|
The Design Of Experiments
''The Design of Experiments'' is a 1935 book by the English statistician Ronald Fisher about the design of experiments and is considered a foundational work in experimental design. Among other contributions, the book introduced the concept of the null hypothesis in the context of the lady tasting tea experiment.OED, "null hypothesis," first usage: 1935 R. A. Fisher, ''The Design of Experiments'' ii. 19, "We may speak of this hypothesis as the 'null hypothesis'...the null hypothesis is never proved or established, but is possibly disproved, in the course of experimentation." A chapter is devoted to the Latin square. Chapters # Introduction # The principles of experimentation, illustrated by a psycho-physical experiment # A historical experiment on growth rate # An agricultural experiment in randomized blocks # The Latin square # The factorial design in experimentation # Confounding # Special cases of partial confounding # The increase of precision by concomitant measurements. Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ronald Fisher
Sir Ronald Aylmer Fisher (17 February 1890 – 29 July 1962) was a British polymath who was active as a mathematician, statistician, biologist, geneticist, and academic. For his work in statistics, he has been described as "a genius who almost single-handedly created the foundations for modern statistical science" and "the single most important figure in 20th century statistics". In genetics, Fisher was the one to most comprehensively combine the ideas of Gregor Mendel and Charles Darwin, as his work used mathematics to combine Mendelian genetics and natural selection; this contributed to the revival of Darwinism in the early 20th-century revision of the theory of evolution known as the Modern synthesis (20th century), modern synthesis. For his contributions to biology, Richard Dawkins declared Fisher to be the greatest of Darwin's successors. He is also considered one of the founding fathers of Neo-Darwinism. According to statistician Jeffrey T. Leek, Fisher is the most in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It shares Anglo-Scottish border, a land border with Scotland to the north and England–Wales border, another land border with Wales to the west, and is otherwise surrounded by the North Sea to the east, the English Channel to the south, the Celtic Sea to the south-west, and the Irish Sea to the west. Continental Europe lies to the south-east, and Ireland to the west. At the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 census, the population was 56,490,048. London is both List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, the largest city and the Capital city, capital. The area now called England was first inhabited by modern humans during the Upper Paleolithic. It takes its name from the Angles (tribe), Angles, a Germanic peoples, Germanic tribe who settled du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, industrial, or social problem, it is conventional to begin with a statistical population or a statistical model to be studied. Populations can be diverse groups of people or objects such as "all people living in a country" or "every atom composing a crystal". Statistics deals with every aspect of data, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of statistical survey, surveys and experimental design, experiments. When census data (comprising every member of the target population) cannot be collected, statisticians collect data by developing specific experiment designs and survey sample (statistics), samples. Representative sampling assures that inferences and conclusions can reasonably extend from the sample ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Design Of Experiments
The design of experiments (DOE), also known as experiment design or experimental design, is the design of any task that aims to describe and explain the variation of information under conditions that are hypothesized to reflect the variation. The term is generally associated with experiments in which the design introduces conditions that directly affect the variation, but may also refer to the design of quasi-experiments, in which natural conditions that influence the variation are selected for observation. In its simplest form, an experiment aims at predicting the outcome by introducing a change of the preconditions, which is represented by one or more independent variables, also referred to as "input variables" or "predictor variables." The change in one or more independent variables is generally hypothesized to result in a change in one or more dependent variables, also referred to as "output variables" or "response variables." The experimental design may also identify ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The American Statistician
''The American Statistician'' is a quarterly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering statistics published by Taylor & Francis on behalf of the American Statistical Association. It was established in 1947. The editor-in-chief An editor-in-chief (EIC), also known as lead editor or chief editor, is a publication's editorial leader who has final responsibility for its operations and policies. The editor-in-chief heads all departments of the organization and is held accoun ... is Daniel R. Jeske, a professor at the University of California, Riverside. External links * Taylor & Francis academic journals Statistics journals Academic journals established in 1947 English-language journals Quarterly journals 1947 establishments in the United States Academic journals associated with learned and professional societies of the United States {{statistics-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biometrics (journal)
''Biometrics'' is a journal that publishes articles on the application of statistics and mathematics to the biological sciences. It is published by the International Biometric Society (IBS).Biometrics homepage Originally published in 1945 under the title ''Biometrics Bulletin'', the journal adopted the shorter title in 1947. Biometrics, Vol. 3, No. 1, Mar., 1947 Page 53 /ref> A notable contributor to the journal was R.A. Fisher, for whom a memorial edition was published in 1964. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis (often denoted ''H''0) is the claim in scientific research that the effect being studied does not exist. The null hypothesis can also be described as the hypothesis in which no relationship exists between two sets of data or variables being analyzed. If the null hypothesis is true, any experimentally observed effect is due to chance alone, hence the term "null". In contrast with the null hypothesis, an alternative hypothesis (often denoted ''H''A or ''H''1) is developed, which claims that a relationship does exist between two variables. Basic definitions The null hypothesis and the ''alternative hypothesis'' are types of conjectures used in statistical tests to make statistical inferences, which are formal methods of reaching conclusions and separating scientific claims from statistical noise. The statement being tested in a test of statistical significance is called the null hypothesis. The test of significance is designed to assess the strength of the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lady Tasting Tea
In the design of experiments in statistics, the lady tasting tea is a randomized experiment devised by Ronald Fisher and reported in his book '' The Design of Experiments'' (1935). The experiment is the original exposition of Fisher's notion of a null hypothesis, which is "never proved or established, but is possibly disproved, in the course of experimentation".OED quote: 1935 R. A. Fisher, '' The Design of Experiments'' ii. 19, "We may speak of this hypothesis as the 'null hypothesis' ..the null hypothesis is never proved or established, but is possibly disproved, in the course of experimentation." The example is loosely based on an event in Fisher's life. The woman in question, phycologist Muriel Bristol, claimed to be able to tell whether the tea or the milk was added first to a cup. Her future husband, William Roach, suggested that Fisher give her eight cups, four of each variety, in random order. One could then ask what the probability was for her getting the specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Square
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion of the Roman Republic, it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. It has greatly influenced many languages, including English, having contributed many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin roots appear frequently in the technical vocabulary used by fields such as theology, the sciences, medicine, and law. By the late Roman Republic, Old Latin had evolved into standardized Classical Latin. Vulgar Latin refers to the less prestigious colloquial registers, attested in inscriptions and some literary works such as those of the comic playwrights Plautus and Terence and the author Petronius. Whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lady Tasting Tea
In the design of experiments in statistics, the lady tasting tea is a randomized experiment devised by Ronald Fisher and reported in his book '' The Design of Experiments'' (1935). The experiment is the original exposition of Fisher's notion of a null hypothesis, which is "never proved or established, but is possibly disproved, in the course of experimentation".OED quote: 1935 R. A. Fisher, '' The Design of Experiments'' ii. 19, "We may speak of this hypothesis as the 'null hypothesis' ..the null hypothesis is never proved or established, but is possibly disproved, in the course of experimentation." The example is loosely based on an event in Fisher's life. The woman in question, phycologist Muriel Bristol, claimed to be able to tell whether the tea or the milk was added first to a cup. Her future husband, William Roach, suggested that Fisher give her eight cups, four of each variety, in random order. One could then ask what the probability was for her getting the specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
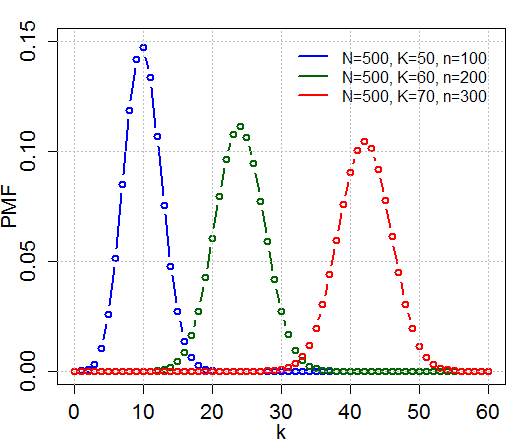
Hypergeometric Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the hypergeometric distribution is a Probability distribution#Discrete probability distribution, discrete probability distribution that describes the probability of k successes (random draws for which the object drawn has a specified feature) in n draws, ''without'' replacement, from a finite Statistical population, population of size N that contains exactly K objects with that feature, wherein each draw is either a success or a failure. In contrast, the binomial distribution describes the probability of k successes in n draws ''with'' replacement. Definitions Probability mass function The following conditions characterize the hypergeometric distribution: * The result of each draw (the elements of the population being sampled) can be classified into one of Binary variable, two mutually exclusive categories (e.g. Pass/Fail or Employed/Unemployed). * The probability of a success changes on each draw, as each draw decreases the population ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |