|
The Winnipeg Light Infantry
The Winnipeg Light Infantry was an infantry regiment of the Non-Permanent Active Militia of the Canadian Militia (now the Canadian Army). In 1955, the regiment was amalgamated with The Royal Winnipeg Rifles. Lineage The Winnipeg Light Infantry * Originated on 1 April 1912, in Winnipeg, Manitoba, as the ''106th Regiment, Winnipeg Light Infantry''. * Redesignated on 12 March 1920, as ''The Winnipeg Light Infantry''. * Redesignated on 15 December 1936, as ''The Winnipeg Light Infantry (Machine Gun)''. * Redesignated on 18 March 1942, as the ''2nd (Reserve) Battalion, The Winnipeg Light Infantry (Machine Gun)''. * Redesignated on 1 June 1945, as ''The Winnipeg Light Infantry (Machine Gun)''. * Redesignated on 1 April 1946, as ''The Winnipeg Light Infantry''. * Amalgamated on 30 June 1955, with ''The Royal Winnipeg Rifles''. Perpetuations North West Rebellion * 91st Winnipeg Battalion of Light Infantry (1885–1888) The Great War * 10th Battalion (Canadians), CEF * 6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2nd Canadian Infantry Brigade
The 2nd Canadian Infantry Brigade was a formation of the Canadian Army that served in both World War I and World War II. The brigade fought on the Western Front during World War I, and in Sicily and Italy during the Second World War. In both wars, the brigade formed part of the 1st Canadian Division. The brigade was first commanded from its formation in September 1914 to September 1915 by Arthur Currie. Order of Battle World War I * 5th Battalion (Western Cavalry), CEF. August 1914 – November 11, 1918; * 6th Battalion (Fort Garrys), CEF. August 1914 – December 1914 (Became Canadian Cavalry Depot); * 7th Battalion (1st British Columbia), CEF. August 1914 – November 11, 1918; * 8th Battalion (90th Winnipeg Rifles), CEF. August 1914 – November 11, 1918; * 10th Battalion (Canadians), CEF. January 1915 – November 11, 1918. World War II * Princess Patricia's Canadian Light Infantry * The Seaforth Highlanders of Canada * The Loyal Edmonton Regiment * 2nd Canadi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Festubert 1915
Festubert is a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department in the Hauts-de-France region of France. The village was on the Western Front during the First World War and was largely destroyed in the May 1915 Battle of Festubert. Geography A farming village some east of Béthune and southwest of Lille, at the junction of the D166 and the D72 roads. Population Places of interest * The church of Notre-Dame, rebuilt, as was much of the village, after the First World War. * The Commonwealth War Graves Commission cemeteries. See also *Communes of the Pas-de-Calais department *Defence of Festubert (November 1914) *Battle of Festubert (May 1915) *Battle of the Lys (1918) The Battle of the Lys, also known as the Fourth Battle of Ypres, was fought from 7 to 29 April 1918 and was part of the German spring offensive in Flanders during the First World War. It was originally planned by General Erich Ludendorff as O ... (Festubert was on the southern extremity of this battle) References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of St
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravenstafel Ridge (Ypres)
During the First World War, the Second Battle of Ypres was fought from for control of the tactically important high ground to the east and south of the Flemish town of Ypres in western Belgium. The First Battle of Ypres had been fought the previous autumn. The Second Battle of Ypres was the first mass use by Germany of poison gas on the Western Front. Background The eminent German chemist Walther Nernst, who was in the army in 1914 as a volunteer driver, saw how trenches produced deadlock. He proposed to Colonel Max Bauer, the German general staff officer responsible for liaison with scientists, that they could empty the opposing trenches by a surprise attack with tear gas. Observing a field test of this idea, the chemist Fritz Haber instead proposed using heavier-than-air chlorine gas The German commander Erich von Falkenhayn agreed to try the new weapon, but intended to use it in a diversionary attack by his 4th Army. Falkenhayn wanted to use the gas to cover the withdr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ypres, 1917
The Third Battle of Ypres (german: link=no, Dritte Flandernschlacht; french: link=no, Troisième Bataille des Flandres; nl, Derde Slag om Ieper), also known as the Battle of Passchendaele (), was a campaign of the First World War, fought by the Allies of World War I, Allies against the German Empire. The battle took place on the Western Front (World War I), Western Front, from July to November 1917, for control of the ridges south and east of the Belgian city of Ypres in West Flanders, as part of a strategy decided by the Allies at conferences in November 1916 and May 1917. Passendale, Passchendaele lies on the last ridge east of Ypres, from Roulers (now Roeselare), a junction of the Bruges-(Brugge)-to-Kortrijk railway. The station at Roulers was on the main supply route of the German 4th Army (German Empire), 4th Army. Once Passchendaele Ridge had been captured, the Allied advance was to continue to a line from Thourout (now Torhout) to Couckelaere (Koekelare). Further opera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ypres, 1915
During the First World War, the Second Battle of Ypres was fought from for control of the tactically important high ground to the east and south of the Flemish town of Ypres in western Belgium. The First Battle of Ypres had been fought the previous autumn. The Second Battle of Ypres was the first mass use by Germany of poison gas on the Western Front. Background The eminent German chemist Walther Nernst, who was in the army in 1914 as a volunteer driver, saw how trenches produced deadlock. He proposed to Colonel Max Bauer, the German general staff officer responsible for liaison with scientists, that they could empty the opposing trenches by a surprise attack with tear gas. Observing a field test of this idea, the chemist Fritz Haber instead proposed using heavier-than-air chlorine gas The German commander Erich von Falkenhayn agreed to try the new weapon, but intended to use it in a diversionary attack by his 4th Army. Falkenhayn wanted to use the gas to cover the withdr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North West Canada, 1885
The North-West Rebellion (french: Rébellion du Nord-Ouest), also known as the North-West Resistance, was a resistance by the Métis people under Louis Riel and an associated uprising by First Nations Cree and Assiniboine of the District of Saskatchewan against the Canadian government. Many Métis felt that Canada was not protecting their rights, their land, and their survival as a distinct people. Riel had been invited to lead the movement of protest; he turned it into a military action with a heavily religious tone. That alienated Catholic clergy, whites, most Indigenous tribes, and some Métis, but he had the allegiance of 200 armed Métis, a smaller number of other Indigenous warriors, and at least one white man at Batoche in May 1885, who confronted 900 Canadian militia and some armed local residents. About 91 people would die in the fighting that occurred that spring before the resistance's collapse. Despite some notable early victories at Duck Lake, Fish Creek, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
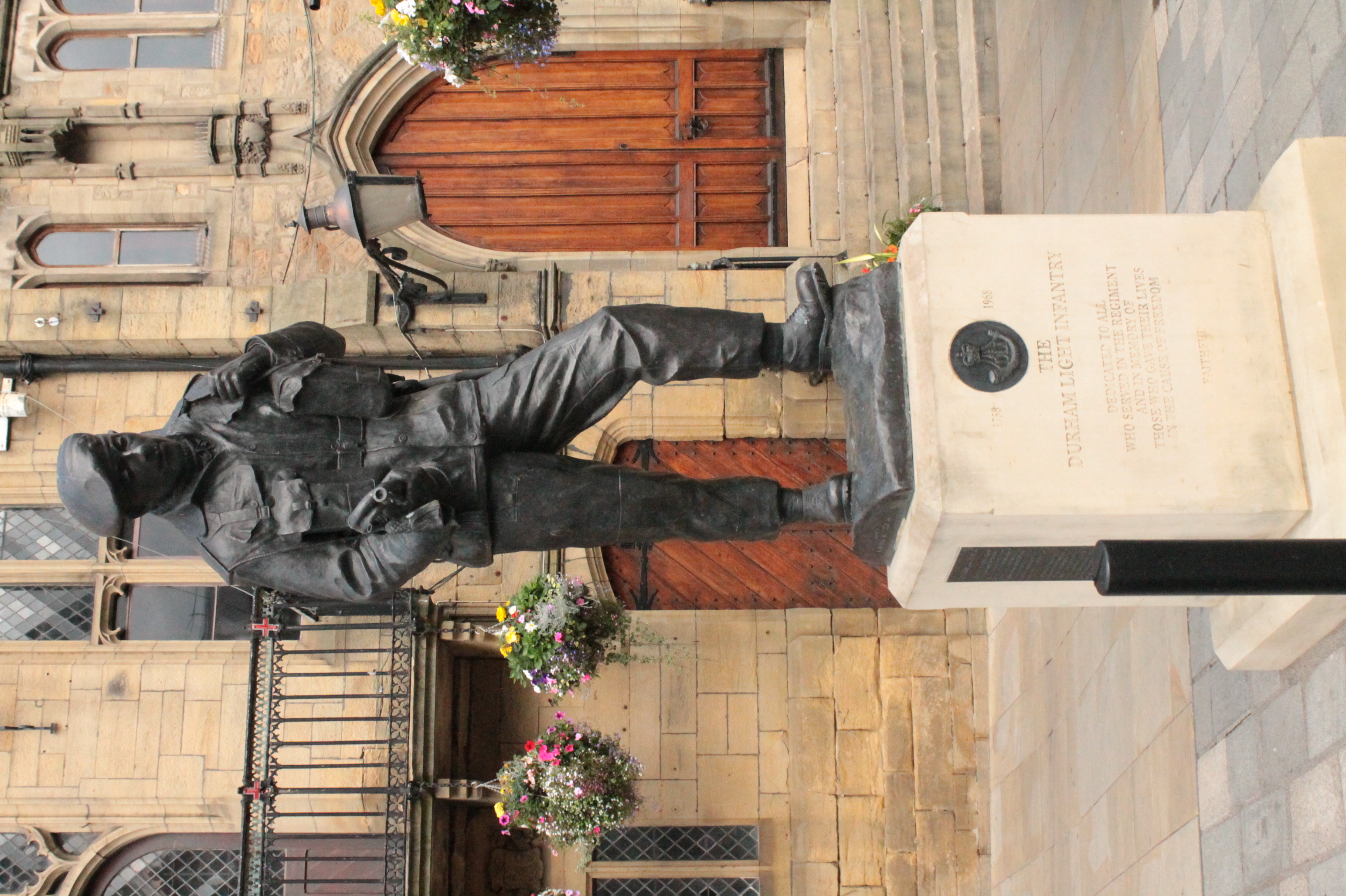
Durham Light Infantry
The Durham Light Infantry (DLI) was a light infantry regiment of the British Army in existence from 1881 to 1968. It was formed in 1881 under the Childers Reforms by the amalgamation of the 68th (Durham) Regiment of Foot (Light Infantry) and the 106th Regiment of Foot (Bombay Light Infantry) along with the Militia and Volunteers of County Durham. The regiment served notably in the Second Boer War, World War I and World War II, the Korean War and the Indonesia–Malaysia confrontation. During times of peace it had duty in India, China, West Germany and Cyprus. In 1968, the regiment was amalgamated with the Somerset and Cornwall Light Infantry, the King's Own Yorkshire Light Infantry and the King's Shropshire Light Infantry to form The Light Infantry, which again amalgamated in 2007 with the Devonshire and Dorset Regiment, the Royal Gloucestershire, Berkshire and Wiltshire Regiment and the Royal Green Jackets to form a new large regiment, The Rifles, which continues the lineag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6th Canadian Infantry Division
The 6th Canadian Infantry Division was an infantry division of the Canadian Army, formed in 1942 during the Second World War. It was attached to Pacific Command. The division had a brigade sent to the Aleutian Islands Campaign, particularly at Kiska, but never saw action. The 6th Division was to have been part of a proposed Commonwealth Corps, formed for a planned invasion of Japan, but was disbanded in 1945, after the war was ended by the bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. History The 6th Canadian Infantry Division was raised as part of a home-defence scheme in Canada, the culmination of various mobilizations throughout 1941 and 1942. The 6th was raised in March 1942 with its headquarters on Vancouver Island in British Columbia. Various composite units were stationed at Port Alberni, Vancouver Island and Vernon. Throughout 1943, the division lost its artillery units to coastal defence work, and other battalions were shipped overseas. In June 1943, these units were sent to Ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
7th Canadian Infantry Division
The 7th Canadian Infantry Division was an infantry Division (military), division of the Canadian Army, mobilized in the spring of 1942 and assigned for home defence within Atlantic Command (Canadian Army), Atlantic Command, during World War II. At the time it was assumed it would consist of volunteers and proceed overseas. By the summer of 1942 it became obvious that there would not be enough volunteers, so National Resource Mobilization Act (NRMA) Conscription, conscripts were assigned to the regiments of the Division to bring their numbers up to war establishment strength. This meant that the Division could only be used for home defence, unless the Parliament of Canada ruled that conscripted men could be sent overseas. Two brigades were assembled in the early fall of 1942 in CFS Debert, Camp Debert in Nova Scotia with the third at Camp Sussex in New Brunswick. Order of battle May 1942 * Headquarters, 7th Division ** 7th Division Intelligence Section ** No. 7 Field Security ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
8th Canadian Infantry Division
The 8th Canadian Infantry Division was a military formation of the Canadian Army that served within Pacific Command in Western Canada during World War II. The Division units were raised on 18 March 1942 and the HQ was raised on 12 May 1942 at Prince George, BC. The Division was a home defence unit, initially consisting of the 19th, 20th, and 21st Canadian Infantry Brigades. In July the home Defence Divisions were reorganised and the 8th Division consisted of the 14th and 16th Infantry Brigades. The 19th Brigade went to the 6th Canadian Infantry Division, the 20th went to the 7th Canadian Infantry Division, and the 21st would remain at Valcartier, PQ as a strategic reserve. The 8th Canadian Infantry Division was disbanded on 15 October 1943, along with the 16th Brigade. The 14th Brigade returned to the 6th Division. Throughout its relatively brief existence, the division was commanded by Major General Hardy N. Ganong. Order of battle June 1942 * Headquarters, 8th Division ** 8t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |