|
The Conquest Of Interplanetary Spaces
''The Conquest of Interplanetary Spaces'' is a science book by Soviet engineer and mathematician Yuri Kondratyuk published in 1929, significant for being one of the first documented proposals for lunar orbit rendezvous. History While working as a mechanic, Yuri Kondratyuk completed the manuscript of a book titled ''The Conquest of Interplanetary Spaces'', dealing with rocket motion and issues concerning the colonization of space. He also suggested using a gravitational slingshot trajectory to accelerate a spacecraft. In 1925, Kondratyuk made contact with Moscow-based scientist Vladimir Vetchinkin and sent him the manuscript. Up to that time, he and his work were unknown to rocketry enthusiasts. While the book was enthusiastically received by scientists in Moscow, no publisher would touch such a fanciful work. Eventually, Kondratyuk paid a Novosibirsk Siberian Union printing shop to produce 2,000 copies of the 72-page work, and even then had to do much of the typesetting and ope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuri Kondratyuk
Yuri Vasilyevich Kondratyuk (russian: Юрий Васильевич Кондратюк; ukr, Юрій Васильович Кондратюк; 21 June 1897 – February 1942), real name Aleksandr Ignatyevich Shargei (russian: Алекса́ндр Игна́тьевич Шарге́й; uk, Олександр Гнатович Шаргей) was a Soviet engineer and mathematician. He was a pioneer of astronautics and spaceflight, a theoretician and a visionary who, in the early 20th century, developed the first known lunar orbit rendezvous (LOR), a key concept for landing and return spaceflight from Earth to the Moon. The LOR was later used for the plotting of the first actual human spaceflight to the Moon. Many other aspects of spaceflight and space exploration are covered in his works. Kondratyuk made his scientific discoveries in circumstances of war (including both World Wars and the Russian Civil War), continuous persecutions from authorities and serious illnesses. In fact, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national republics; in practice, both its government and its economy were highly centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kiev (Ukrainian SSR), Minsk ( Byelorussian SSR), Tashkent (Uzbek SSR), Alma-Ata (Kazakh SSR), and Novosibirsk (Russian SFSR). It was the largest country in the world, covering over and spanning eleven time zones. The country's roots lay in the October Revolution of 1917, when the Bolsheviks, under the leadership of Vladimir Lenin, overthrew the Russian Provisional Government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Orbit Rendezvous
Lunar orbit rendezvous (LOR) is a process for landing humans on the Moon and returning them to Earth. It was utilized for the Apollo program missions in the 1960s and 1970s. In a LOR mission, a main spacecraft and a smaller lunar lander travel to lunar orbit. The lunar lander then independently descends to the surface of the Moon, while the main spacecraft remains in lunar orbit. After completion of the mission there, the lander returns to lunar orbit to rendezvous and re- dock with the main spacecraft, then is discarded after transfer of crew and payload. Only the main spacecraft returns to Earth. Lunar orbit rendezvous was first proposed in 1919 by Ukrainian engineer Yuri Kondratyuk, as the most economical way of sending a human on a round-trip journey to the Moon. The most famous example involved Project Apollo's command and service module (CSM) and lunar module (LM), where they were both sent to a translunar flight in a single rocket stack. However, variants where the land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocket
A rocket (from it, rocchetto, , bobbin/spool) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using the surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely from propellant carried within the vehicle; therefore a rocket can fly in the vacuum of space. Rockets work more efficiently in a vacuum and incur a loss of thrust due to the opposing pressure of the atmosphere. Multistage rockets are capable of attaining escape velocity from Earth and therefore can achieve unlimited maximum altitude. Compared with airbreathing engines, rockets are lightweight and powerful and capable of generating large accelerations. To control their flight, rockets rely on momentum, airfoils, auxiliary reaction engines, gimballed thrust, momentum wheels, deflection of the exhaust stream, propellant flow, spin, or gravity. Rockets for military and recreational uses date back to at least 13th-century China. Signific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Colonization
Space colonization (also called space settlement or extraterrestrial colonization) is the use of outer space or celestial bodies other than Earth for permanent habitation or as extraterrestrial territory. The inhabitation and territorial use of extraterrestrial space has been proposed to be realized by for example building space settlements or extraterrestrial mining enterprises. To date, no permanent space settlement other than temporary space habitats have been set up, nor any extraterrestrial territory or land has been legally claimed. Making territorial claims in space is prohibited by international space law, defining space as a common heritage. International space law has had the goal to prevent colonial claims and militarization of space, advocating the installation of international regimes to regulate access to and sharing of space, particularly for specific locations such as the limited space of geostationary orbit or the Moon. Many arguments both for and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
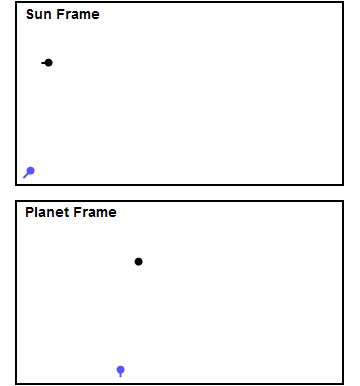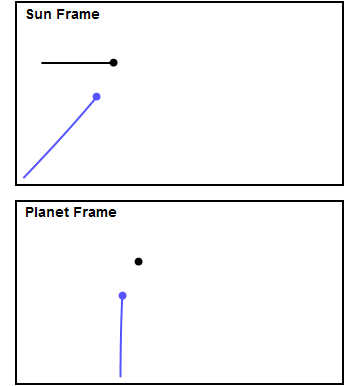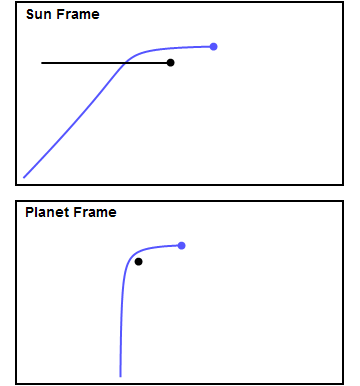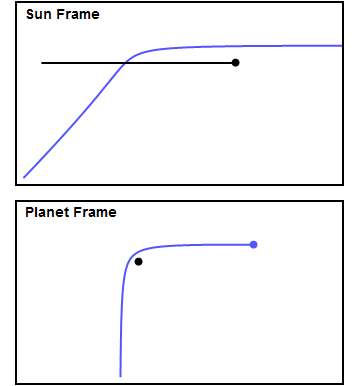
Gravity Assist
In orbital mechanics and aerospace engineering, a gravitational slingshot, gravity assist maneuver, or swing-by is the use of the relative movement (e.g. orbit around the Sun) and gravity of a planet or other astronomical object to alter the path and speed of a spacecraft, typically to save propellant and reduce expense. Gravity assistance can be used to accelerate a spacecraft, that is, to increase or decrease its speed or redirect its path. The "assist" is provided by the motion of the gravitating body as it pulls on the spacecraft. Any gain or loss of kinetic energy and velocity by a passing spacecraft is correspondingly lost or gained by the gravitational body, in accordance with Newton's Third Law. The gravity assist maneuver was first used in 1959 when the Soviet probe Luna 3 photographed the far side of Earth's Moon and it was used by interplanetary probes from Mariner 10 onward, including the two Voyager probes' notable flybys of Jupiter and Saturn. Explanation A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Vetchinkin
Vladimir Petrovich Vetchinkin (russian: Владимир Петрович Ветчинкин) (June 29, 1888 - March 6, 1950) was a Soviet Union, Soviet scientist in the field of aerodynamics, aeronautics, and Wind power, wind energy, Doctor of Sciences, Doctor of Technical Sciences (1927), Honored Science Worker of the RSFSR (1946). Biography Vladimir Petrovich was born in Kutno (then in the Russian division of Poland), the son of a Russian military officer. Vetchinkin graduated from Moscow Higher Technical School (MVTU) in 1915, the favorite student of Nikolay Zhukovsky (scientist), Nikolay Zhukovsky and generally viewed as his successor. In 1913, they had created a vortex-sheet theory of aircraft propellers. In 1916, Vetchinkin and Zhukovsky created the aviation calculation and test bureau in the wind-tunnel laboratory of the Moscow Higher Technical School, and in 1918 he helped found the Central Aerohydrodynamic Institute, Zhukovsky Central Institute of Aerodynamics (TsAGI). He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equation
In mathematics, an equation is a formula that expresses the equality of two expressions, by connecting them with the equals sign . The word ''equation'' and its cognates in other languages may have subtly different meanings; for example, in French an ''équation'' is defined as containing one or more variables, while in English, any well-formed formula consisting of two expressions related with an equals sign is an equation. ''Solving'' an equation containing variables consists of determining which values of the variables make the equality true. The variables for which the equation has to be solved are also called unknowns, and the values of the unknowns that satisfy the equality are called solutions of the equation. There are two kinds of equations: identities and conditional equations. An identity is true for all values of the variables. A conditional equation is only true for particular values of the variables. An equation is written as two expressions, connected by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konstantin Tsiolkovsky
Konstantin Eduardovich Tsiolkovsky (russian: Константи́н Эдуа́рдович Циолко́вский , , p=kənstɐnʲˈtʲin ɪdʊˈardəvʲɪtɕ tsɨɐlˈkofskʲɪj , a=Ru-Konstantin Tsiolkovsky.oga; – 19 September 1935) was a Russian and Soviet rocket scientist who pioneered astronautic theory. Along with the Frenchman Robert Esnault-Pelterie, the Germans Hermann Oberth and Fritz von Opel, and the American Robert H. Goddard, he is one of the founding fathers of modern rocketry and astronautics. His works later inspired leading Soviet rocket-engineers Sergei Korolev and Valentin Glushko, who contributed to the success of the Soviet space program. Tsiolkovsky spent most of his life in a log house on the outskirts of Kaluga, about southwest of Moscow. A recluse by nature, his unusual habits made him seem bizarre to his fellow townsfolk. Early life Tsiolkovsky was born in Izhevskoye (now in Spassky District, Ryazan Oblast), in the Russian Empire, to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Spaceflight
Spaceflight began in the 20th century following theoretical and practical breakthroughs by Konstantin Tsiolkovsky, Robert H. Goddard, and Hermann Oberth. First successful large-scale rocket programs were initiated in the 1920s Germany by Fritz von Opel and Max Valier, and eventually in Nazi Germany by Wernher von Braun. The Soviet Union took the lead in the post-war Space Race, launching the first satellite, the first man and the first woman into orbit. The United States caught up with, and then passed, their Soviet rivals during the mid-1960s, landing the first men on the Moon in 1969. In the same period, France, the United Kingdom, Japan and China were concurrently developing more limited launch capabilities. Following the end of the Space Race, spaceflight has been characterized by greater international co-operation, cheaper access to low Earth orbit and an expansion of commercial ventures. Interplanetary probes have visited all of the planets in the Solar System, and huma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spaceflight Books
Spaceflight (or space flight) is an application of astronautics to fly spacecraft into or through outer space, either with or without humans on board. Most spaceflight is uncrewed and conducted mainly with spacecraft such as satellites in orbit around Earth, but also includes space probes for flights beyond Earth orbit. Such spaceflight operates either by telerobotic or autonomous control. The more complex human spaceflight has been pursued soon after the first orbital satellites and has reached the Moon and permanent human presence in space around Earth, particularly with the use of space stations. Human spaceflight programs include the Soyuz, Shenzhou, the past Apollo Moon landing and the Space Shuttle programs, with currently the International Space Station as the main destination of human spaceflight missions while China's Tiangong Space Station is under construction. Spaceflight is used for placing in Earth's orbit communications satellites, reconnaissance satelli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1929 Non-fiction Books
Nineteen or 19 may refer to: * 19 (number), the natural number following 18 and preceding 20 * one of the years 19 BC, AD 19, 1919, 2019 Films * ''19'' (film), a 2001 Japanese film * ''Nineteen'' (film), a 1987 science fiction film Music * 19 (band), a Japanese pop music duo Albums * ''19'' (Adele album), 2008 * ''19'', a 2003 album by Alsou * ''19'', a 2006 album by Evan Yo * ''19'', a 2018 album by MHD * ''19'', one half of the double album ''63/19'' by Kool A.D. * ''Number Nineteen'', a 1971 album by American jazz pianist Mal Waldron * ''XIX'' (EP), a 2019 EP by 1the9 Songs * "19" (song), a 1985 song by British musician Paul Hardcastle. * "Nineteen", a song by Bad4Good from the 1992 album ''Refugee'' * "Nineteen", a song by Karma to Burn from the 2001 album ''Almost Heathen''. * "Nineteen" (song), a 2007 song by American singer Billy Ray Cyrus. * "Nineteen", a song by Tegan and Sara from the 2007 album '' The Con''. * "XIX" (song), a 2014 song by Slipknot. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |