|
The Clay Minerals Society
The Clay Minerals Society is an international non-profit organization devoted to the study of clays and clay minerals. History The Clay Minerals Society began as the Clay Minerals Committee of the National Academy of Sciences—National Research Council in 1952, in response to the need for a formal way to hold national clay conferences. By 1962, the Clay Minerals Committee had become strong enough to stand on its own, and The Clay Minerals Society was incorporated. From 1952 to 1964, Proceedings of the annual conferences were published. The journal Clays and Clay Minerals was first published in 1964. Position Statement The primary purpose of The Clay Minerals Society is to stimulate research and to disseminate information relating to all aspects of clay science and technology. Through its conferences and publications, the Society offers individuals a means of following the many-sided growth of the clay sciences and of meeting fellow scientists with widely different backgrou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clays
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4). Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay particles, but become hard, brittle and non–plastic upon drying or firing. Most pure clay minerals are white or light-coloured, but natural clays show a variety of colours from impurities, such as a reddish or brownish colour from small amounts of iron oxide. Clay is the oldest known ceramic material. Prehistoric humans discovered the useful properties of clay and used it for making pottery. Some of the earliest pottery shards have been dated to around 14,000 BC, and clay tablets were the first known writing medium. Clay is used in many modern industrial processes, such as paper making, cement production, and chemical filtering. Between one-half and two-thirds of the world's population live or work in buildings made with clay, often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petroleum Geologist
A petroleum geologist is an earth scientist who works in the field of petroleum geology, which involves all aspects of oil discovery and production. Petroleum geologists are usually linked to the actual discovery of oil and the identification of possible oil deposits, gas caps, or leads. It can be a very labor-intensive task involving several different fields of science and elaborate equipment. Petroleum geologists look at the structural and sedimentary aspects of the stratum/strata to identify possible oil traps or tight shale plays. Profile Petroleum geologists make the decision of where to drill for petroleum. This is done by locating prospects within a sedimentary basin. Petroleum geologists determine a prospect's viability looking at seven main aspects in conventional petroleum geology: * Source: the presence of an organic-rich source rock capable of generating hydrocarbons during deep burial. * Reservoir: the usually porous rock and permeable unit that collects the hydrocar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Societies
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology, and so is treated as one major aspect of integrated Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface, and the processes that have shaped that structure. It also provides tools to determine the relative and absolute ages of rocks found in a given location, and also to describe the histories of those rocks. By combining these tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole, and also to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and the Earth's past climates. Geologists broadly study the properties and processes of Earth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
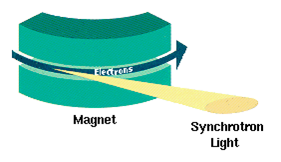
Synchrotron Radiation
Synchrotron radiation (also known as magnetobremsstrahlung radiation) is the electromagnetic radiation emitted when relativistic charged particles are subject to an acceleration perpendicular to their velocity (). It is produced artificially in some types of particle accelerators, or naturally by fast electrons moving through magnetic fields. The radiation produced in this way has a characteristic polarization and the frequencies generated can range over a large portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. Synchrotron radiation is similar to bremsstrahlung radiation, which is emitted by a charged particle when the acceleration is parallel to the direction of motion. The general term for radiation emitted by particles in a magnetic field is ''gyromagnetic radiation'', for which synchrotron radiation is the ultra-relativistic special case. Radiation emitted by charged particles moving non-relativistically in a magnetic field is called cyclotron emission. For particles in the mildly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellowstone National Park
Yellowstone National Park is an American national park located in the western United States, largely in the northwest corner of Wyoming and extending into Montana and Idaho. It was established by the 42nd U.S. Congress with the Yellowstone National Park Protection Act and signed into law by President Ulysses S. Grant on March 1, 1872. Yellowstone was the first national park in the U.S. and is also widely held to be the first national park in the world. The park is known for its wildlife and its many geothermal features, especially the Old Faithful geyser, one of its most popular. While it represents many types of biomes, the subalpine forest is the most abundant. It is part of the South Central Rockies forests ecoregion. While Native Americans have lived in the Yellowstone region for at least 11,000 years, aside from visits by mountain men during the early-to-mid-19th century, organized exploration did not begin until the late 1860s. Management and control of the park ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrochemical
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry concerned with the relationship between electrical potential difference, as a measurable and quantitative phenomenon, and identifiable chemical change, with the potential difference as an outcome of a particular chemical change, or vice versa. These reactions involve electrons moving via an electronically-conducting phase (typically an external electrical circuit, but not necessarily, as in electroless plating) between electrodes separated by an ionically conducting and electronically insulating electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). When a chemical reaction is driven by an electrical potential difference, as in electrolysis, or if a potential difference results from a chemical reaction as in an electric battery or fuel cell, it is called an ''electrochemical'' reaction. Unlike in other chemical reactions, in electrochemical reactions electrons are not transferred directly between atoms, ions, or molecules, but via the af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scanning Probe Microscopy
Scan may refer to: Acronyms * Schedules for Clinical Assessment in Neuropsychiatry (SCAN), a psychiatric diagnostic tool developed by WHO * Shared Check Authorization Network (SCAN), a database of bad check writers and collection agency for bad checks * Space Communications and Navigation Program (SCaN) * Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience (journal) * Scientific content analysis (SCAN), also known as statement analysis Businesses * Scan Furniture, Washington, D.C., US chain * SCAN Health Plan, not-for-profit health care company based in Long Beach, California * Scan AB or Scan Foods UK Ltd, the Swedish and UK subsidiaries of the Finnish HKScan Oyj * Seattle Community Access Network, Seattle, Washington, US TV channel * Scan (company), a software company based in Provo, Utah, US Electronics or computer related * 3D scanning * Counter-scanning, in physical micro and nanotopography measuring instruments like scanning probe microscope * Elevator algorithm (also SC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
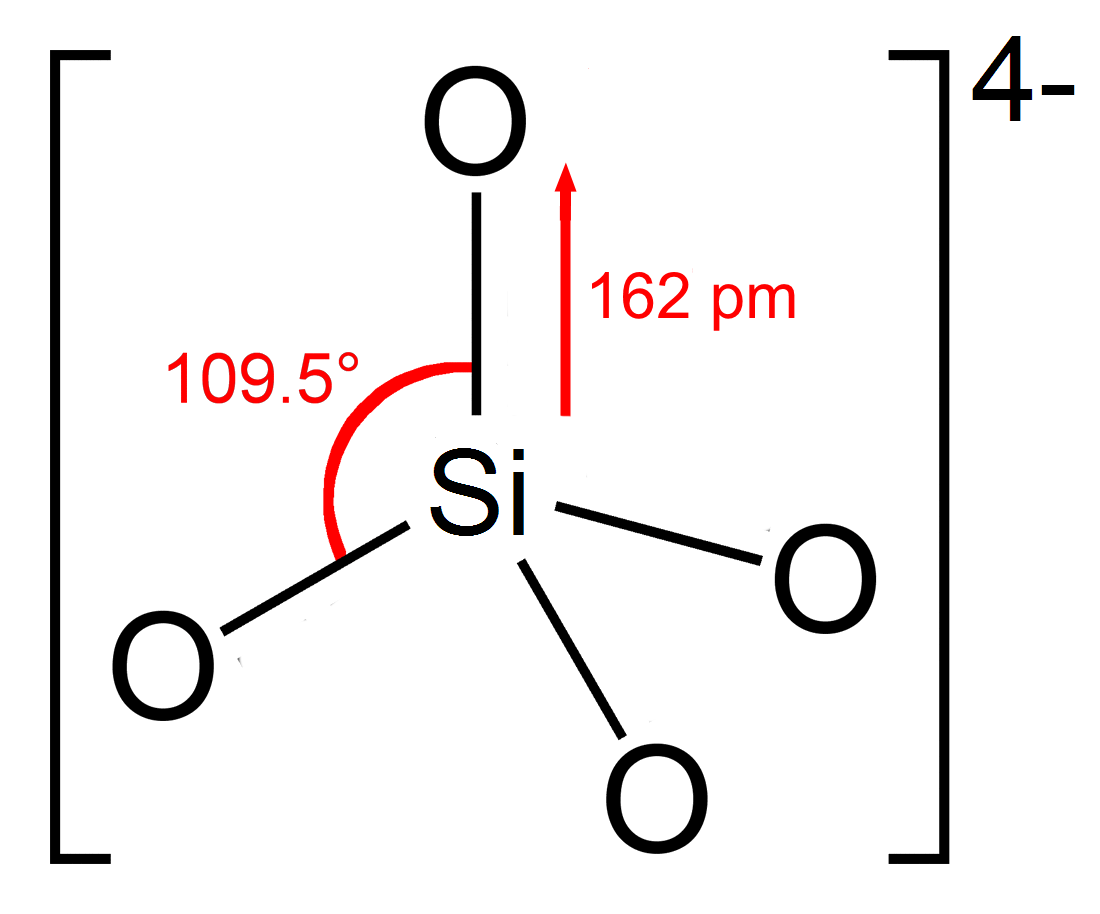
Silicate
In chemistry, a silicate is any member of a family of polyatomic anions consisting of silicon and oxygen, usually with the general formula , where . The family includes orthosilicate (), metasilicate (), and pyrosilicate (, ). The name is also used for any salt of such anions, such as sodium metasilicate; or any ester containing the corresponding chemical group, such as tetramethyl orthosilicate. The name "silicate" is sometimes extended to any anions containing silicon, even if they do not fit the general formula or contain other atoms besides oxygen; such as hexafluorosilicate .Most commonly, silicates are encountered as silicate minerals. For diverse manufacturing, technological, and artistic needs, silicates are versatile materials, both natural (such as granite, gravel, and garnet) and artificial (such as Portland cement, ceramics, glass, and waterglass). Structural principles In all silicates, silicon atom occupies the center of an idealized tetrahedron whose corner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Powder Diffraction
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz ( to ) and energies in the range 145 eV to 124 keV. X-ray wavelengths are shorter than those of UV rays and typically longer than those of gamma rays. In many languages, X-radiation is referred to as Röntgen radiation, after the German scientist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who discovered it on November 8, 1895. He named it ''X-radiation'' to signify an unknown type of radiation.Novelline, Robert (1997). ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. . Spellings of ''X-ray(s)'' in English include the variants ''x-ray(s)'', ''xray(s)'', and ''X ray(s)''. The most familiar use of X-rays is checking for fractures (broken bones), but X-rays are also used in other ways. For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheological
Rheology (; ) is the study of the flow of matter, primarily in a fluid (liquid or gas) state, but also as "soft solids" or solids under conditions in which they respond with plastic flow rather than deforming elastically in response to an applied force. Rheology is a branch of physics, and it is the science that deals with the deformation and flow of materials, both solids and liquids.W. R. Schowalter (1978) Mechanics of Non-Newtonian Fluids Pergamon The term ''rheology'' was coined by Eugene C. Bingham, a professor at Lafayette College, in 1920, from a suggestion by a colleague, Markus Reiner.The Deborah Number The term was inspired by the of |
Thermal Analysis
Thermal analysis is a branch of materials science where the properties of materials are studied as they change with temperature. Several methods are commonly used – these are distinguished from one another by the property which is measured: * Dielectric thermal analysis: dielectric permittivity and loss factor * Differential thermal analysis: temperature difference versus temperature or time * Differential scanning calorimetry: heat flow changes versus temperature or time * Dilatometer, Dilatometry: volume changes with temperature change * Dynamic mechanical analysis: measures storage modulus (stiffness) and loss modulus (damping) versus temperature, time and frequency * Evolved gas analysis: analysis of gases evolved during heating of a material, usually decomposition products * Isothermal titration calorimetry * Isothermal microcalorimetry * Laser flash analysis: thermal diffusivity and thermal conductivity * Thermogravimetric analysis: mass change versus temperature or time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mineralogical Society Of Great Britain And Ireland
The Mineralogical Society of Great Britain and Ireland began in 1876. Its main purpose is to disseminate scientific knowledge of the Mineral Sciences (mineralogy) as it may be applied to the fields of crystallography, geochemistry, petrology, environmental science and economic geology. In support of this vision, the society publishes scientific journals, books and monographs. It also organizes and sponsors scientific meetings, and the society connects with other societies which have similar scientific interests. Some of these other societies are the International Mineralogical Association, the European Mineralogical Union, the Mineralogical Society of America, the Mineralogical Association of Canada, the Geological Society of London, IOM3, the North of England Institute of Mining and Mechanical Engineers and the Microbiology Society. Publications The Society publishes a variety of book series; these are entitled the "Landmark Series", the "Mineralogical Society Special Seri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |