|
The MacArthur Museum Of Arkansas Military History
The Tower Building of the Little Rock Arsenal, also known as the Main Building of the U.S. Arsenal at Little Rock, or Headquarters Building of the Little Rock Barracks, is the home of the MacArthur Museum of Arkansas Military History. It is also a part of the MacArthur Park Historic District, in Little Rock, Arkansas. Built between 1840 and 1841, it was part of Little Rock's first U.S. military installation. Since decommissioning, the building has housed two local museums. It was home to the Arkansas Museum of Natural History and Antiquities from 1942 to 1997 and the MacArthur Museum of Arkansas Military History since 2001. It has also housed the Little Rock Æsthetic Club since 1894. The building receives its name from its distinct octagonal tower. Besides being the last remaining structure of the original U.S. military installation and one of the oldest buildings in central Arkansas, it was also the birthplace of General Douglas MacArthur, who became the supreme commander of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Little Rock, Arkansas
(The Little Rock, The "Little Rock") , government_type = council-manager government, Council-manager , leader_title = List of mayors of Little Rock, Arkansas, Mayor , leader_name = Frank Scott Jr. , leader_party = Democratic Party (United States), D , leader_title2 = City council, Council , leader_name2 = Little Rock Board of Directors , unit_pref = Imperial , area_total_sq_mi = 123.00 , area_total_km2 = 318.58 , area_land_sq_mi = 120.05 , area_land_km2 = 310.92 , area_metro_sq_mi = 4090.34 , area_metro_km2 = 10593.94 , population_as_of = 2020 United States Census, 2020 , population_est = , pop_est_as_of = , population_demonym = Little Rocker , population_footnotes = , population_total = 202591 , population_rank = US: List of United States cities by population, 118 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Register Of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures and objects deemed worthy of preservation for their historical significance or "great artistic value". A property listed in the National Register, or located within a National Register Historic District, may qualify for tax incentives derived from the total value of expenses incurred in preserving the property. The passage of the National Historic Preservation Act (NHPA) in 1966 established the National Register and the process for adding properties to it. Of the more than one and a half million properties on the National Register, 95,000 are listed individually. The remainder are contributing resources within historic districts. For most of its history, the National Register has been administered by the National Park Service (NPS), an agency within the U.S. Department of the Interior. Its goals are to help property owners and inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
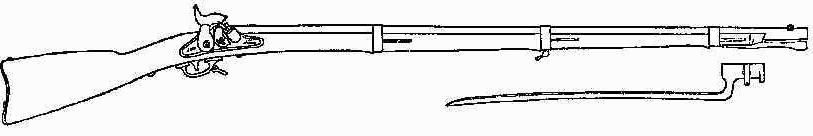
Springfield Model 1855
The Springfield Model 1855 was a rifled musket widely used in the American Civil War. It exploited the advantages of the new conical Minié ball, which could be deadly at over . It was a standard infantry weapon for Union and Confederates alike, until the Springfield Model 1861 supplanted it, obviating the use of the insufficiently weather resistant Maynard tape primer. Origins The Model 1855 Springfield was a rifled musket used in the mid-19th century. It was manufactured by the Springfield Armory in Massachusetts and at the Harpers Ferry Armory in Virginia (modern-day West Virginia West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian, Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States.The Census Bureau and the Association of American Geographers classify West Virginia as part of the Southern United States while the Bur ...) along with the Eli Whitney, Whitney Armory. Earlier Musket, muskets had mostly been smoothbore Flintlock, flintlocks. In the 1840s, the unreliab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Model 1822 Musket
The Springfield Model 1822 was a .69 caliber flintlock musket manufactured by the United States in the early 19th century. The Model 1822 was an improvement to the Springfield Model 1816. Some documents refer to the Model 1822 as its own separate model, but other documents refer to it as a variant of the Model 1816 designated as the Type II. Like the Model 1816, the Model 1822 was a .69 caliber smoothbore flintlock, with a barrel and an overall length of . One of the most noticeable differences in the Model 1822 is the attachment of the lower sling swivel. The forward part of the trigger guard was provided with an enlargement which was drilled to receive the sling swivel rivet. Previously, the sling swivel had been affixed to a stud in front of the trigger guard."Guns on the Early Frontiers" by Carl P. Russell, Published by U of Nebraska Press, 1980 In addition to the Springfield and Harpers Ferry armories, the Model 1822 was produced by numerous other independent contractors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulaski Light Artillery
The 3rd Arkansas Field Battery (1860–1865) was a Confederate Army artillery battery from Pulaski County, Arkansas, during the American Civil War. The battery is also known as the Totten Light Artillery, Pulaski Light Artillery, the Weaver Light Artillery, Woodruff's Battery, and Marshall's Battery. The battery originated as a pre-war Militia company, initially enrolled in state service. After the Battle of Wilson's Creek, the battery was released from state service and eventually reorganized for Confederate Service. The battery provided the initial training for the leaders of numerous other Arkansas artillery batteries during the Civil War. The battery spent its entire service in the Department of the Trans-Mississippi. Organization The Pulaski Light Artillery was organized at Little Rock, Pulaski County, Arkansas, in December 1860. This was a time when sectional strife between the Deep South and the northern states caused the young men in many southern cities to form mili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John M
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died c. AD 30), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (lived c. AD 30), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * Pope Joh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memphis, Tennessee
Memphis is a city in the U.S. state of Tennessee. It is the seat of Shelby County in the southwest part of the state; it is situated along the Mississippi River. With a population of 633,104 at the 2020 U.S. census, Memphis is the second-most populous city in Tennessee, after Nashville. Memphis is the fifth-most populous city in the Southeast, the nation's 28th-largest overall, as well as the largest city bordering the Mississippi River. The Memphis metropolitan area includes West Tennessee and the greater Mid-South region, which includes portions of neighboring Arkansas, Mississippi and the Missouri Bootheel. One of the more historic and culturally significant cities of the Southern United States, Memphis has a wide variety of landscapes and distinct neighborhoods. The first European explorer to visit the area of present-day Memphis was Spanish conquistador Hernando de Soto in 1541. The high Chickasaw Bluffs protecting the location from the waters of the Mississipp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Totten
James Totten (September 11, 1818 – October 1, 1871) was a career American soldier who served in the United States Army and retired from active service in 1870 as the Assistant Inspector General. He served as an officer in the Union Army and Missouri militia general during the American Civil War. He may be related to Chief Engineer of the U.S. Army Brigadier General Joseph Totten. Early life and career Totten was born in 1818 in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, He graduated from the United States Military Academy in 1841 and subsequently became a first lieutenant in 1847 before fighting Seminole Indians in Florida during 1849-50. After attaining the rank of captain in 1855, he went to Bleeding Kansas to try to suppress the disturbances there. Civil War service In February 1861, shortly before the American Civil War began, Totten was in command of the Little Rock Arsenal with just 65 men. He was forced to evacuate his forces to St. Louis when about 5,000 pro-secession volunteers led by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Massey Rector
Henry Massie Rector (May 1, 1816August 12, 1899) was an American politician and lawyer who served as the sixth governor of Arkansas from 1860 to 1862. Early life and education Henry Massie Rector was born in Louisville, Kentucky, the son of Fannie Bardella (Thruston) and Elias Rector. His Rector family descended from the German-speaking families of Germanna in the Colony of Virginia, though both parents were also of English descent. He was educated by his mother and attended two years of school in Louisville. He moved to Arkansas in 1835, where he was later appointed U.S. Marshal. Political career Rector was elected to the Arkansas Senate and served in that body from 1848 to 1850. He studied law and was admitted to the bar in 1854. From 1853 to 1857, he served as U.S. Surveyor-General of Arkansas for several years. From 1855 to 1859, he served in the Arkansas House of Representatives and spent one term as a justice of the Arkansas Supreme Court. Rector was elected Governo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Territory
The Indian Territory and the Indian Territories are terms that generally described an evolving land area set aside by the Federal government of the United States, United States Government for the relocation of Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans who held aboriginal title to their land as a sovereign independent state. In general, the tribes ceded land they occupied in exchange for Land grant#United States, land grants in 1803. The concept of an Indian Territory was an outcome of the US federal government's 18th- and 19th-century policy of Indian removal. After the Indian Territory in the American Civil War, American Civil War (1861–1865), the policy of the US government was one of Cultural assimilation of Native Americans#Americanization and assimilation (1857–1920), assimilation. The term ''Indian Reserve (1763), Indian Reserve'' describes lands the Kingdom of Great Britain, British set aside for Indigenous tribes between the Appalachian Mountains and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Sevier Conway
James Sevier Conway (December 9, 1796 – March 3, 1855) was an American politician who served as the first governor of Arkansas from 1836 to 1840. Early life James Sevier Conway was born on December 4, 1796, in Greene County, Tennessee, to Thomas and Ann ( Rector) Conway. Conway's father was born in Pittsylvania County, Virginia, in 1771. His paternal ancestors originated in Conwy, Wales. Thomas employed private tutors to teach his seven sons and three daughters. In 1818, the family moved to St. Louis, where Conway learned the art of land surveying from his uncle William Rector, surveyor-general in Illinois, Missouri, and Arkansas. In 1820, Conway resigned a Cole County, Missouri, circuit clerk's position to serve as deputy-surveyor in the newly established Arkansas Territory, where he purchased a tract of land in Hempstead (present-day Lafayette) County. While living there, Conway met Mary Jane Bradley, who had migrated with her family from Wilson County, Tennessee. They wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The MacArthur Museum Of Arkansas Military History
The Tower Building of the Little Rock Arsenal, also known as the Main Building of the U.S. Arsenal at Little Rock, or Headquarters Building of the Little Rock Barracks, is the home of the MacArthur Museum of Arkansas Military History. It is also a part of the MacArthur Park Historic District, in Little Rock, Arkansas. Built between 1840 and 1841, it was part of Little Rock's first U.S. military installation. Since decommissioning, the building has housed two local museums. It was home to the Arkansas Museum of Natural History and Antiquities from 1942 to 1997 and the MacArthur Museum of Arkansas Military History since 2001. It has also housed the Little Rock Æsthetic Club since 1894. The building receives its name from its distinct octagonal tower. Besides being the last remaining structure of the original U.S. military installation and one of the oldest buildings in central Arkansas, it was also the birthplace of General Douglas MacArthur, who became the supreme commander of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |