks. Repin began working on early versions of the canvas in 1884, at his country house in Martyshkino. He displayed it the same year in the 12th travelling exhibition of the Peredvizhniki, a group of Russian realist artists who travelled around Russia to host art exhibitions, first in Saint-Petersburg and then in other cities of Russia. It was purchased by Pavel Tretyakov in 1885 for display in his gallery. However, Repin continued to work on the painting after it was purchased, making several changes in 1885, 1887 and 1888, primarily to the face of the man entering the room. Russian artist and art critic Igor Grabar wrote that the paintings ''They Did Not Expect Him'' and ''Ivan the Terrible and His Son Ivan'' beca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Language
Russian (russian: русский язык, russkij jazyk, link=no, ) is an East Slavic languages, East Slavic language mainly spoken in Russia. It is the First language, native language of the Russians, and belongs to the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. It is one of four living East Slavic languages, and is also a part of the larger Balto-Slavic languages. Besides Russia itself, Russian is an official language in Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan, and is used widely as a lingua franca throughout Ukraine, the Caucasus, Central Asia, and to some extent in the Baltic states. It was the De facto#National languages, ''de facto'' language of the former Soviet Union,1977 Soviet Constitution, Constitution and Fundamental Law of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, 1977: Section II, Chapter 6, Article 36 and continues to be used in public life with varying proficiency in all of the post-Soviet states. Russian has over 258 million total speakers worldwide. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its Metropolitan France, metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra, and Spain in continental Europe, as well as the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Netherlands, Suriname, and Brazil in the Americas via its overseas territories in French Guiana and Saint Martin (island), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ne Zhdali (1st Version)
NE, Ne or ne may refer to: Arts and entertainment * Neutral Evil, an alignment in the American role-playing game ''Dungeons & Dragons'' * New Edition, an American vocal group * Nicomachean Ethics, a collection of ten books by Greek philosopher Aristotle Businesses and organizations * National Express, an English public transport operator * Natural England, an English government agency * New England Patriots, a professional American football team in Foxborough, Massachusetts * New Hope (Macau), a Macau political party * SkyEurope Airlines, a Slovakian airline * New Era Cap Company, an American headwear company Language * Ne (cuneiform), a cuneiform sign * Ne (kana), a Japanese written character * Nepali language * Modern English, sometimes abbreviated NE (to avoid confusion with Middle English) Places * NE postcode area, UK, a postcode for the City of Newcastle upon Tyne, Tyne and Wear * Ne, Liguria, Italy, a ''comune'' in the Province of Genoa * Né (river), a river in southwes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lomonosov, Russia
Lomonosov (russian: Ломоно́сов; before 1948: Oranienbaum, ) is a administrative divisions of Saint Petersburg, municipal town in Petrodvortsovy District of the federal cities of Russia, federal city of Saint Petersburg, Russia, located on the southern coast of the Gulf of Finland, west of Saint Petersburg proper. Population: Lomonosov is the site of the 18th-century royal Oranienbaum, Russia, Oranienbaum park and palace complex, notable as being the only palace in the vicinity of Saint Petersburg that was not captured by Nazi Germany during World War II. History Oranienbaum was granted town status in 1710, and was initially applied to the Oranienbaum, Russia, Oranienbaum palace complex, built between 1710 and 1725 opposite Kronstadt, in the neighbourhood of the royal residence Peterhof Palace, by the architects Giovanni Mario Fontana and Gottfried Johann Schadel, and was intended for Alexander Danilovich Menshikov, Alexander Menshikov, a close associate of Peter t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dacha
A dacha ( rus, дача, p=ˈdatɕə, a=ru-dacha.ogg) is a seasonal or year-round second home, often located in the exurbs of post-Soviet countries, including Russia. A cottage (, ') or shack serving as a family's main or only home, or an outbuilding, is not considered a dacha, although some dachas recently have been converted to year-round residences and vice versa. The noun "dacha", coming from verb "davat" (''to give''), originally referred to land allotted by the tsar to his nobles; and indeed the dacha in Soviet times is similar to the allotment in some Western countries – a piece of land allotted, normally free, to citizens by the local government for gardening or growing vegetables for personal consumption. With time the name for the land was applied to the building on it. In some cases, owners occupy their dachas for part of the year and rent them to urban residents as summer retreats. People living in dachas are colloquially called ''dachniki'' (); the term usually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narodniks
The Narodniks (russian: народники, ) were a politically conscious movement of the Russian intelligentsia in the 1860s and 1870s, some of whom became involved in revolutionary agitation against tsarism. Their ideology, known as Narodism, Narodnism or (russian: народничество; , similar to the German ), was a form of agrarian socialism though is often misunderstood as populism. The (; meaning 'going to the people') campaigns were the central impetus of the Narodnik movement. The Narodniks were in many ways the intellectual and political forebears and, in notable cases, direct participants of the Russian Revolution—in particular of the Socialist-Revolutionary Party, which went on to greatly influence Russian history in the early 20th century. History Narodnichestvo as a philosophy was influenced by the works of Alexander Herzen (1812–1870) and Nikolay Gavrilovich Chernyshevsky (1828–1889), whose convictions were refined by Pyotr Lavrov (1823–1900) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
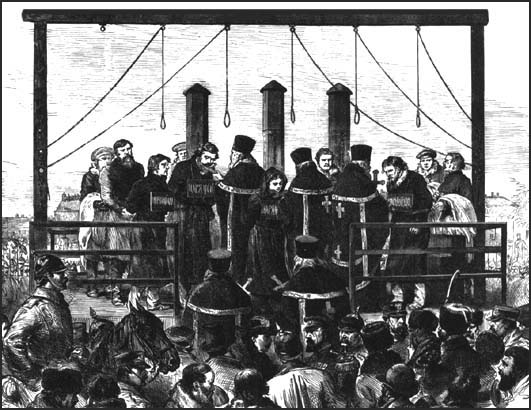
Pervomartovtsy
Pervomartovtsy (russian: Первома́ртовцы; a compound term literally meaning ''those of March 1'') were the Russian revolutionaries, members of ''Narodnaya Volya'', planners and executors of the assassination of Alexander II of Russia (March 1, 1881) and the attempted assassination of Alexander III of Russia (March 1, 1887, also known as "The Second First of March"). March 1, 1881 The assassination in 1881 was planned by Narodnaya Volya's Executive Committee. Andrei Zhelyabov was the main organizer. After his arrest on February 27, he was replaced by Sophia Perovskaya. Alexander II was killed on March 1, 1881 by a bomb, thrown by Ignacy Hryniewiecki. Hryniewiecki wounded himself fatally in the assassination; Nikolai Sablin committed suicide. Accomplices - Zhelyabov, Perovskaya, Nikolai Kibalchich, Hesya Helfman, Timofei Mikhailov, Nikolai Rysakov - were tried by the Special Tribunal of the Ruling Senate on March 26-29 and sentenced to death by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander II Of Russia
Alexander II ( rus, Алекса́ндр II Никола́евич, Aleksándr II Nikoláyevich, p=ɐlʲɪˈksandr ftɐˈroj nʲɪkɐˈlajɪvʲɪtɕ; 29 April 181813 March 1881) was Emperor of Russia, Congress Poland, King of Poland and Grand Duke of Finland from 2 March 1855 until Assassination of Alexander II of Russia, his assassination in 1881. Alexander's most significant reform as emperor was the emancipation reform of 1861, emancipation of Serfdom in Russia, Russia's serfs in 1861, for which he is known as Alexander the Liberator ( rus, Алекса́ндр Освободи́тель, r=Aleksándr Osvobodytel, p=ɐlʲɪˈksandr ɐsvəbɐˈdʲitʲɪlʲ). The tsar was responsible for other reforms, including reorganizing the judicial system, setting up elected local judges, abolishing corporal punishment, promoting local self-government through the ''zemstvo'' system, imposing universal military service, ending some privileges of the nobility, and promoting university e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
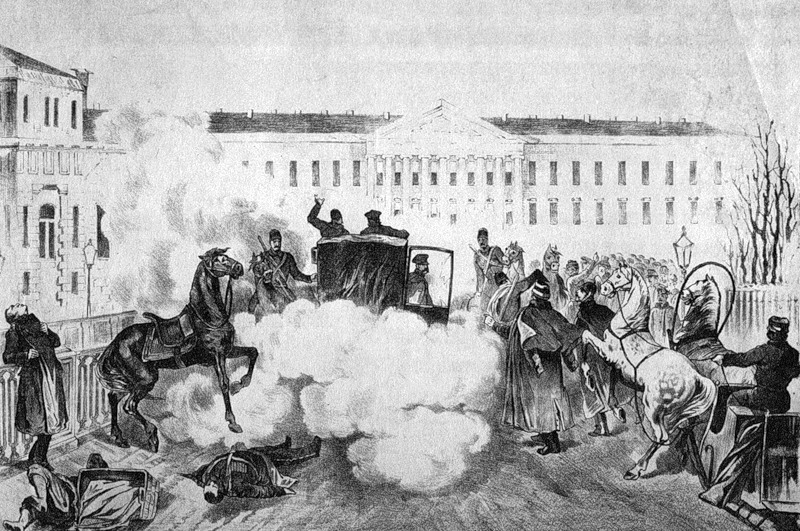
Assassination Of Alexander II Of Russia
On 13 March Old Style], 1881, Alexander II of Russia, Alexander II, the Emperor of Russia, was assassinated in Saint Petersburg, Russian Empire, Russia while returning to the Winter Palace from Mikhailovsky Manège in a closed carriage. The assassination was planned by the Executive Committee of ''Narodnaya Volya'' ("People's Will"), chiefly by Andrei Zhelyabov. Of the four assassins coordinated by Sophia Perovskaya, two of them actually committed the deed. One assassin, Nikolai Rysakov, threw a bomb which damaged the carriage, prompting the Tsar to disembark. At this point a second assassin, Ignacy Hryniewiecki, threw a bomb that fatally wounded Alexander II. Alexander II had previously survived several attempts on his life, including the attempts by Dmitry Karakozov and Alexander Soloviev, the attempt to dynamite the imperial train in Zaporizhzhia, and the bombing of the Winter Palace in February 1880. The assassination is popularly considered to be the most successful action ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Stasov
Vladimir Vasilievich Stasov (also Stassov; rus, Влади́мир Васи́льевич Ста́сов; 14 January Adoption_of_the_Gregorian_calendar#Adoption_in_Eastern_Europe.html" ;"title="/nowiki> O.S._2_January.html" ;"title="Adoption of the Gregorian calendar#Adoption in Eastern Europe">O.S. 2 January">Adoption of the Gregorian calendar#Adoption in Eastern Europe">O.S. 2 January/small> 1824 – 23 October .S. 10 October/small> 1906), was a Russian critic of music and art. Born into a wealthy, noble family Stasov became a prominent figure in mid-19th-century Russian culture. He discovered a large number of its greatest talents, inspired many of their works and fought their battles in numerous articles and letters to the press. As such, he carried on a lifelong debate with Russian novelist and playwright Ivan Turgenev, who considered Stasov "our great all-Russian critic." He wanted Russian art to liberate itself from what he saw as Europe's hold. By copying the west, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religious Procession In Kursk Governorate
'' Religious Procession in Kursk Governorate'' (also known as ''Easter Procession in the District of Kursk'' or ''A Religious Procession in Kursk Gubernia) (Russian: ''Крестный ход в Курской губернии'') is a large oil on canvas painting by the Russian realist painter and sculptor Ilya Repin (1844–1930). Completed between 1880 and 1883, the work shows a seething, huddled mass attending the annual ''crucession'' (cross-carrying Eastern Orthodox religious procession) which carried the famous icon Our Lady of Kursk from its home at the to the nearby city of Kursk, western Russia. The procession is led through a dusty landscape by robed, Orthodox priests holding icons, festoons and banners over their heads.Brinton, Christian. "Modern Artists", 2007. 146. Behind them follow a crowd mostly of peasants, but ranging from beggars and disabled people, police and military officers to figures from the provincial elite. ''Religious Procession'' led to controv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


.jpg)