|
Theravāda Abhidhamma
The Theravāda Abhidhamma is a scholastic systematization of the Theravāda school's understanding of the highest Buddhist teachings ( Abhidhamma). These teachings are traditionally believed to have been taught by the Buddha, though modern scholars date the texts of the ''Abhidhamma Piṭaka'' to the 3rd century BCE. Theravāda traditionally sees itself as the ''vibhajjavāda'' ("the teaching of analysis"), which reflects the analytical (''vibhajjati'') method used by the Buddha and early Buddhists to investigate the nature of the person and other phenomena. According to Bhikkhu Bodhi, a modern Theravāda scholar, the Abhidhamma is "simultaneously a philosophy, a psychology and an ethics, all integrated into the framework of a program for liberation."Bodhi (2000), p. 3. There are different textual layers of Abhidhamma literature. The earliest Abhidhamma works are found in the Pali Canon. Then there are exegetical works which were composed in Sri Lanka in the 5th century. There a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erich Frauwallner
Erich Frauwallner (December 28, 1898 – July 5, 1974) was an Austrian professor, a pioneer in the field of Buddhist studies.Walter Slaje: Rezensionen, Stuchlik, Jakob: Der arische Ansatz. Erich Frauwallner und der Nationalsozialismus, Asiatische Studien – Études Asiatiques 64, p. 447–463 (2010PDF/ref>Stuchlik, Replik auf Walter Slajes Rezension meines Buches Der arische Ansatz. Erich Frauwallner und der Nationalsozialismus, Asiatische Studien - Études Asiatiques Bd. 65.1, 287-308 (2011PDF/ref> Career and life Frauwallner studied classical philology and Sanskrit philology in Vienna. He taught Indology from 1928-29 at the University of Vienna. His primary interest was Buddhist logic and epistemology, and later Indian Brahmanic philosophy, with close attention to primary source texts. In 1938 Frauwallner joined the Department of Indian and Iranian philosophy at the Oriental Institute after its Jewish director, Bernhard Geiger, was forced out; Frauwallner became director in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dhammasaṅgaṇī
The Dhammasaṅgaṇī (Pāli; ), also known as the ''Dhammasaṅgaha'', is a Buddhist scripture, part of the Pali Canon of Theravada Buddhism. It is the first of the seven texts of the Abhidhamma Pitaka. The book begins with a ''matika'' (Pali for "matrix"), which is a list of classifications of dhammas, variously translated as ideas, phenomena, states, patterns etc. The text lacks a nidana, though the commentaries record that attempts were made at creating one that depicted the Buddha preaching the Abhidhamma in one of the heavenly realms. Theravada tradition attributes the Dhammasaṅgaṇī to Sariputra, who is held to have recited the Abhidhamma as part of the sutta texts at the First Buddhist Council, and regards it as one of the canonical teachings that Mahinda brought to Sri Lanka from the empire of Asoka. Its title is abbreviated 'Dhs' in Pāli scholarship. Format Following the ''matika'', the main body of the book is in four parts, as follows. * The first part dea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atthasālinī
Atthasālinī (Pali) is a Buddhist text composed by Buddhaghosa in the Theravada Abhidharma tradition. The title has been translated as "The Expositor"van Gorkom (2009)Preface or "Providing the Meaning". In the ''Atthasālinī'', Buddhaghosa explains the meaning of terms that occur in the Dhammasangani, a Buddhist text that is part of the Pali Canon of Theravada Buddhism. Mental factors Within the ''Atthasālinī'', Buddhaghosa explains the meanings of the fifty-two mental factors (Pali: cetasikas) described in the Dhammasangani. Translations * Buddhaghosa, Maung Tin, et al. (1958), ''The Expositor'', Pali Text Society The Pali Text Society is a text publication society founded in 1881 by Thomas William Rhys Davids "to foster and promote the study of Pāli texts". Pāli is the language in which the texts of the Theravada school of Buddhism are preserved. The Pā ... References Sources * * Aṭṭhakathā {{buddhist-text-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atthakatha
Aṭṭhakathā (Pali for explanation, commentary) refers to Pali-language Theravadin Buddhist commentaries to the canonical Theravadin Tipitaka. These commentaries give the traditional interpretations of the scriptures. The major commentaries were based on earlier ones, now lost, in Prakrit and Sinhala, which were written down at the same time as the Canon, in the last century BCE. Some material in the commentaries is found in canonical texts of other schools of Buddhism, suggesting an early common source. According to K.R. Norman: There is no direct evidence that any commentarial material was in fact recited at the first council, but there is clear evidence that some parts of the commentaries are very old, perhaps even going back to the time of the Buddha, because they afford parallels with texts which are regarded as canonical by other sects, and must therefore pre-date the schisms between the sects. As has already been noted, some canonical texts include commentarial pas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
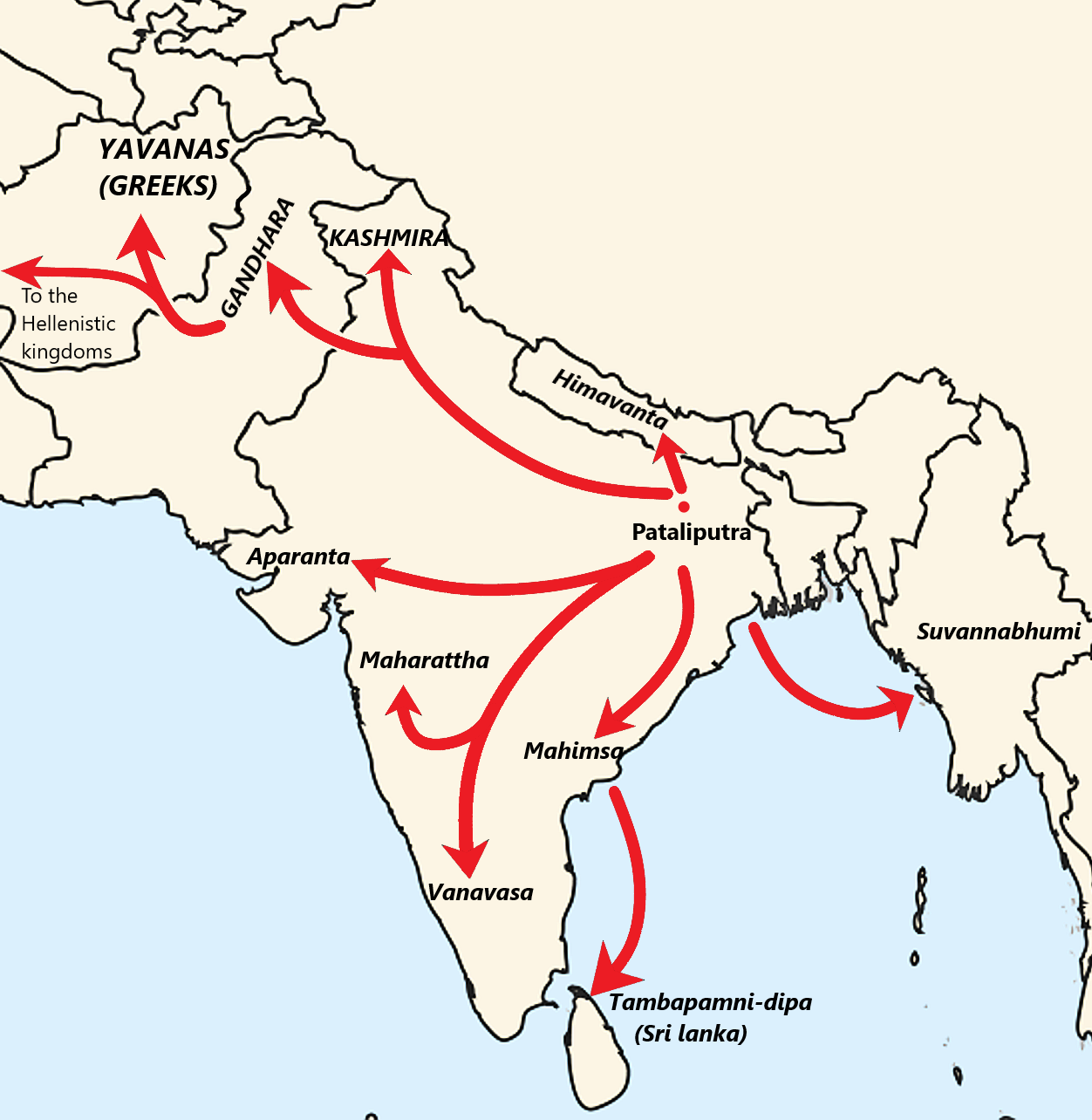
Buddhism In Sri Lanka
Theravada Buddhism is the largest and official religion of Sri Lanka, practiced by 70.2% of the population as of 2012. Practitioners of Sri Lankan Buddhism can be found amongst the majority Sinhalese population as well as among the minority ethnic groups. Sri Lankan Buddhists share many similarities with Southeast Asian Buddhists, specifically Myanmar Buddhists and Thai Buddhists due to traditional and cultural exchange. Sri Lanka is one of five nations with a Theravada Buddhist majority. Buddhism has been declared as the state religion under Article 9 of the Sri Lankan Constitution which can be traced back to an attempt to bring the status of Buddhism back to the status it enjoyed prior to the colonial era. Proselytizing from Buddhism has been illegal in Sri Lanka since 2009, due to the increase in conversions to Catholicism, however converting into Buddhism is highly encouraged by the government to be considered a person of Sinhalese origin. Sri Lanka is one of the oldest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peṭakopadesa
The Petakopadesa () is a Buddhist scripture, sometimes included in the Khuddaka Nikaya of the Pali Canon of Theravada Buddhism. The nature of this book is a matter of some disagreement among scholars. The translator, supported by Professor George Bond of Northwestern University, holds it is a guide to those who understand the teaching in presenting it to others. However, A. K. Warder, Professor Emeritus of Sanskrit in the University of Toronto, maintains that it covers all aspects of interpretation, not just that. The text is often connected to another para-canonical text, the Nettipakaraṇa. Oskar von Hinüber suggests that both of these texts originated from outside the Theravada tradition as handbooks on the interpretation of the sutras. Warder, in his examination of the ''Paṭisambhidāmagga Gaṇṭhipada'' in the Introduction to the ''Path of Discrimination'', notes: “The ''Gaṇṭhipada'' (p. 106), however, provides the positive information that this ''Peṭaka'' is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nettipakaraṇa
The Nettipakaraṇa (Pali, also called Nettippakarana, abbreviated Netti) is a mythological Buddhist scripture, sometimes included in the Khuddaka Nikaya of Theravada Buddhism's Pali Canon. The main theme of this text is Buddhist Hermeneutics through a systematization of the Buddha's teachings. It is regarded as canonical by the Burmese Theravada tradition, but isn't included in other Theravada canons. Origins and Dating The nature of the Nettipakarana was a matter of some disagreement among scholars. Initially, Western scholars classified it as a commentary, rather than as a canonical text. Further study and comparison with a closely related text, the Petakopadesa eventually revealed that it was a guide to interpretation and the composition of definitive commentaries. Its translator, supported by Professor George Bond of Northwestern University, described it is a guide to help those who already understand the teaching present it to others. However, A. K. Warder disagreed, mainta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niddesa
The Niddesa (abbrev., "Nidd") is a Buddhist scripture, part of the Pali Canon of Theravada Buddhism. It is included there in the Sutta Pitaka's Khuddaka Nikaya. It is in the form of a commentary on parts of the Suttanipata. The tradition ascribes it to the Buddha's disciple Sariputta. It is divided into two parts: * Maha Niddesa (mahā-) (abbrev., "Nidd I" or "Nd1"), commenting on the ''Atthaka Vagga'' ("Octet Chapter," Sn 4); * Culla or Cula Niddesa () (abbrev., "Nidd II" or "Nd2"), commenting on the ''Parayana Vagga'' ("Way to the Far Shore Chapter,"Sn 5) and ''Khaggavisana Sutta'' ("Rhinoceros Horn Discourse," Sn 1.3). This text is believed to have been most likely composed no later than the 1st century BC.Hinüber (2000), p. 59, para. 118, writes: :The age of Nidd has been discussed at great length by S.Lévi 1925, who arrives at a date in the 2nd century AD, arguing from the geographical horizon of the text. This date has been disputed recently by Norman 1983: 84,86, who ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paṭisambhidāmagga
The Patisambhidamagga (; Pali for "path of discrimination"; sometimes called just Patisambhida for short; abbrevs.: ) is a Buddhist scripture, part of the Pali Canon of Theravada Buddhism. It is included there as the twelfth book of the Sutta Pitaka's Khuddaka Nikaya. Tradition ascribes it to the Buddha's disciple Sariputta. It comprises 30 chapters on different topics, of which the first, on knowledge, makes up about a third of the book. History Tradition ascribes the Patisambhidamagga to the Buddha's great disciple, Sariputta. It bears some similarities to the Dasuttarasutta Sutta of the Digha Nikaya, which is also attributed to Sariputta. According to German tradition of Indology this text was likely composed around the 2nd century CE.Hinüber (2000), p. 60. Indications of the relative lateness of the text include numerous quotations from the Sutta and Vinaya Pitaka, as well as an assumed familiarity with a variety of Buddhist legends and stories- for example, the names of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dīgha Nikāya
The Digha Nikaya (dīghanikāya; "Collection of Long Discourses") is a Buddhist scriptures collection, the first of the five Nikāyas, or collections, in the Sutta Pitaka, which is one of the "three baskets" that compose the Pali Tipitaka of Theravada Buddhism. Some of the most commonly referenced suttas from the Digha Nikaya include the ''Mahāparinibbāṇa Sutta'' (DN 16), which described the final days and passing of the Lord Buddha, the ''Sigālovāda Sutta'' (DN 31) in which the Buddha discusses ethics and practices for lay followers, and the ''Samaññaphala Sutta'' (DN 2), ''Brahmajāla Sutta'' (DN 1) which describes and compares the point of view of Lord Buddha and other ascetics in India about the universe and time (past, present, and future); and the '' Poṭṭhapāda'' (DN 9) Suttas, which describe the benefits and practice of Samatha meditation. Structure and contents The Digha Nikaya consists of 34 discourses, broken into three groups: *Silakkhandha-vagga—T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johannes Bronkhorst
Johannes Bronkhorst (born 17 July 1946, Schiedam) is a Dutch Orientalist and Indologist, specializing in Buddhist studies and early Buddhism. He is emeritus professor at the University of Lausanne. Life After studying Mathematics, Physics, and Astronomy at the Vrije Universiteit in Amsterdam (B.Sc. 1968), he moved to India, where he turned to Sanskrit and Pāli, first at the University of Rajasthan (Jaipur), then the University of Pune (M.A. 1976, Ph.D. 1979). In Pune he read with traditional Sanskrit scholars, specializing in Sanskrit grammar and Indian philosophy. Back in the Netherlands, he did a second doctorate (1980) at the University of Leiden. Having worked for research projects funded by the Nederlandse Organisatie voor Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek, he was appointed in 1987 to the position of Professor of Sanskrit and Indian studies at the University of Lausanne. He retired in 2011. Work Bronkhorst has concentrated on the history of Indian thought and published on a wide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |