|
The Enemies Of Promise
''Enemies of Promise'' is a critical and autobiographical work written by Cyril Connolly first published in 1938. It comprises three parts, the first dedicated to Connolly's observations about English literature and the English literary world of his time, the second a list of adverse elements that affect the ability to be a good writer and the last an account of Connolly's early life. The overarching theme of the book is the search for understanding why Connolly, though he was widely recognised as a leading man of letters and a highly distinguished critic, failed to produce a major work of literature. Part 1 "Predicament" This part consists of an erudite discussion of literary styles, with Connolly posing the question of what the following ten years would bring in the world of literature and what sort of writing would last. He summarises the two main styles as follows: :"We have seen that there are two styles which it is convenient to describe as the realist, or vernacular, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyril Connolly
Cyril Vernon Connolly CBE (10 September 1903 – 26 November 1974) was an English literary critic and writer. He was the editor of the influential literary magazine ''Horizon'' (1940–49) and wrote '' Enemies of Promise'' (1938), which combined literary criticism with an autobiographical exploration of why he failed to become the successful author of fiction that he had aspired to be in his youth. Early life Cyril Connolly was born in Coventry, Warwickshire, the only child of Major Matthew William Kemble Connolly (1872–1947), an officer in the King's Own Yorkshire Light Infantry, by his Anglo-Irish wife, Muriel Maud Vernon, daughter of Colonel Edward Vernon (1838–1913) J.P., D.L., of Clontarf Castle, Co. Dublin. His parents had met while his father was serving in Ireland, and his father's next posting was to South Africa.Jeremy Lewis, ''Cyril Connolly: A Life'', Jonathan Cape, 1997. Connolly's father was also a malacologist (the scientific study of the Mollusca, i.e. sna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malva
''Malva'' is a genus of herbaceous annual, biennial, and perennial plants in the family Malvaceae. It is one of several closely related genera in the family to bear the common English name mallow. The genus is widespread throughout the temperate, subtropical and tropical regions of Africa, Asia and Europe. The leaves are alternate, palmately lobed. The flowers are from 0.5–5 cm diameter, with five pink, lilac, purple or white petals. Etymology The word "mallow" is derived from Old English "mealwe", which was imported from Latin "malva", cognate with Ancient Greek μαλάχη (malakhē) meaning "mallow", both perhaps reflecting a Mediterranean term. The colour mauve was in 1859 named after the French name for this plant. Uses Ornamental plant Several species are widely grown as garden flowers. Very easily grown, short-lived perennials are often grown as ornamental plants. Food Many species are edible as leaf vegetables and commonly foraged in the West. Known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alec Douglas-Home
Alexander Frederick Douglas-Home, Baron Home of the Hirsel (; 2 July 1903 – 9 October 1995), styled as Lord Dunglass between 1918 and 1951 and being The 14th Earl of Home from 1951 till 1963, was a British Conservative politician who served as Prime Minister from October 1963 to October 1964. He is notable for being the last Prime Minister to hold office while being a member of the House of Lords, before renouncing his peerage and taking up a seat in the House of Commons for the remainder of his premiership. His reputation, however, rests more on his two spells as the UK's foreign secretary than on his brief premiership. Within six years of first entering the House of Commons in 1931, Douglas-Home (then called by the courtesy title Lord Dunglass) became parliamentary aide to Neville Chamberlain, witnessing at first hand Chamberlain's efforts as Prime Minister to preserve peace through appeasement in the two years before the outbreak of the Second World War. In 1940 D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winthrop Mackworth Praed
Winthrop Mackworth Praed (28 July 180215 July 1839)—typically written as W. Mackworth Praed—was an English politician and poet. Life Early life Praed was born in London, United Kingdom. The family name of Praed was derived from the marriage of the poet's great-grandfather to a Cornish heiress. Winthrop's father, William Mackworth Praed, was a serjeant-at-law (1756–1835) and revising barrister for Bath. His mother belonged to the English branch of the New England family of Winthrop. In 1814 Praed was sent to Eton College, where he founded a manuscript periodical called ''Apis matina''. This was succeeded in October 1820 by the ''Etonian'', a paper projected and edited by Praed and Walter Blount, which appeared every month until July 1821, when the chief editor, who signed his contributions "Peregrine Courtenay," left Eton, and the paper died. Henry Nelson Coleridge, William Sidney Walker, and John Moultrie were the three best known of his collaborators on this peri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyril Alington
Cyril Argentine Alington (22 October 1872 – 16 May 1955) was an English educationalist, scholar, cleric, and author. He was successively the headmaster of Shrewsbury School and Eton College. He also served as chaplain to King George V and as Dean of Durham. Early life Dr Alington was the second son of the Rev. Henry Giles Alington, an inspector of schools, and his wife Jane Margaret Booth (d. 1910), daughter of Rev. Thomas Willingham Booth. His father came from a long line of clerics, a branch of the landed gentry Alington family of Little Barford Manor House, St Neots, Huntingdonshire, and was descended from the Alingtons of Horseheath, an ancient Cambridgeshire family, from which also descended the Barons Alington. He was educated at Marlborough College and Trinity College, Oxford. He gained a First in Classical Moderations (Latin and Greek) in 1893 and a First in Literae Humaniores (Philosophy and Ancient History) in 1895. He was elected a Fellow of All Souls College, O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dadie Rylands
George Humphrey Wolferstan Rylands (23 October 1902 – 16 January 1999), known as Dadie Rylands, was a British literary scholar and theatre director. Rylands was born at the Down House, Tockington, Gloucestershire, to Thomas Kirkland Rylands, a land agent, and Bertha Nisbet Wolferstan (née Thomas). His grandfather was the Liberal politician Peter Rylands. Educated at Eton College and King's College, Cambridge, he was a Fellow of King's from 1927 until his death. While at Cambridge, he became a friend of John Maynard Keynes, also a student and Fellow at King’s. He also befriended Cecil Beaton there. As well as studying Shakespeare, he was actively involved in the theatre. He directed and acted in many productions for The Marlowe Society, and was chairman of the Cambridge Arts Theatre from 1946 to 1982. Rylands' 1939 Shakespeare anthology ''Ages of Man'' was the basis of John Gielgud's Ages of Man (play), one-man show of the same title. Though Rylands specialised in di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North-West Frontier Province (1901–1955)
The North-West Frontier Province (NWFP; ps, شمال لویدیځ سرحدي ولایت, ) was a Chief Commissioner's Province of British India, established on 9 November 1901 from the north-western districts of the Punjab Province. Following the referendum in 1947 to join either Pakistan or India, the province voted hugely in favour of joining Pakistan and it acceded accordingly on 14th August, 1947. It was dissolved to form a unified province of West Pakistan in 1955 upon creation of One Unit Scheme and was re-established in 1970. It was known by this name until 19 April 2010, when it was redesignated as the province of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa following the passing of the Eighteenth Amendment to the Constitution of Pakistan by erstwhile President of Pakistan, President Asif Ali Zardari. The province covered an area of , including much of the current Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province but excluding the Federally Administered Tribal Areas and the former princely states of Amb (princely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria Cross
The Victoria Cross (VC) is the highest and most prestigious award of the British honours system. It is awarded for valour "in the presence of the enemy" to members of the British Armed Forces and may be awarded posthumously. It was previously awarded by countries of the Commonwealth of Nations, most of which have established their own honours systems and no longer recommend British honours. It may be awarded to a person of any military rank in any service and to civilians under military command. No civilian has received the award since 1879. Since the first awards were presented by Queen Victoria in 1857, two-thirds of all awards have been personally presented by the British monarch. The investitures are usually held at Buckingham Palace. The VC was introduced on 29 January 1856 by Queen Victoria to honour acts of valour during the Crimean War. Since then, the medal has been awarded 1,358 times to 1,355 individual recipients. Only 15 medals, of which 11 to members of the Britis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Godfrey Meynell
Godfrey Meynell VC, MC (20 May 1904 – 29 September 1935) was a British Indian Army officer and an English recipient of the Victoria Cross, the highest and most prestigious award for gallantry in the face of the enemy that can be awarded to British and Commonwealth forces. Early life and education Meynell was the son of an army officer who was also named Godfrey Meynell, by his wife Edith Violet Cammell. He won a scholarship to Eton College. He was commended to Cyril Connolly when he arrived there as a boy with character. After an initial amount of bullying, (from Godfrey to Cecil) the two became firm friends as described in ''Enemies of Promise''. Military career Meynell had graduated 13th at Sandhurst before he volunteered for the British Indian Army. He was awarded the Military Cross in 1933 for his work in Chitral. Victoria Cross Meynell was thirty-one years old, and a captain in the 5th Battalion ( Queen Victoria's Own Corps of Guides), 12th Frontier Force Regiment duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cecil Beaton
Sir Cecil Walter Hardy Beaton, (14 January 1904 – 18 January 1980) was a British fashion, portrait and war photographer, diarist, painter, and interior designer, as well as an Oscar–winning stage and costume designer for films and the theatre. Early life and education Beaton was born on 14 January 1904 in Hampstead, north London, the son of Ernest Walter Hardy Beaton (1867–1936), a prosperous timber merchant, and his wife, Esther "Etty" Sisson (1872–1962). His grandfather, Walter Hardy Beaton (1841–1904), had founded the family business of "Beaton Brothers Timber Merchants and Agents", and his father followed into the business. Ernest Beaton was an amateur actor and met his wife, Cecil's mother Esther ("Etty"), when playing the lead in a play. She was the daughter of a Cumbrian blacksmith named Joseph Sisson and had come to London to visit her married sister. Ernest and Etty Beaton had four children – Cecil; two daughters, Nancy Elizabeth Louise Hardy Beaton (190 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Cyprian's School
St Cyprian's School was an English preparatory school for boys, which operated in the early 20th century in Eastbourne, East Sussex. Like other preparatory schools, its purpose was to train pupils to do well enough in the examinations (usually taken around the age of 13) to gain admission to leading public schools, and to provide an introduction to boarding school life. History St Cyprian's was founded in 1899 by Lewis Vaughan Wilkes and his wife Cicely Comyn, a newly married couple in their twenties. It originally operated in a large house in Carlisle Road, but by 1906 had grown sufficiently to move into new purpose-built facilities with extensive playing fields behind Summerdown Road. The school ran with the prevailing ethos of Muscular Christianity which had typified private education since the time of Thomas Arnold of Rugby, and placed much emphasis on developing self-reliance and integrity ("Character"). In these and many other respects St Cyprian's was little different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samite
Samite was a luxurious and heavy silk fabric worn in the Middle Ages, of a twill-type weave, often including gold or silver thread. The word was derived from Old French ''samit'', from medieval Latin ''samitum, examitum'' deriving from the Byzantine Greek ἑξάμιτον ''hexamiton'' "six threads", usually interpreted as indicating the use of six yarns in the warp. Samite is still used in ecclesiastical robes, vestments, ornamental fabrics, and interior decoration. Structurally, samite is a weft-faced compound twill, plain or figured (patterned), in which the main warp threads are hidden on both sides of the fabric by the floats of the ground and patterning wefts, with only the binding warps visible.Anna Muthesius, "Silk in the Medieval World". In David Jenkins, ed.: ''The Cambridge History of Western Textiles'', Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 2003, , p.343 By the later medieval period, the term ''samite'' was applied to any rich, heavy silk material which had a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

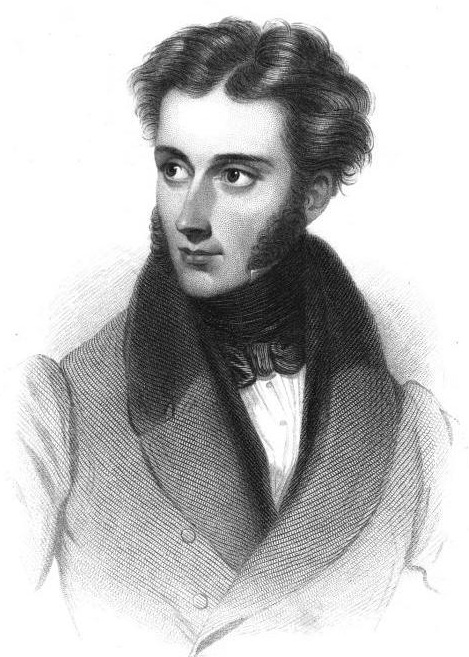


.jpg)