|
Theobromine
Theobromine, also known as xantheose, is the principal alkaloid of ''Theobroma cacao'' (cacao plant). Theobromine is slightly water-soluble (330 mg/L) with a bitter taste. In industry, theobromine is used as an additive and precursor to some cosmetics. It is found in chocolate, as well as in a number of other foods, including the leaves of the tea plant, and the kola nut. It is a white or colourless solid, but commercial samples can appear yellowish. Structure Theobromine is a flat molecule, a derivative of purine. It is also classified as a di methyl xanthine. Related compounds include theophylline, caffeine, paraxanthine, and 7-methylxanthine, each of which differ in the number or placement of the methyl groups. History Theobromine was first discovered in 1841 in cacao beans by Russian chemist Aleksandr Voskresensky. Synthesis of theobromine from xanthine was first reported in 1882 by Hermann Emil Fischer. Etymology ''Theobromine'' is derived from '' Theobroma'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caffeine
Caffeine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant of the methylxanthine class. It is mainly used recreationally as a cognitive enhancer, increasing alertness and attentional performance. Caffeine acts by blocking binding of adenosine to the adenosine A1 receptor, which enhances release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Caffeine has a three-dimensional structure similar to that of adenosine, which allows it to bind and block its receptors. Caffeine also increases cyclic AMP levels through nonselective inhibition of phosphodiesterase. Caffeine is a bitter, white crystalline purine, a methylxanthine alkaloid, and is chemically related to the adenine and guanine bases of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). It is found in the seeds, fruits, nuts, or leaves of a number of plants native to Africa, East Asia and South America, and helps to protect them against herbivores and from competition by preventing the germination of nearby seeds, as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chocolate02
Chocolate is a food made from roasted and ground cacao seed kernels that is available as a liquid, solid, or paste, either on its own or as a flavoring agent in other foods. Cacao has been consumed in some form since at least the Olmec civilization (19th-11th century BCE), and the majority of Mesoamerican people ─ including the Maya and Aztecs ─ made chocolate beverages. The seeds of the cacao tree have an intense bitter taste and must be fermented to develop the flavor. After fermentation, the seeds are dried, cleaned, and roasted. The shell is removed to produce cocoa nibs, which are then ground to cocoa mass, unadulterated chocolate in rough form. Once the cocoa mass is liquefied by heating, it is called chocolate liquor. The liquor may also be cooled and processed into its two components: cocoa solids and cocoa butter. Baking chocolate, also called bitter chocolate, contains cocoa solids and cocoa butter in varying proportions, without any added sugar. Pow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaloid
Alkaloids are a class of basic BASIC (Beginners' All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code) is a family of general-purpose, high-level programming languages designed for ease of use. The original version was created by John G. Kemeny and Thomas E. Kurtz at Dartmouth College ..., natural product, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar structure may also be termed alkaloids. In addition to carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen, alkaloids may also contain oxygen, sulfur and, more rarely, other elements such as chlorine, bromine, and phosphorus.Chemical Encyclopedia: alkaloids xumuk.ru Alkaloids are produced by a large variety of organisms includi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chocolate
Chocolate is a food made from roasted and ground cacao seed kernels that is available as a liquid, solid, or paste, either on its own or as a flavoring agent in other foods. Cacao has been consumed in some form since at least the Olmec civilization (19th-11th century BCE), and the majority of Mesoamerican people ─ including the Maya civilization, Maya and Aztecs ─ made chocolate beverages. The seeds of the cacao tree have an intense bitter (taste), bitter taste and must be fermentation (food), fermented to develop the flavor. After fermentation, the seeds are dried, cleaned, and roasted. The shell is removed to produce cocoa nibs, which are then ground to cocoa mass, unadulterated chocolate in rough form. Once the cocoa mass is liquefied by heating, it is called chocolate liquor. The liquor may also be cooled and processed into its two components: cocoa solids and cocoa butter. Baking chocolate, also called bitter chocolate, contains cocoa solids and cocoa butter in varyi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cocoa Bean
The cocoa bean (technically cocoa seed) or simply cocoa (), also called the cacao bean (technically cacao seed) or cacao (), is the dried and fully fermented seed of '' Theobroma cacao'', from which cocoa solids (a mixture of nonfat substances) and cocoa butter (the fat) can be extracted. Cocoa beans are the basis of chocolate, and Mesoamerican foods including tejate, an indigenous Mexican drink that also includes maize, and pinolillo, a similar Nicaraguan drink made from a cornmeal & cocoa powder. Etymology The word ''cocoa'' comes from the Spanish word , which is derived from the Nahuatl word . The Nahuatl word, in turn, ultimately derives from the reconstructed Proto-Mixe–Zoquean word ''kakawa''. Used on its own, the term ''cocoa'' may also mean: * Hot cocoa, the drink more known as '' hot chocolate'' Terms derived from ''cocoa'' include: * Cocoa paste, ground cocoa beans: the mass is melted and separated into: ** Cocoa butter, a pale, yellow, edible fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theobroma Cacao
''Theobroma cacao'', also called the cacao tree and the cocoa tree, is a small ( tall) evergreen tree in the family Malvaceae. Its seeds, cocoa beans, are used to make chocolate liquor, cocoa solids, cocoa butter and chocolate. The largest producer of cocoa beans in 2018 was Ivory Coast, 2.2 million tons. Description Its leaves are alternate, entire, unlobed, long and broad. Flowers The flowers are produced in clusters directly on the trunk and older branches; this is known as cauliflory. The flowers are small, diameter, with pink calyx. The floral formula, used to represent the structure of a flower using numbers, is ✶ K5 C5 A(5°+52) (5). While many of the world's flowers are pollinated by bees ( Hymenoptera) or butterflies/moths ( Lepidoptera), cacao flowers are pollinated by tiny flies, '' Forcipomyia'' midges in the subfamily Forcipomyiinae. Using the natural pollinator ''Forcipomyia'' midges for ''Theobroma cacao'' was shown to have more fruit production ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kola Nut
The term kola nut usually refers to the seeds of certain species of plant of the genus ''Cola'', placed formerly in the cocoa family Sterculiaceae and now usually subsumed in the mallow family Malvaceae (as subfamily Sterculioideae). These cola species are trees native to the tropical rainforests of Africa. Their caffeine-containing seeds are used as flavoring ingredients in beverages applied to various carbonated soft drinks, from which the name ''cola'' originates. General description The kola nut is a caffeine-containing nut of evergreen trees of the genus ''Cola'', primarily of the species '' Cola acuminata'' and '' Cola nitida''. ''Cola acuminata'', an evergreen tree about 20 meters in height, has long, ovoid leaves pointed at both the ends with a leathery texture. The trees have cream flowers with purplish-brown striations, and star-shaped fruit consisting of usually 5 follicles. Inside each follicle, about a dozen prismatic seeds develop in a white seed-shell. The nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleksandr Voskresensky
Aleksandr Abramovich Voskresensky (Russian: Александр Абрамович Воскресенский; 25 November 1808 – 21 January 1880) was a Russian chemist who served as rector of Saint Petersburg Imperial University in 1861–1863 and 1865–1867. Dmitri Mendeleev regarded him as a "grandfather of Russian chemistry". One of his major scientific achievements is the discovery of theobromine, the major alkaloid of cacao beans. Biography Voskresensky was born to a family of a poor priest, who died in 1814. He had one sister and one brother. From early ages he showed talents for sciences, and, after graduating from the St. Petersburg Institute of Pedagogy in 1836, was sent to Germany to continue his education. There he attended courses of Eilhard Mitscherlich, Heinrich Rose and Justus von Liebig, who considered Voskresensky one his most talented students. With Liebig he started his own chemical research. After returning to Russia in 1838 he was appointed as assistant t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraxanthine
Paraxanthine, or 1,7-dimethylxanthine, is a di methyl derivative of xanthine, structurally related to caffeine. Production and metabolism Paraxanthine is not known to be produced by plants but is observed in nature as a metabolite of caffeine in animals and some species of bacteria. After intake, roughly 84% of caffeine is demethylated at the 3-position to yield paraxanthine, making it the primary metabolite of caffeine in humans. Paraxanthine is also a major metabolite of caffeine in humans and other animals, such as mice. Shortly after ingestion, caffeine is metabolized into paraxanthine by hepatic cytochrome P450, which removes a methyl group from the N3 position of caffeine. After formation, paraxanthine can be broken down to 7-methylxanthine by demethylation of the N1 position, which is subsequently demethylated into xanthine or oxidized by CYP2A6 and CYP1A2 into 1,7-dimethyluric acid. In another pathway, paraxanthine is broken down into 5-acetylamino-6-formylamino-3-methyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theophylline
Theophylline, also known as 1,3-dimethylxanthine, is a phosphodiesterase inhibiting drug used in therapy for respiratory diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma under a variety of brand names. As a member of the xanthine family, it bears structural and pharmacological similarity to theobromine and caffeine, and is readily found in nature, being present in tea (''Camellia sinensis'') and cocoa (''Theobroma cacao''). A small amount of theophylline is one of the products of caffeine metabolic processing in the liver. Medical uses The main actions of theophylline involve: * relaxing bronchial smooth muscle * increasing heart muscle contractility and efficiency (positive inotrope) * increasing heart rate (positive chronotropic) * increasing blood pressure * increasing renal blood flow * anti-inflammatory effects * central nervous system stimulatory effect mainly on the medullary respiratory center. The main therapeutic uses of theophylline are a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xanthine
Xanthine ( or ; archaically xanthic acid; systematic name 3,7-dihydropurine-2,6-dione) is a purine base found in most human body tissues and fluids, as well as in other organisms. Several stimulants are derived from xanthine, including caffeine, theophylline, and theobromine. Xanthine is a product on the pathway of purine degradation. * It is created from guanine by guanine deaminase. * It is created from hypoxanthine by xanthine oxidoreductase. * It is also created from xanthosine by purine nucleoside phosphorylase. Xanthine is subsequently converted to uric acid by the action of the xanthine oxidase enzyme. Use and manufacturing Xanthine is used as a drug precursor for human and animal medications, and is manufactured as a pesticide ingredient. Clinical significance Derivatives of xanthine (known collectively as xanthines) are a group of alkaloids commonly used for their effects as mild stimulants and as bronchodilators, notably in the treatment of asthma or influen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
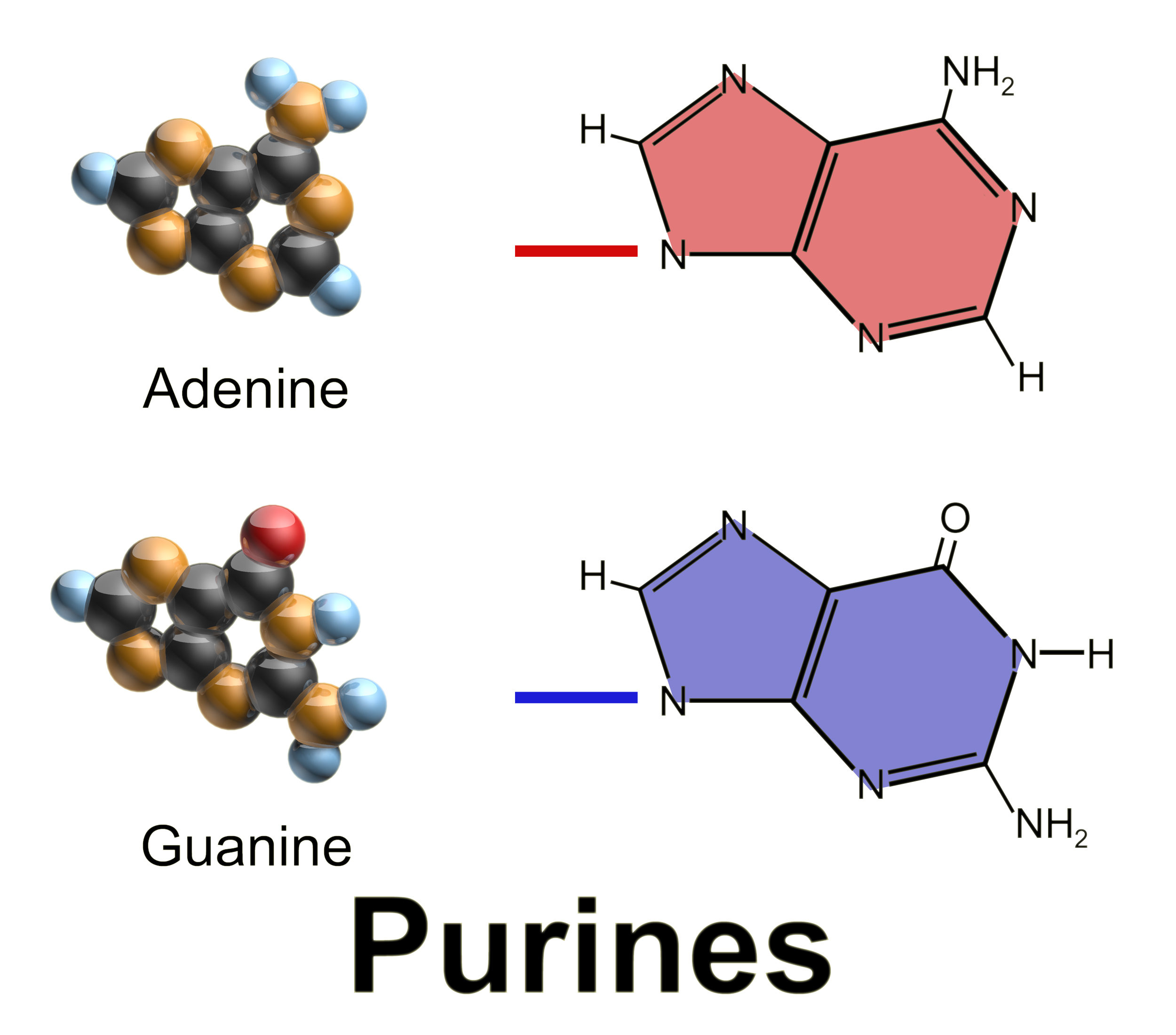
Purine
Purine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound that consists of two rings ( pyrimidine and imidazole) fused together. It is water-soluble. Purine also gives its name to the wider class of molecules, purines, which include substituted purines and their tautomers. They are the most widely occurring nitrogen-containing heterocycles in nature. Dietary sources Purines are found in high concentration in meat and meat products, especially internal organs such as liver and kidney. In general, plant-based diets are low in purines. High-purine plants and algae include some legumes (lentils and black eye peas) and spirulina. Examples of high-purine sources include: sweetbreads, anchovies, sardines, liver, beef kidneys, brains, meat extracts (e.g., Oxo, Bovril), herring, mackerel, scallops, game meats, yeast (beer, yeast extract, nutritional yeast) and gravy. A moderate amount of purine is also contained in red meat, beef, pork, poultry, fish and seafood, asparagus, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |