|
The History Of A Book
''The History of a Book'' is an 1873 novel by Annie Carey. The novel is an it-narrative following the experiences of a copy of ''Robinson Crusoe, The Life and Adventures of Robinson Crusoe''. It was received favorably by the British literary press. Background and publication ''The History of a Book'' was written by Annie Carey and published in 1873 by Cassell (publisher), Cassell, Petter & Galpin in London. Carey was an author of the it-narrative, a genre of Victorian literature giving the stories of objects; she earlier wrote ''Autobiography of a Lump of Coal; A Grain of Salt; A Drop of Water; A Bit of Old Iron; and A Piece of Old Flint'' (1870). Carey's novel follows a copy of ''Robinson Crusoe, The Life and Adventures of Robinson Crusoe'' as it is being made. The New Book is left at an auction house, and the other books fail to respect him; once they learn that the New Book is ''Robinson Crusoe'', they respect him and label him "Daniel Defoe, Defoe Senior". In Carey's time, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
It-narrative
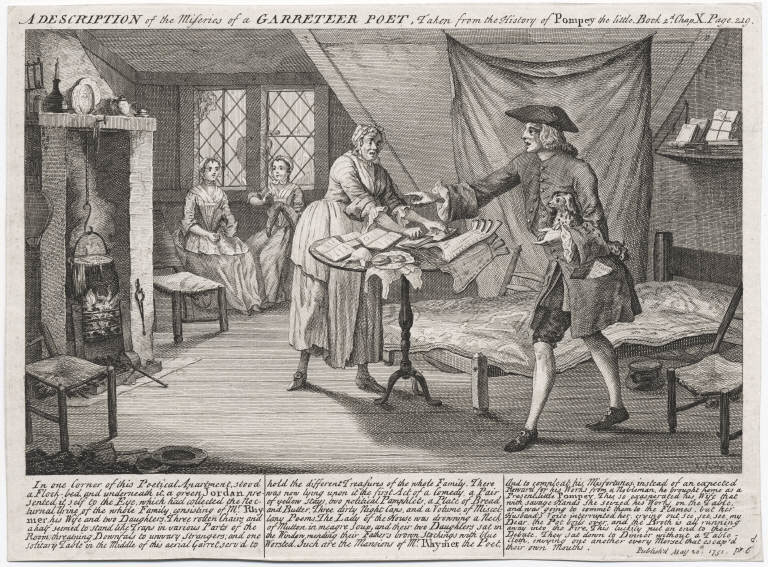
The novel of circulation, otherwise known as the it-narrative, or object narrative, is a genre of novel common at one time in British literature, and follows the fortunes of an object, for example a coin, that is passed around between different owners. Sometimes, instead, it involves a pet or other domestic animal, as for example in Francis Coventry's ''The History of Pompey the Little'' (1751). This and other such works blended satire with the interest for contemporary readers of a ''roman à clef''. They also use objects such as hackney-carriages and bank-notes to interrogate what it meant to live in an increasingly mobile society, and to consider the effect of circulation on human relations. Examples *1709 Charles Gildon, ''The Golden Spy'' has been regarded by modern scholars as "the first, fully-fledged it-narrative in English". But for his contemporaries, it tends to be read as "a Menippean satire, a re-adaptation of Apuleius's ''The Golden Ass'' and a sequel to ''The New Met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Walter (editor, Born 1776)
John Walter (23 February 1776 – 28 July 1847) was an English newspaper editor and politician. He was the son of John Walter, the founder of ''The Times'', and succeeded his father as the newspaper's second editor. Biography Walter was educated at Merchant Taylors' School and Trinity College, Oxford. About 1798 he was associated with his elder brother in the management of his father's business, and in 1803 became not only sole manager, but also editor of ''The Times''. Walter expressed his opposition to the administration of William Pitt the Younger, which cost him government advertisements and the loss of his appointment as printer to the Customs. It also brought the hostility of officials. When the King of Portugal sent him, via the Portuguese ambassador, a service of gold plate, he returned it. Walter insisted on the anonymity of those whom he hired. From about 1810, he delegated to others editorial supervision, first to Sir John Stoddart, then to Thomas Barnes, and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Children's Novels
Children's literature or juvenile literature includes stories, books, magazines, and poems that are created for children. Modern children's literature is classified in two different ways: genre or the intended age of the reader. Children's literature can be traced to traditional stories like fairy tales, that have only been identified as children's literature in the eighteenth century, and songs, part of a wider oral tradition, that adults shared with children before publishing existed. The development of early children's literature, before printing was invented, is difficult to trace. Even after printing became widespread, many classic "children's" tales were originally created for adults and later adapted for a younger audience. Since the fifteenth century much literature has been aimed specifically at children, often with a moral or religious message. Children's literature has been shaped by religious sources, like Puritan traditions, or by more philosophical and scientifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1873 Novels
Events January–March * January 1 ** Japan adopts the Gregorian calendar. ** The California Penal Code goes into effect. * January 17 – American Indian Wars: Modoc War: First Battle of the Stronghold – Modoc Indians defeat the United States Army. * February 11 – The Spanish Cortes deposes King Amadeus I, and proclaims the First Spanish Republic. * February 12 ** Emilio Castelar, the former foreign minister, becomes prime minister of the new Spanish Republic. ** The Coinage Act of 1873 in the United States is signed into law by President Ulysses S. Grant; coming into effect on April 1, it ends bimetallism in the U.S., and places the country on the gold standard. * February 20 ** The University of California opens its first medical school in San Francisco. ** British naval officer John Moresby discovers the site of Port Moresby, and claims the land for Britain. * March 3 – Censorship: The United States Congress enacts the Comsto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Representations
''Representations'' is an interdisciplinary journal in the humanities published quarterly by the University of California Press. The journal was established in 1983 and is the founding publication of the New Historicism movement of the 1980s. It covers topics including literary, historical, and cultural studies. The founding editorial board was chaired by Stephen Greenblatt and Svetlana Alpers. ''Representations'' frequently publishes thematic special issues, for example, the 2007 issue on the legacies of American Orientalism, the 2006 issue on cross-cultural mimesis Mimesis (; grc, μίμησις, ''mīmēsis'') is a term used in literary criticism and philosophy that carries a wide range of meanings, including ''imitatio'', imitation, nonsensuous similarity, receptivity, representation, mimicry, the act ..., and the 2005 issue on political and intellectual redress. Topics covered * The Body, Gender, and Sexuality * Culture and Law * Empire, Imperialism, and The New Worl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princeton University Press
Princeton University Press is an independent publisher with close connections to Princeton University. Its mission is to disseminate scholarship within academia and society at large. The press was founded by Whitney Darrow, with the financial support of Charles Scribner, as a printing press to serve the Princeton community in 1905. Its distinctive building was constructed in 1911 on William Street in Princeton. Its first book was a new 1912 edition of John Witherspoon's ''Lectures on Moral Philosophy.'' History Princeton University Press was founded in 1905 by a recent Princeton graduate, Whitney Darrow, with financial support from another Princetonian, Charles Scribner II. Darrow and Scribner purchased the equipment and assumed the operations of two already existing local publishers, that of the ''Princeton Alumni Weekly'' and the Princeton Press. The new press printed both local newspapers, university documents, ''The Daily Princetonian'', and later added book publishing to it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Victorian Culture
The ''Journal of Victorian Culture'' is a quarterly academic journal of cultural history. Established in 1996 and published by Oxford University Press, it tries to promote the best work on all aspects of nineteenth-century society, culture, and the material world including: literature, art, performance, politics, science, medicine, technology, lived experience, and ideas. The journal welcomes submissions which address a broad Victorian era, Victorian studies readership and explore new questions and approaches. Concerned with the long nineteenth century, its legacies, and echoes in the present day, the journal encourages articles which interrogate periodization, historiography and critical traditions. The ''Journal of Victorian Culture's'' editors are Trev Broughton (University of York), Nancy Henry (University of Tennessee, Knoxville), Alastair Owens (Queen Mary University of London), and Jane Hamlett (Royal Holloway, University of London). The ''Journal of Victorian Culture'' is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheffield Daily Telegraph
The ''Sheffield Telegraph'' is a weekly newspaper published in Sheffield, England. Founded in 1855 as the ''Sheffield Daily Telegraph'', it became known as the ''Sheffield Telegraph'' in 1938. History The ''Sheffield Telegraph'' was founded in 1855 as the ''Sheffield Daily Telegraph''. It was the city's first daily newspaper, published at 08:00 each morning. The newspaper struggled until W. C. Leng became editor in 1864, moving the business to Aldine Court, introducing Linotype printing and using it to support the Conservative Party. After taking over the ''Sheffield and Rotherham Independent'' in 1938, it dropped the "Daily" from its name. The history of Sheffield's "Telegraph" is intertwined with that of ''The Star'' and the ''Green Un''. All three newspapers are published today by Johnston Press PLC. As has been the case for its sister publications, the ''Telegraph'' has undergone several name changes during its history. The ''Sheffield Daily Telegraph'' was first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippolyte Auguste Marinoni
Hippolyte Auguste Marinoni (1823, Paris – 7 January 1904, Paris) was a builder of rotary printing presses; most of which used the rotogravure process. He was also a media patron and owned several periodicals; notably '' Le Petit Journal''. His is considered to be one of the first to apply modern printing technology to mass-produced publications. Biography His father was originally from Brescia and had served as a dragoon in the Napoleonic armies. At the time of his birth, his father was serving as a brigadier in the National Gendarmerie of Paris, and he was born in the barracks of at the Barrière d’Enfer. After his father's death in 1830, he was apprenticed to a turner mechanic. In 1837, aged only fourteen, he received a patent on a device for husking rice and cottonseeds. The following year, he found employment at the firm of Pierre-Alexandre Gaveaux (1782–1844); a manufacturer of printing equipment. In 1847, he built his first press with two cylinders, dubbed "The Jet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gutenberg Press
A printing press is a mechanical device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a print medium (such as paper or cloth), thereby transferring the ink. It marked a dramatic improvement on earlier printing methods in which the cloth, paper or other medium was brushed or rubbed repeatedly to achieve the transfer of ink, and accelerated the process. Typically used for texts, the invention and global spread of the printing press was one of the most influential events in the second millennium. In Germany, around 1440, goldsmith Johannes Gutenberg invented the movable-type printing press, which started the Printing Revolution. Modelled on the design of existing screw presses, a single Renaissance movable-type printing press could produce up to 3,600 pages per workday, compared to forty by hand-printing and a few by hand-copying. Gutenberg's newly devised hand mould made possible the precise and rapid creation of metal movable type in large quantities. His two invent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robinson Crusoe
''Robinson Crusoe'' () is a novel by Daniel Defoe, first published on 25 April 1719. The first edition credited the work's protagonist Robinson Crusoe as its author, leading many readers to believe he was a real person and the book a travelogue of true incidents. Epistolary, confessional, and didactic in form, the book is presented as an autobiography of the title character (whose birth name is Robinson Kreutznaer) – a castaway who spends 28 years on a remote tropical desert island near the coasts of Venezuela and Trinidad, roughly resembling Tobago, encountering cannibals, captives, and mutineers before being rescued. The story has been thought to be based on the life of Alexander Selkirk, a Scottish castaway who lived for four years on a Pacific island called "Más a Tierra" (now part of Chile) which was renamed Robinson Crusoe Island in 1966. Despite its simple narrative style, ''Robinson Crusoe'' was well received in the literary world and is often credited as ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Printing Press
A printing press is a mechanical device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a printing, print medium (such as paper or cloth), thereby transferring the ink. It marked a dramatic improvement on earlier printing methods in which the cloth, paper or other medium was brushed or rubbed repeatedly to achieve the transfer of ink, and accelerated the process. Typically used for texts, the invention and global spread of the printing press was one of the most influential events in the second millennium. In Germany, around 1440, goldsmith Johannes Gutenberg invented the movable-type printing press, which started the Printing Revolution. Modelled on the design of existing screw presses, a single Renaissance movable-type printing press could produce up to 3,600 pages per workday, compared to forty by History of typography in East Asia, hand-printing and a few by scribe, hand-copying. Gutenberg's newly devised matrix (printing), hand mould made possible the precise and ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)





