|
Thamnidium
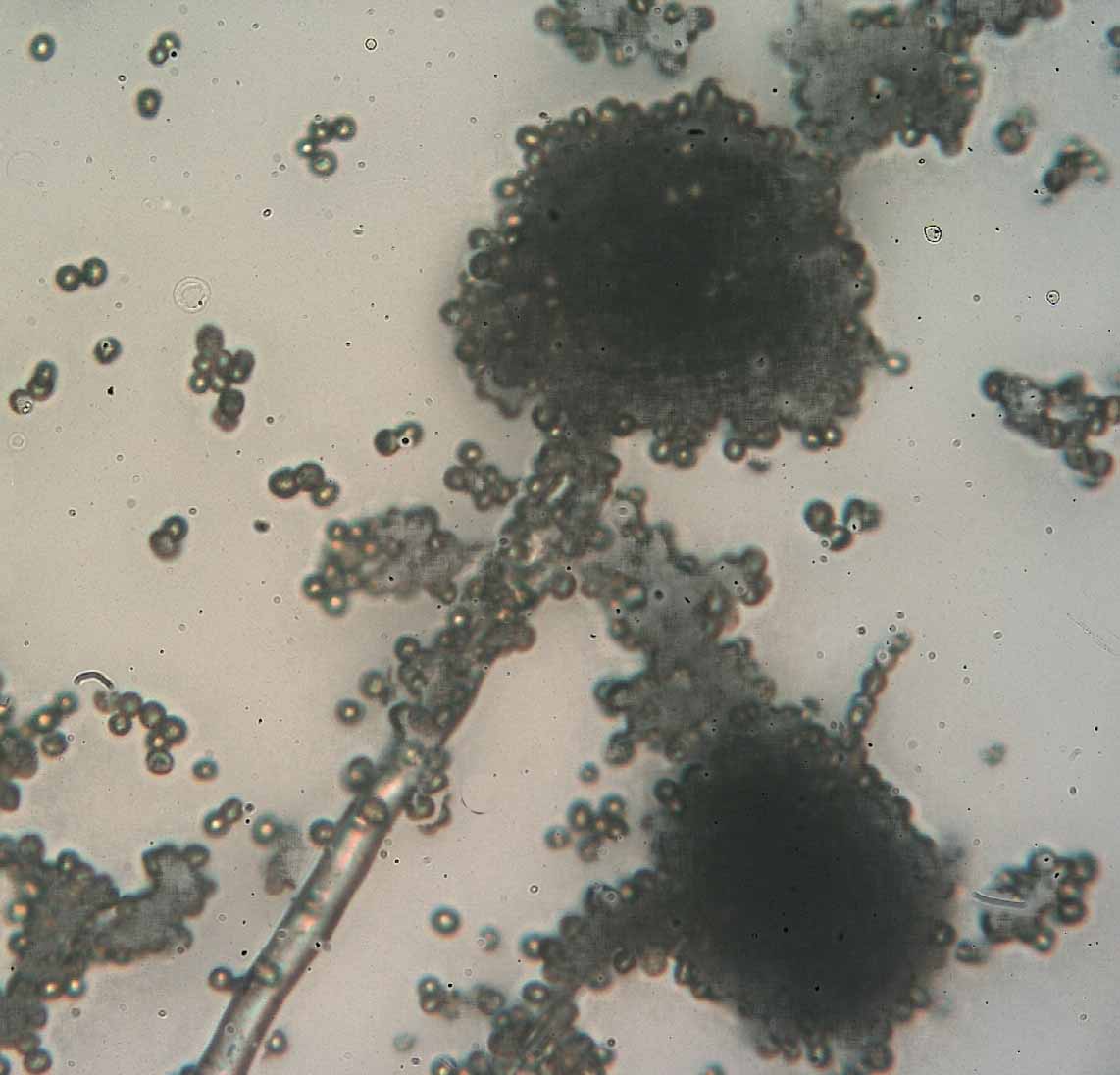
''Thamnidium'' is a genus of fungi belonging to the family Mucoraceae. The genus was circumscribed in 1809 by Johann Heinrich Friedrich Link. ''Thamnidium'' molds are key participants in the aging process for dry aged beef, producing protease and collagenase enzymes that naturally tenderize the meat. ''Thamnidium'' forms pale grey patches of mold called 'whiskers' on fatty areas of a carcass or cut during the aging process. The genus has also been implicated in the spoiling of meat in cold storage, alongside other fungal genera such as ''Acremonium'', ''Mucor'' and ''Rhizopus ''Rhizopus'' is a genus of common saprophytic fungi on plants and specialized parasites on animals. They are found in a wide variety of organic substances, including "mature fruits and vegetables", jellies, syrups, leather, bread, peanuts, and ...''. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q10694977 Mucoraceae Zygomycota genera Taxa named by Johann Heinrich Friedrich Link Taxa described in 1809 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thamnidium Ctenidium
''Thamnidium'' is a genus of fungi belonging to the family Mucoraceae. The genus was circumscribed in 1809 by Johann Heinrich Friedrich Link. ''Thamnidium'' molds are key participants in the aging process for dry aged beef, producing protease and collagenase enzyme Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ...s that naturally tenderize the meat. ''Thamnidium'' forms pale grey patches of mold called 'whiskers' on fatty areas of a carcass or cut during the aging process. The genus has also been implicated in the spoiling of meat in cold storage, alongside other fungal genera such as '' Acremonium'', '' Mucor'' and '' Rhizopus''. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q10694977 Mucoraceae Zygomycota genera Taxa named by Johann Heinrich Friedrich Link Taxa described in 1809 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thamnidium Elegans
''Thamnidium'' is a genus of fungi belonging to the family Mucoraceae. The genus was circumscribed in 1809 by Johann Heinrich Friedrich Link. ''Thamnidium'' molds are key participants in the aging process for dry aged beef, producing protease and collagenase enzyme Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ...s that naturally tenderize the meat. ''Thamnidium'' forms pale grey patches of mold called 'whiskers' on fatty areas of a carcass or cut during the aging process. The genus has also been implicated in the spoiling of meat in cold storage, alongside other fungal genera such as '' Acremonium'', '' Mucor'' and '' Rhizopus''. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q10694977 Mucoraceae Zygomycota genera Taxa named by Johann Heinrich Friedrich Link Taxa described in 1809 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thamnidium Anomalum
''Thamnidium'' is a genus of fungi belonging to the family Mucoraceae. The genus was circumscribed in 1809 by Johann Heinrich Friedrich Link. ''Thamnidium'' molds are key participants in the aging process for dry aged beef, producing protease and collagenase enzyme Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ...s that naturally tenderize the meat. ''Thamnidium'' forms pale grey patches of mold called 'whiskers' on fatty areas of a carcass or cut during the aging process. The genus has also been implicated in the spoiling of meat in cold storage, alongside other fungal genera such as '' Acremonium'', '' Mucor'' and '' Rhizopus''. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q10694977 Mucoraceae Zygomycota genera Taxa named by Johann Heinrich Friedrich Link Taxa described in 1809 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beef Aging
Beef aging (American English) or ageing is a process of preparing beef for consumption by aging it, in order to break down the connective tissue within the meat. Dry-aged beef Dry-aged beef is beef that has been hung or placed on a rack to dry for several weeks. After the animal is slaughtered and cleaned, it is hung as a full or half carcass. Primal (large distinct sections) or sub primal cuts, such as strip loins, rib eyes, and sirloin, are placed in a refrigerator unit, also known as a "hot box". This process involves considerable expense, as the beef must be stored near freezing temperatures. Subprimal cuts can be dry aged on racks either in specially climate-controlled coolers or within a moisture-permeable drybag. Moreover, only the higher grades of meat can be dry aged, as the process requires meat with a large, evenly distributed fat content. Because of this, dry-aged beef is seldom available outside of steak restaurants and upscale butcher shops or groceries. The key ef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucoraceae
The Mucoraceae are a family of fungi of the order Mucorales, characterized by having the thallus not segmented or ramified. Pathogenic genera include ''Absidia'', ''Apophysomyces'', ''Mucor'', ''Rhizomucor'', and ''Rhizopus''. According to a 2008 estimate, the family contains 25 genera and 129 species. Genera The family consists of the following genera: * '' Actinomucor'' * ''Apophysomyces'' * '' Benjaminiella'' * '' Chaetocladium'' * ''Circinella'' * ''Cokeromyces'' * ''Dicranophora'' * '' Ellisomyces'' * ''Helicostylum'' * '' Hyphomucor'' * '' Kirkomyces'' * ''Mucor'' * '' Parasitella'' * ''Pilaira'' * '' Pilophora'' * '' Pirella'' * ''Rhizomucor'' * '' Rhizopodopsis'' * ''Rhizopus'' * '' Sporodiniella'' * '' Syzygites'' * ''Thamnidium ''Thamnidium'' is a genus of fungi belonging to the family Mucoraceae. The genus was circumscribed in 1809 by Johann Heinrich Friedrich Link. ''Thamnidium'' molds are key participants in the aging process for dry aged beef, producing prote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygomycota Genera
Zygomycota, or zygote fungi, is a former division or phylum of the kingdom Fungi. The members are now part of two phyla: the Mucoromycota and Zoopagomycota. Approximately 1060 species are known. They are mostly terrestrial in habitat, living in soil or on decaying plant or animal material. Some are parasites of plants, insects, and small animals, while others form symbiotic relationships with plants. Zygomycete hyphae may be coenocytic, forming septa only where gametes are formed or to wall off dead hyphae. Zygomycota is no longer recognised as it was not believed to be truly monophyletic. Etymology The name ''Zygomycota'' refers to the zygosporangia characteristically formed by the members of this clade, in which resistant spherical spores are formed during sexual reproduction. ''Zygos'' is Greek for "joining" or "a yoke", referring to the fusion of two hyphal strands which produces these spores, and ''-mycota'' is a suffix referring to a division of fungi. Spores The term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhizopus
''Rhizopus'' is a genus of common saprophytic fungi on plants and specialized parasites on animals. They are found in a wide variety of organic substances, including "mature fruits and vegetables", jellies, syrups, leather, bread, peanuts, and tobacco. They are multicellular. Some ''Rhizopus'' species are opportunistic human pathogens that often cause fatal disease called mucormycosis. This widespread genus includes at least eight species. ''Rhizopus'' species grow as filamentous, branching hyphae that generally lack cross-walls (i.e., they are coenocytic). They reproduce by forming asexual and sexual spores. In asexual reproduction, sporangiospores are produced inside a spherical structure, the sporangium. Sporangia are supported by a large apophysate columella atop a long stalk, the sporangiophore. Sporangiophores arise among distinctive, root-like rhizoids. In sexual reproduction, a dark zygospore is produced at the point where two compatible mycelia fuse. Upon germination, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucor
''Mucor'' is a microbial genus of approximately 40 species of molds in the family Mucoraceae. Species are commonly found in soil, digestive systems, plant surfaces, some cheeses like Tomme de Savoie, rotten vegetable matter and iron oxide residue in the biosorption process. Description Colonies of this fungal genus are typically white to beige or grey and fast-growing. Colonies on culture medium may grow to several centimeters in height. Older colonies become grey to brown in color due to the development of spores. The species 'Mucor' belongs to the microbial kingdom: Fungi. ''Mucor'' spores or sporangiospores can be simple or branched and form apical, globular sporangia that are supported and elevated by a column-shaped columella. ''Mucor'' species can be differentiated from molds of the genera ''Absidia'', ''Rhizomucor'', and ''Rhizopus'' by the shape and insertion of the columella, and the lack of stolons and rhizoids. Some ''Mucor'' species produce chlamydospores. They fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acremonium
''Acremonium'' is a genus of fungi in the family Hypocreaceae. It used to be known as ''Cephalosporium''. Description ''Acremonium'' species are usually slow-growing and are initially compact and moist. Their hyphae are fine and hyaline, and produce mostly simple phialides. Their conidia are usually one-celled (i.e. ameroconidia), hyaline or pigmented, globose to cylindrical, and mostly aggregated in slimy heads at the apex of each phialide. ''Epichloë'' species are closely related and were once included in ''Acremonium'', but were later split off into a new genus ''Neotyphodium'', which has now been restructured within the genus ''Epichloë''. Clinical significance The genus ''Acremonium'' contains about 100 species, of which most are saprophytic, being isolated from dead plant material and soil. Many species are recognized as opportunistic pathogens of man and animals, causing eumycetoma, onychomycosis, and hyalohyphomycosis. Infections of humans by fungi of this genus are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Heinrich Friedrich Link
Johann Heinrich Friedrich Link (2 February 1767 – 1 January 1851) was a German naturalist and botanist. Biography Link was born at Hildesheim as a son of the minister August Heinrich Link (1738–1783), who taught him love of nature through collection of 'natural objects'. He studied medicine and natural sciences at the Hannoverschen Landesuniversität of Göttingen, and graduated as MD in 1789, promoting on his thesis ''"Flora der Felsgesteine rund um Göttingen"'' (Flora of the rocky beds around Göttingen). One of his teachers was the famous natural scientist Johann Friedrich Blumenbach (1752–1840). He became a private tutor (''Privatdozent'') in Göttingen. In 1792 he became the first professor of the new department of chemistry, zoology and botany at the University of Rostock. During his stay at Rostock, he became an early follower of the antiphlogistic theory of Lavoisier, teaching about the existence of oxygen instead of phlogiston. He was also a proponent of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collagenase
Collagenases are enzymes that break the peptide bonds in collagen. They assist in destroying extracellular structures in the pathogenesis of bacteria such as ''Clostridium''. They are considered a virulence factor, facilitating the spread of gas gangrene. They normally target the connective tissue in muscle cells and other body organs. Collagen, a key component of the animal extracellular matrix, is made through cleavage of pro-collagen by collagenase once it has been secreted from the cell. This stops large structures from forming inside the cell itself. In addition to being produced by some bacteria, collagenase can be made by the body as part of its normal immune response. This production is induced by cytokines, which stimulate cells such as fibroblasts and osteoblasts, and can cause indirect tissue damage. Therapeutic uses Collagenases have been approved for medical uses for: * treatment of Dupuytren's contracture and Peyronie's disease (Xiaflex). * wound healing (Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |