|
The Switchback (CR)
The Switchback was a railway line in the East End of Glasgow, Scotland, constructed by the Caledonian Railway (CR). Connecting the lines at Rutherglen on the south side of the city with Robroyston on the north side, this route also served a number of industrial sidings and rail yards. History South of London Road In 1858, the CR honed plans for the one-mile Rutherglen–Dalmarnock line, to be called the Dalmarnock branch. Primarily for the transport of coal, the terminus was the Dalmarnock Gas Works, Bridgeton, which had formerly been supplied via a canal from the river. No explicit commitment was made to introduce a passenger service. The building of the seven-span Dalmarnock Railway Bridge during 1859–1861 across the River Clyde was integral to the branch opening in 1861. The terminus was initially known as Dalmarnock. Illustrating 1867 traffic volumes, consecutive returning coal trains heading southeast towards Hamilton Junction, after leaving the branch, caused an accide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glasgow
Glasgow ( ; sco, Glesca or ; gd, Glaschu ) is the most populous city in Scotland and the fourth-most populous city in the United Kingdom, as well as being the 27th largest city by population in Europe. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 635,640. Straddling the border between historic Lanarkshire and Renfrewshire, the city now forms the Glasgow City Council area, one of the 32 council areas of Scotland, and is governed by Glasgow City Council. It is situated on the River Clyde in the country's West Central Lowlands. Glasgow has the largest economy in Scotland and the third-highest GDP per capita of any city in the UK. Glasgow's major cultural institutions – the Burrell Collection, Kelvingrove Art Gallery and Museum, the Royal Conservatoire of Scotland, the Royal Scottish National Orchestra, Scottish Ballet and Scottish Opera – enjoy international reputations. The city was the European Capital of Culture in 1990 and is notable for its architecture, cult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackhill, Glasgow
__NOTOC__ Blackhill ( gd, Cnoc Dubh) is an area of north east Glasgow, Scotland. It is directly bordered by the M80 motorway to the west and the M8 motorway to the south. The neighbourhood falls within the North East ward under Glasgow City Council. History Blackhill was developed as a council housing estate in the 1930s. Most of the new development was designated ''Rehousing'', the lowest grade of council housing intended for those cleared from Glasgow's 19th century slums, particularly those in the Garngad (now Royston) area. The new buildings were three-storey, slate-roofed tenements built of reconstituted stone. The eastern side of Blackhill, nearer to Provanmill and Riddrie, was designated ''Intermediate'', a grade up from ''Rehousing'', and housing was of the cottage flat-type with front and rear gardens and a measure of landscaping in the streets ("Rehousing" areas cost £250 per house to build, while "Intermediate" areas cost £1000). The area has been historic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glasgow East End Regeneration Route
The A728 is a route number in Glasgow, Scotland applied to two connected roads. The eastern branch, known as the Glasgow East End Regeneration Route runs from Polmadie to the Forge Shopping Centre in Camlachie in the east of the city. The first phase was opened in 2011 with the second phase opened in mid-2012; these two phases are officially known as the A728 Clyde Gateway. An extension to junction 13 of the M8, which is also the terminus of the M80, was planned as well, for construction in 2018. After delay, it was scrapped in 2021 due to climate concerns. The western branch of the route runs from the Albert Bridge near the city centre, where it meets the A8 and A74, and converges with the other branch near Toryglen Park in Polmadie. Both branches continue along the same road south towards King's Park.\ in the south of the city. Eastern branch Inner Ring Road plans The history of the route goes back to the Glasgow Inner Ring Road (IRR) project of the 1960s. Owin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commonwealth Arena And Sir Chris Hoy Velodrome
