|
The Fur Trade At Lachine National Historic Site
The Fur Trade at Lachine National Historic Site (''Lieu historique national de la Commerce-de-la-Fourrure-à-Lachine'') is a historic building located in the borough of Lachine in Montreal, Quebec, Canada, at the western end of the Lachine Canal. It is a National Historic Site of Canada. Beginning in the 17th century, voyageurs would launch their canoes from this location to transport trade goods thousands of miles into the interior of North America lands. At that time the Lachine Rapids prevented large ships from going any further west along the Saint Lawrence River. A stone warehouse was erected in 1803 to store the furs gathered as a result of fur trade. It is now a Parks Canada museum dedicated to the history of this strategic location as a departure and arrival point for fur trading expeditions. The site is separate from Lachine Canal National Historic Site, with which it is inextricably connected. Montreal was the start of nearly all westward canoe routes. See Canadian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lachine Canal
The Lachine Canal ( in French (language), French) is a canal passing through the southwestern part of the Island of Montreal, Quebec, Canada, running 14.5 kilometres (9 miles) from the Old Port of Montreal to Lake Saint-Louis, through the boroughs of Lachine (borough), Lachine, LaSalle, Quebec, Lasalle and Le Sud-Ouest, Sud-Ouest. Before the canal construction there was a lake, Lac St. Pierre or or Petit Lac St. Pierre. The lake and its rivers can be seen on the maps of Montreal of the years 1700, 1744 and on the map titled "The isles of Montreal. As they have been surveyed by the French engineers" (1761). The lake is now filled in and located near the Turcot Interchange on Autoroute 20. The canal gets its name from the French word for China (). The European explorers sought to find a route from New France to the Western Sea, and from there to China and hence auspiciously the region where the canal was built was named Lachine. Due to the continuous disposal of industrial wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montreal Island
The Island of Montreal (french: Île de Montréal) is a large island in southwestern Quebec, Canada, that is the site of a number of municipalities including most of the city of Montreal and is the most populous island in Canada. It is the main island of the Hochelaga Archipelago at the confluence of the Saint Lawrence and Ottawa rivers. Name The first French name for the island was ''l'ille de Vilmenon'', noted by Samuel de Champlain in a 1616 map, and derived from the sieur de Vilmenon, a patron of the founders of Quebec at the court of Louis XIII. However, by 1632 Champlain referred to the ''Isle de Mont-real'' in another map. The island derived its name from Mount Royal ( French ''Mont Royal'', then pronounced ), and gradually spread its name to the town, which had originally been called Ville-Marie. In Kanien’kéha, the island is called Tiohtià:ke tsi ionhwéntsare ('broken in two', referring to the Lachine Rapids to the island's southwest) or Otsirà:ke (meaning ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
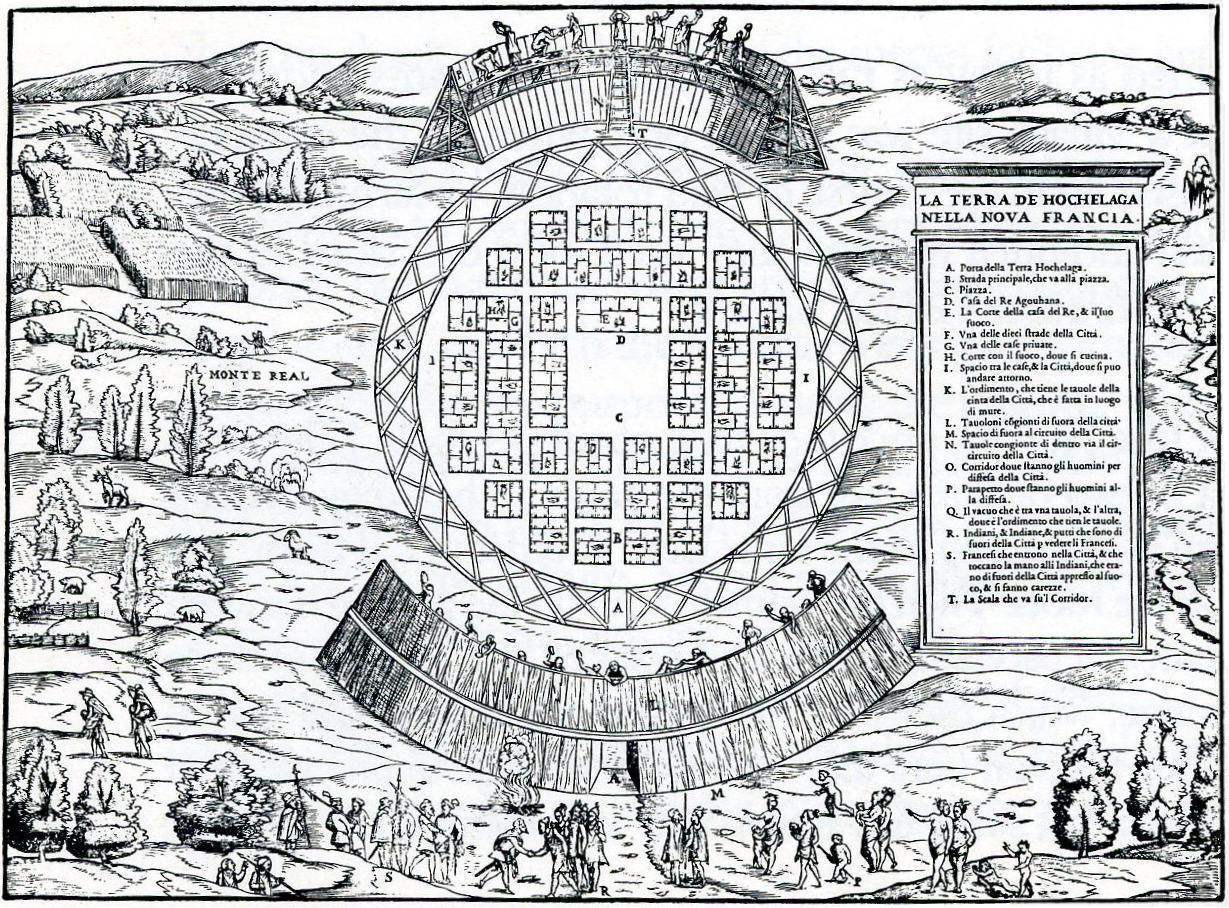
History Of Montreal
The history of the area around what is now known as Montreal, Montreal itself was established in 1642, located in what is now known as the province of Quebec, Canada, spans about 8,000 years. At the time of European contact, the area was inhabited by the St. Lawrence Iroquoians, a discrete and distinct group of Iroquoian-speaking indigenous people. They spoke Laurentian. Jacques Cartier became the first European to reach the area now known as Montreal in 1535 when he entered the village of '' Hochelaga'' on the Island of Montreal while in search of a passage to Asia during the Age of Exploration. Seventy years later, Samuel de Champlain unsuccessfully tried to create a fur trading post but the Mohawk of the Iroquois defended what they had been using as their hunting grounds. A fortress named Ville Marie was built in 1642 as part of a project to create a French colonial empire. Ville Marie became a centre for the fur trade and French expansion into New France until 1760, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Museums In Montreal
Montreal was referred to as "''Canada's Cultural Capital''" by Monocle Magazine. The city is Canada's centre for French-language television productions, radio, theatre, film, multimedia, and print publishing. The ''Quartier Latin'' is a neighbourhood crowded with cafés animated by this literary and musical activity. Montreal's many cultural communities have given it a distinct local culture. As a North American city, Montreal shares many of the cultural features characteristic of the other metropolis on the continent, including representations in all traditional manifestations of high culture, a long-lasting tradition of jazz and rock music, and tentative experimentation in visual arts, theatre, music, and dance. Yet, being at the confluence of the French and the English traditions, Montreal has developed a unique and distinguished cultural face in the world. Another distinctive characteristic of Montreal culture life is to be found in the animation of its downtown, particularly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fur Trade
The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur. Since the establishment of a world fur market in the early modern period, furs of boreal, polar and cold temperate mammalian animals have been the most valued. Historically the trade stimulated the exploration and colonization of Siberia, northern North America, and the South Shetland and South Sandwich Islands. Today the importance of the fur trade has diminished; it is based on pelts produced at fur farms and regulated fur-bearer trapping, but has become controversial. Animal rights organizations oppose the fur trade, citing that animals are brutally killed and sometimes skinned alive. Fur has been replaced in some clothing by synthetic imitations, for example, as in ruffs on hoods of parkas. Continental fur trade Russian fur trade Before the European colonization of the Americas, Russia was a major supplier of fur pelts to Western Europe and parts of Asia. Its trade developed in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Museums In Quebec
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well as the memory, discovery, collection, organization, presentation, and interpretation of these events. Historians seek knowledge of the past using historical sources such as written documents, oral accounts, art and material artifacts, and ecological markers. History is not complete and still has debatable mysteries. History is also an academic discipline which uses narrative to describe, examine, question, and analyze past events, and investigate their patterns of cause and effect. Historians often debate which narrative best explains an event, as well as the significance of different causes and effects. Historians also debate the nature of history as an end in itself, as well as its usefulness to give perspective on the problems of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virtual Museum Of Canada
The Digital Museums Canada (DMC; , ''MNC'') is a funding program in Canada "dedicated to online projects by the museum and heritage community," helping organizations to build digital capacity. Administered by the Canadian Museum of History (CMH) with the financial support of the Government of Canada, DMC provides investments of CA$15,000 to $250,000 for audience-engaging online projects by Canadian museums and heritage organizations. As of 2021, Digital Museums Canada took the place of the Virtual Museum of Canada (VMC), a national virtual museum. With a directory of over 3,000 Canadian heritage institutions and a database of over 600 virtual exhibits, VMC's site was scheduled to discontinue hosting exhibits after 30 June 2021. Virtual Museum of Canada Virtual Museum of Canada (VMC) was a national virtual museum that was replaced by Digital Museums Canada as of 2021. VMC was administered by the Canadian Museum of History (CMH), and its content was created by Canadian museums. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Heritage Information Network
, nativename_a = , nativename_r = , logo = Logo of Canadian Heritage Information Network.png , logo_caption = , seal = , seal_width = , seal_caption = , picture = , picture_width = , picture_caption = , formed = , preceding1 = National Inventory Programme , preceding2 = , dissolved = , superseding = , jurisdiction = , headquarters = 1030 Innes Road Ottawa, Ontario , coordinates = , motto = , employees = , budget = $2.76 m CAD (2017-18)http://publications.gc.ca/collections/collection_2020/pch/CH57-1-2-2018-eng.pdf , minister1_name = , minister1_pfo = , minister2_name = , minister2_pfo = , deputyminister1_name = , deputyminister1_pfo = , deputyminister2_name = , deputyminister2_pfo = , chief1_name = Jérôme Moisan , chief1_position = Director General of Heritage Group , chief2_name = , chief2_position = , chief3_name = , chief3_position = , chief4_name = , chief4_position = , chief5_name = , chief5_position = , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Museums Association
The Canadian Museums Association (CMA; french: Association des musées canadiens, ''ACM''), is a national non-profit organization for the promotion of museums in Canada. It represents Canadian museum professionals both within Canada and internationally. As with most trade associations, it aims to improve the recognition, growth and stability of its constituency. Its staff supports their nearly 2,000 members with conferences, publications, and networking opportunities. CMA members include national museums, non-profit museums, art galleries, science centres, aquariums, archives, sport halls-of-fame, artist-run centres, zoos and historic sites across Canada. They range from large metropolitan galleries to small community museums. All are dedicated to preserving and presenting Canada's cultural heritage to the public. History In 1932, British Museums Association President Sir Henry Miers visited museums in Canada and found them "in a deplorable state and far behind those of the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Simpson (administrator)
Sir George Simpson ( – 7 September 1860) was a Scottish explorer and colonial governor of the Hudson's Bay Company during the period of its greatest power. From 1820 to 1860, he was in practice, if not in law, the British viceroy for the whole of Rupert's Land, an enormous territory of 3.9 millions square kilometers in northern North America. His efficient administration of the west was a precondition for the confederation of western and eastern Canada. He was noted for his grasp of administrative detail and his physical stamina in traveling through the wilderness. Excepting voyageurs and their Siberian equivalents, few men have spent as much time traveling in the wilderness. Simpson was the first person known to have circumnavigated the world by land. Early life Born at Dingwall, Ross-Shire, Scotland, as the illegitimate son of George Simpson, Writer to the Signet, he was raised by two aunts and his paternal grandmother, Isobel Simpson (1731–1821), daughter of George M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
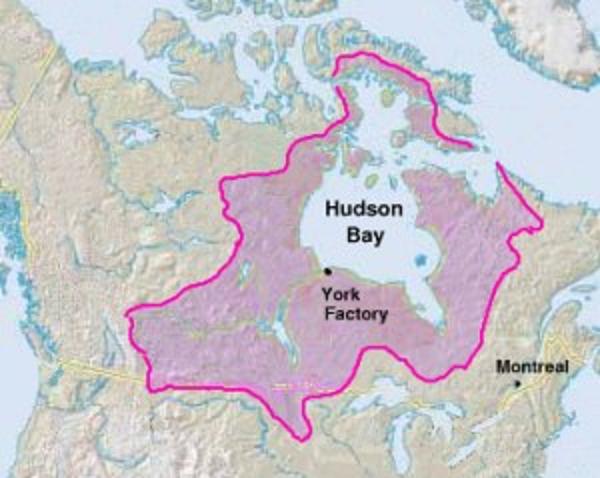
Northwest Company
The North West Company was a fur trading business headquartered in Montreal from 1779 to 1821. It competed with increasing success against the Hudson's Bay Company in what is present-day Western Canada and Northwestern Ontario. With great wealth at stake, tensions between the companies increased to the point where several minor armed skirmishes broke out, and the two companies were forced by the Government of the United Kingdom, British government to merge. Before the Company After the French landed in Quebec in 1608, spread out and built a fur trade empire in the St. Lawrence basin. The French competed with the Dutch (from 1614) and English (1664) in New York and the English in Hudson Bay (1670). Unlike the French who travelled into the northern interior and traded with First Nations in their camps and villages, the English made bases at trading posts on Hudson Bay, inviting the indigenous people to trade. After 1731, pushed trade west beyond Lake Winnipeg. After the British ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Canoe Routes (early)
This article covers the water based Canadian canoe routes used by early explorers of Canada with special emphasis on the fur trade. Introduction European exploration of Canada was principally by river. The land has many navigable rivers with short portages between them. There are no serious barriers to water-borne travel east of the Rockies. The fur trade, principally in beaver, drove and financed exploration and initial settlement. Traders obtained furs from the natives and exported them to Europe. Canada and Siberia Both Canada and Siberia are largely covered by Boreal Forest. Both were opened up by water-borne fur traders. In both countries the problem was to find streams that flowed in approximately the right direction and to find short portages to move from one river basin to the next. Both regions are flat. One can move from the Saint Lawrence to the Rockies or from the Urals almost to the Pacific with only a few short portages. In both countries furs were obtained by n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)