|
Theodore Angelos
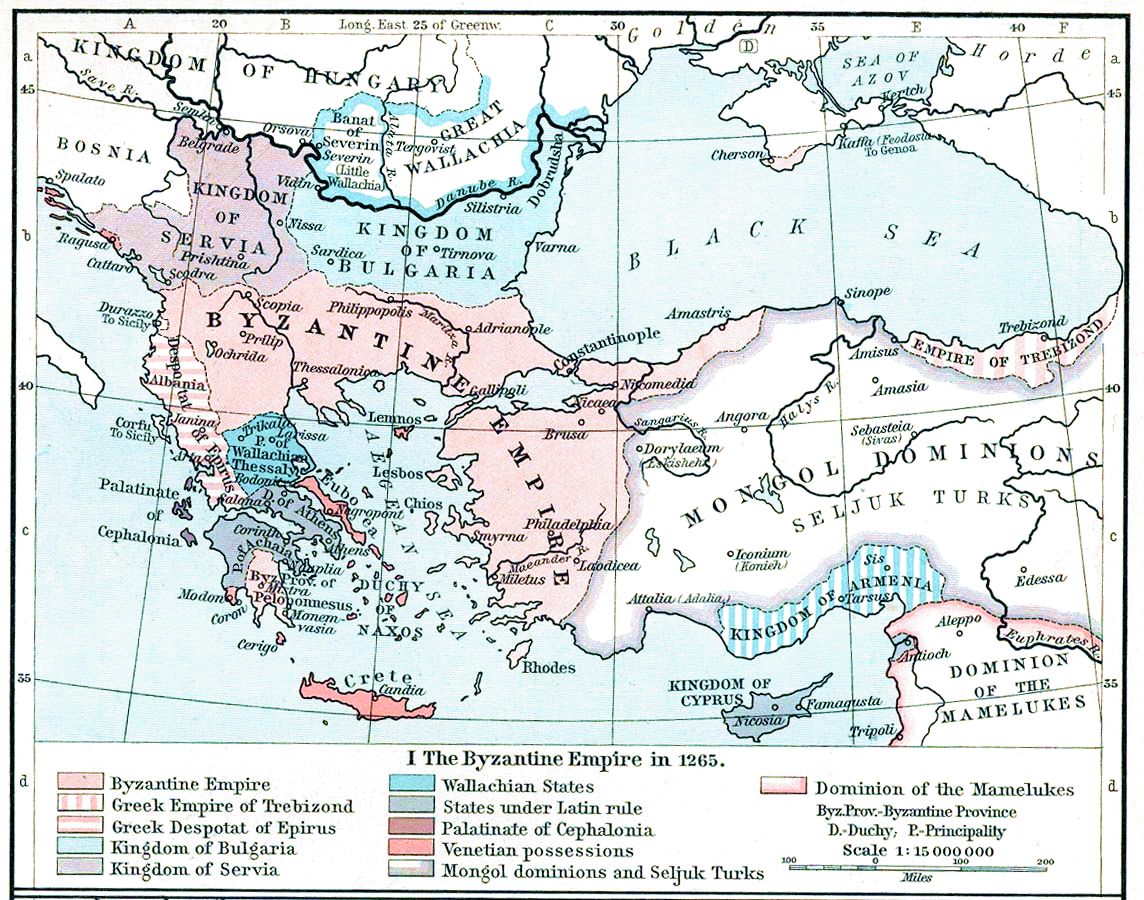
Theodore Angelos ( gr, Θεόδωρος Ἄγγελος, Theodōros Angelos) was co-ruler of Thessaly from to his death in . Theodore was the third son of John I Doukas, ruler of Thessaly by his wife, who is only known by her monastic name Hypomone ("Patience"). When John died in or shortly before 1289, he was succeeded by Theodore's older brother Constantine, but Theodore served as his co-ruler. Initially, the two brothers were under the tutelage of Anna Palaiologina Kantakouzene as they were underage. Awarded the title of ''sebastokrator'' from the Byzantine emperor in 1295, he was scheduled to marry the Armenian princess Theophano, but this project fell through. He was defeated in battle by the Byzantine general Michael Doukas Glabas Tarchaneiotes, and died in . References Sources * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Angelos, Theodore 13th-century births 1299 deaths People from Thessaly Medieval rulers of Thessaly 13th-century Byzantine people Theodore Theodore may refer to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sebastokrator
''Sebastokrator'' ( grc-byz, Σεβαστοκράτωρ, Sevastokrátor, August Ruler, ; bg, севастократор, sevastokrator; sh, sebastokrator), was a senior court title in the late Byzantine Empire. It was also used by other rulers whose states bordered the Empire or were within its sphere of influence ( Bulgarian Empire, Serbian Empire). The word is a compound of '' sebastós'' (, the Greek equivalent of the Latin ''Augustus'') and ''krátōr'' ('ruler', the same element as is found in '' autokrator'', 'emperor'). The wife of a ''Sebastokrator'' was named ''sebastokratorissa'' (, ''sevastokratórissa'') in Greek, ''sevastokratitsa'' () in Bulgarian and ''sebastokratorica'' in Serbian. Eastern Roman Empire The title was created by Emperor Alexios I Komnenos () to honour his elder brother Isaac Komnenos.. According to Anna Komnene, Alexios did this to raise Isaac above the rank of ''Caesar'', which he had already promised to his brother-in-law, Nikephoros Melissenos. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval Thessaly
The history of Thessaly covers the history of the region of Thessaly in north-central Greece from antiquity to the present day. Topography Thessaly is characterized by the large Thessalian plain, formed by the Pineios River, which is surrounded by mountains, most notably the Pindus mountain range to the west, which separates Thessaly from Epirus. Only two passes, the Porta pass and, in the summer, the pass of Metsovo, connect the two regions. From the south, the narrow coastal pass of Thermopylae connects Thessaly with southern Greece. In the north Thessaly borders on Macedonia, either through the coast or the pass of Servia towards Thessalonica, or in the northwest towards western Macedonia. Antiquity The first evidence of human habitation in Thessaly dates to the late Paleolithic, but in the early Neolithic this expanded rapidly. Over 400 archaeological sites dating to the period are known, including fortified ones. The most notable of these is at Sesklo. During the Mycenaea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Komnenodoukas Dynasty
The House of Angelos (; gr, Ἄγγελος), feminine form Angelina (), plural Angeloi (), was a Byzantine Greek noble lineage which rose to prominence through the marriage of its founder, Constantine Angelos, with Theodora Komnene, the youngest daughter of Emperor Alexios I Komnenos. As imperial relatives, the Angeloi held various high titles and military commands under Emperor Manuel I Komnenos. In 1185, following a revolt against Andronikos I Komnenos, Isaac II Angelos rose to the throne, the first of three Angeloi emperors who ruled until 1204. The period was marked by the decline and fragmentation of the Byzantine Empire, culminating in its dissolution by the Fourth Crusade in 1204. After the Fourth Crusade, another branch of the family managed to establish an independent state in Epirus. The members of this branch largely eschewed the use of the 'Angelos' surname in favour of the more prestigious 'Doukas' and 'Komnenos', and are collectively known as the Komnenodoukai () ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
13th-century Byzantine People
The 13th century was the century which lasted from January 1, 1201 ( MCCI) through December 31, 1300 ( MCCC) in accordance with the Julian calendar. The Mongol Empire was founded by Genghis Khan, which stretched from Eastern Asia to Eastern Europe. The conquests of Hulagu Khan and other Mongol invasions changed the course of the Muslim world, most notably the Siege of Baghdad (1258), the destruction of the House of Wisdom and the weakening of the Mamluks and Rums which, according to historians, caused the decline of the Islamic Golden Age. Other Muslim powers such as the Mali Empire and Delhi Sultanate conquered large parts of West Africa and the Indian subcontinent, while Buddhism witnessed a decline through the conquest led by Bakhtiyar Khilji. The Southern Song dynasty would begin the century as a prosperous kingdom but would eventually be invaded and annexed into the Yuan dynasty of the Mongols. The Kamakura Shogunate of Japan would be invaded by the Mongols. Goryeo resist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval Rulers Of Thessaly
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the Post-classical, post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern history, modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early Middle Ages, Early, High Middle Ages, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralized authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Thessaly
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, or legal responsibility. The defining features of personhood and, consequently, what makes a person count as a person, differ widely among cultures and contexts. In addition to the question of personhood, of what makes a being count as a person to begin with, there are further questions about personal identity and self: both about what makes any particular person that particular person instead of another, and about what makes a person at one time the same person as they were or will be at another time despite any intervening changes. The plural form "people" is often used to refer to an entire nation or ethnic group (as in "a people"), and this was the original meaning of the word; it subsequently acquired its use as a plural form of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1299 Deaths
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
13th-century Births
The 13th century was the century which lasted from January 1, 1201 ( MCCI) through December 31, 1300 ( MCCC) in accordance with the Julian calendar. The Mongol Empire was founded by Genghis Khan, which stretched from Eastern Asia to Eastern Europe. The conquests of Hulagu Khan and other Mongol invasions changed the course of the Muslim world, most notably the Siege of Baghdad (1258), the destruction of the House of Wisdom and the weakening of the Mamluks and Rums which, according to historians, caused the decline of the Islamic Golden Age. Other Muslim powers such as the Mali Empire and Delhi Sultanate conquered large parts of West Africa and the Indian subcontinent, while Buddhism witnessed a decline through the conquest led by Bakhtiyar Khilji. The Southern Song dynasty would begin the century as a prosperous kingdom but would eventually be invaded and annexed into the Yuan dynasty of the Mongols. The Kamakura Shogunate of Japan would be invaded by the Mongols. Goryeo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Doukas Glabas Tarchaneiotes
Michael Doukas Glabas Tarchaneiotes or Michael Tarchaneiotes Glabas ( el, ; – after 1304) was a notable Byzantine aristocrat and general. He served under emperors Michael VIII Palaiologos and Andronikos II Palaiologos in the Balkans, fighting against the Second Bulgarian Empire, Serbia, the Angevins of Naples and the Despotate of Epirus. He is also notable as the patron of several churches, most notably the Pammakaristos Church in Constantinople (mod. Istanbul), where he was buried. Life Military career Michael Doukas Glabas Tarchaneiotes was born , and is first mentioned in , when he was assigned to capture the city of Mesembria on the Black Sea coast from the deposed Bulgarian tsar Mitso Asen ()... In he defeated a Bulgarian army at Bizye, fortified Brysis, and proceeded to capture the fortresses Skopos, Petra and Skopelos, and the cities of Agathopolis, Sozopolis, Debeltos and Anchialos. He re-appears in 1278–79, leading another campaign against Bulgaria, where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Thessaly
The history of Thessaly covers the history of the region of Thessaly in north-central Greece from antiquity to the present day. Topography Thessaly is characterized by the large Thessalian plain, formed by the Pineios (Thessaly), Pineios River, which is surrounded by mountains, most notably the Pindus mountain range to the west, which separates Thessaly from Epirus. Only two passes, the Porta, Thessaly, Porta pass and, in the summer, the pass of Metsovo, connect the two regions. From the south, the narrow coastal pass of Thermopylae connects Thessaly with southern Greece. In the north Thessaly borders on Macedonia (region), Macedonia, either through the coast or the pass of Servia, Greece, Servia towards Thessalonica, or in the northwest towards western Macedonia. Antiquity The first evidence of human habitation in Thessaly dates to the late Paleolithic, but in the early Neolithic this expanded rapidly. Over 400 archaeological sites dating to the period are known, including fortifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient Rome a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_1938.jpg)