The Commonwealth Arena and Sir Chris Hoy Velodrome, known for sponsorship reasons as the Emirates Arena, is an indoor arena and velodrome in Dalmarnock, Glasgow, Scotland. Built for the 2014 Commonwealth Games, these venues hosted the badminton and track cycling events. Situated opposite Celtic Park in the East End of Glasgow, the complex is the headquarters of Sportscotland and Scottish Cycling. History It was built on a site at a cost of £113 million. The construction work took place between 2009 and 2012. The venue opened in October 2012. In September 2017, neighbours Celtic F.C. had plans approved for the construction of a hotel complex within their land, situated directly across the road from the arena and velodrome. Indoor arena The Indoor Arena has a capacity of 6,500 and during the Commonwealth Games it had twelve badminton courts in three indoor sports halls. The arena has a hydraulically lifted 200m indoor running track that hosted the Aviva International Matc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brownfield Land
In urban planning, brownfield land is any previously developed land that is not currently in use. It may be potentially contaminated, but this is not required for the area to be considered brownfield. The term is also used to describe land previously used for industrial or commercial purposes with known or suspected pollution including soil contamination due to hazardous waste. Examples sites include abandoned factories, landfills, dry cleaning establishments and gas stations. Typical contaminants include hydrocarbon spillages, solvents and pesticides, as well as heavy metals like lead, tributyl tins and asbestos. Many contaminated brownfield sites sit unused for decades as involuntary parks because cleaning cost is more than land worth after redevelopment. Previously unknown underground wastes can increase the cost for study and clean-up. Acquisition, adaptive re-use, and disposal of a brownfield site requires advanced and specialized appraisal analysis techniques. Rem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Forge Shopping Centre
The Forge Shopping Centre (or Parkhead Forge) is in the East End of Glasgow, in Parkhead. The shopping centre bore the name from the former William Beardmore and Company steel works site, which had closed in 1983. History Construction The GEAR ( Glasgow Eastern Area Renewal) scheme was founded in 1976, then Europe's largest urban regeneration project of its kind, to provide "core areas with development potential" in the east end of Glasgow. A new shopping centre was part of the plan, ideally to replace the then recently closed Parkhead Forge plant of the Beardmore's steel works. The shopping centre was going to contain a supermarket, a new multiplex cinema and at least 40 units. Work on the shopping centre began in 1986, and the building was opened to the public on 10 October 1988. The main anchor tenant was a Gateway supermarket (at the time the largest in Scotland), but this changed over to Asda early in 1990 and has remained as such ever since. The main entrances to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalmarnock Railway Station (geograph 2447289)
, symbol_location = gb , symbol = rail , image = Dalmarnock777.JPG , caption = Dalmarnock station (pre-2014 refurbishment), looking towards the tunnel , borough = Dalmarnock, Glasgow , country = Scotland , coordinates = , grid_name = Grid reference , grid_position = , manager = ScotRail , platforms = 2 , code = DAK , transit_authority = SPT , original = Glasgow Central Railway , pregroup = Caledonian Railway , postgroup = LMS , years = 1 November 1895Butt (1995), page 76 , events = Opened , years1 = 5 October 1964 , events1 = Closed , years2 = 5 November 1979 , events2 = Re-opened , years3 = 3 June 2012 , events3 = Temporarily closed for refurbishment , years4 = 23 May 2013 , eve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M8 Motorway (Scotland)
The M8 is the busiest motorway in Scotland and one of the busiest in the United Kingdom. It connects the country's two largest cities, Glasgow and Edinburgh, and serves other large communities including Airdrie, Coatbridge, Greenock, Livingston and Paisley. The motorway is long. A major construction project to build the final section between Newhouse and Baillieston was completed on 30 April 2017. The motorway has one service station, Heart of Scotland Services, previously named Harthill due to its proximity to the village. History With the advent of motorway-building in the United Kingdom in the late 1950s, the M8 was planned as one of a core of new motorways, designed to replace the A8 road as a high-capacity alternative for intercity travel. The motorway was constructed piecemeal in several stages bypassing towns, beginning in 1965 with the opening by Minister of State for Scotland George Willis of the bypass of Harthill. In 1968 the Renfrew Bypass was opened as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M80 Motorway
The M80 is a motorway in Scotland's central belt, running between Glasgow and Stirling via Cumbernauld and Denny and linking the M8, M73 and M9 motorways. Following completion in 2011, the motorway is long. Despite being only a two lane motorway, parts of the M80 Stepps Bypass are used by around 60,000 vehicles per day. The M80 was constructed in three sections. The first section, from the village of Haggs to the M9 near Stirling, opened in 1974, followed in 1992 by the section from the M8 to the small town of Stepps. The section from Stepps to Haggs was completed in September 2011, though it partially opened in February 2011 when the Moodiesburn bypass, from Stepps to the M73 at Mollinsburn, was completed; the section of the A80 from Mollinsburn to Haggs was then upgraded. Route M8 to Stepps (Junctions 1 to 3) This section of road was originally envisioned during the M8's construction in the 1960s, but was not realised until 1992, and is also known as the 'Stepps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Newspaper Archive
The British Newspaper Archive web site provides access to searchable digitized archives of British and Irish newspapers. It was launched in November 2011. History The British Library Newspapers section was based in Colindale in north London, until 2013, and is now divided between the St Pancras and Boston Spa sites. The library has an almost complete collection of British and Irish newspapers since 1840. This is partly because of the legal deposit legislation of 1869, which required newspapers to supply a copy of each edition of a newspaper to the library. London editions of national daily and Sunday newspapers are complete back to 1801. In total, the collection consists of 660,000 bound volumes and 370,000 reels of microfilm containing tens of millions of newspapers with 52,000 titles on 45 km of shelves. After the closure of Colindale in November 2013, access to the 750 million original printed pages was maintained via an automated and climate-controlled storage facil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beeching Cuts
The Beeching cuts (also Beeching Axe) was a plan to increase the efficiency of the nationalised railway system in Great Britain. The plan was outlined in two reports: ''The Reshaping of British Railways'' (1963) and ''The Development of the Major Railway Trunk Routes'' (1965), written by Richard Beeching and published by the British Railways Board. The first report identified 2,363 stations and of railway line for closure, amounting to 55% of stations, 30% of route miles, and 67,700 British Rail positions, with an objective of stemming the large losses being incurred during a period of increasing competition from road transport and reducing the rail subsidies necessary to keep the network running. The second report identified a small number of major routes for significant investment. The 1963 report also recommended some less well-publicised changes, including a switch to the now-standard practice of containerisation for rail freight, and the replacement of some services w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
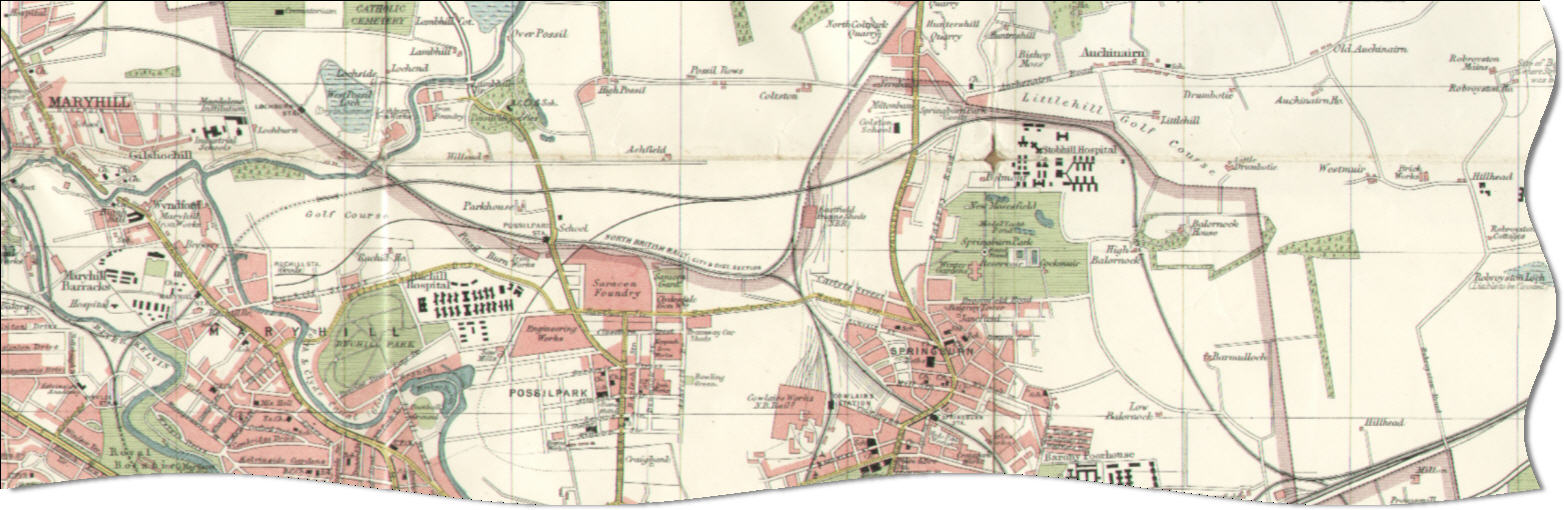
Hamiltonhill Branch
The Hamiltonhill Branch was constructed by the Caledonian Railway in 1894 with the intention to provide a large goods yard at Hamiltonhill on the Forth and Clyde Canal. There was also a branch to the Saracen Foundry but this had to be closed as it was in breach of an agreement with the North British Railway. History The Hamiltonhill yard closed at an early date, however the section of the line was extended by the Lanarkshire and Dunbartonshire Railway to Dumbarton and gave the Caledonian Railway access to Balloch, linking through to the Garnkirk and Glasgow Railway to the east. Part of the route between Eastfield and Possil was built along the course of an old waggonway which had run from pits at Eastfield to the Forth and Clyde Canal at Ruchill. Much of the former trackbed is still visible to this day. Current operations The line is now closed. Connections to other lines * Lanarkshire and Dunbartonshire Railway at Possil Junction * Garnkirk and Glasgow Railway The Ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
.jpg)