|
Thallane
Thallane (systematically named trihydridothallium) is an inorganic compound with the empirical chemical formula . It has not yet been obtained in bulk, hence its bulk properties remain unknown. However, molecular thallane has been isolated in solid gas matrices. Thallane is mainly produced for academic purposes. It is the simplest thallanes. Thallium is the heaviest member of the Group 13 metals; the stability of group 13 hydride Group 13 hydrides are chemical compounds containing group 13-hydrogen bonds (elements of group 13: boron, aluminium, gallium, indium, thallium). Trihydrides The simplest series has the chemical formula XH3, with X representing any of the boron fa ...s decreases with increasing periodic number. This is commonly attributed to poor overlap of the metal valence orbitals with that of the 1s orbital of Hydrogen. Despite encouraging early reports, it is unlikely that a thallane species has been isolated. Thallanes have been observed only in matrix isolation s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
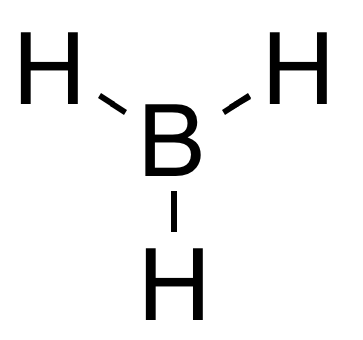
Group 13 Hydride
Group 13 hydrides are chemical compounds containing group 13-hydrogen bonds (elements of group 13: boron, aluminium, gallium, indium, thallium). Trihydrides The simplest series has the chemical formula XH3, with X representing any of the boron family. The great variety of boranes show a huge covalent cluster chemistry, but the heavier group 13 hydrides do not. Despite their formulae, however, they tend to form polymers. Alane(aluminum trihydride) is a strong reducing agent with octahedrally coordinated aluminium atoms. Gallane is even harder to synthesise and decomposes to gallium and hydrogen at room temperature. Indigane and thallane are too unstable to exist for any significant time when not coordinated. Simple MH3 group 13 hydrides have a trigonal planar molecular geometry. This is due to the sp2 hybridized center and vacant p-orbital, and contrasts with the trigonal pyramidal geometry of the pnictogen hydrides which are sp3 hybridized and contain a non-bonding lone pair o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inorganic Chemistry
Inorganic chemistry deals with synthesis and behavior of inorganic and organometallic compounds. This field covers chemical compounds that are not carbon-based, which are the subjects of organic chemistry. The distinction between the two disciplines is far from absolute, as there is much overlap in the subdiscipline of organometallic chemistry. It has applications in every aspect of the chemical industry, including catalysis, materials science, pigments, surfactants, coatings, medications, fuels, and agriculture. Key concepts Many inorganic compounds are ionic compounds, consisting of cations and anions joined by ionic bonding. Examples of salts (which are ionic compounds) are magnesium chloride MgCl2, which consists of magnesium cations Mg2+ and chloride anions Cl−; or sodium oxide Na2O, which consists of sodium cations Na+ and oxide anions O2−. In any salt, the proportions of the ions are such that the electric charges cancel out, so that the bulk compound is e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element is therefore not a compound. A compound can be transformed into a different substance by a chemical reaction, which may involve interactions with other substances. In this process, bonds between atoms may be broken and/or new bonds formed. There are four major types of compounds, distinguished by how the constituent atoms are bonded together. Molecular compounds are held together by covalent bonds; ionic compounds are held together by ionic bonds; intermetallic compounds are held together by metallic bonds; coordination complexes are held together by coordinate covalent bonds. Non-stoichiometric compounds form a disputed marginal case. A chemical formula specifies the number of atoms of each element in a compound molecule, using the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empirical Formula
In chemistry, the empirical formula of a chemical compound is the simplest whole number ratio of atoms present in a compound. A simple example of this concept is that the empirical formula of sulfur monoxide, or SO, would simply be SO, as is the empirical formula of disulfur dioxide, S2O2. Thus, sulfur monoxide and disulfur dioxide, both compounds of sulfur and oxygen, have the same empirical formula. However, their molecular formulas, which express the number of atoms in each molecule of a chemical compound, are not the same. An empirical formula makes no mention of the arrangement or number of atoms. It is standard for many ionic compounds, like calcium chloride (CaCl2), and for macromolecules, such as silicon dioxide (SiO2). The molecular formula, on the other hand, shows the number of each type of atom in a molecule. The structural formula shows the arrangement of the molecule. It is also possible for different types of compounds to have equal empirical formulas. Sampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Formula
In chemistry, a chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and ''plus'' (+) and ''minus'' (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include Subscript and superscript, subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical nomenclature, chemical name, and it contains no words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulae can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than chemical names and structural formulae. The simplest types of chemical formulae are called ''empirical formulae'', which use letters and numbers ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
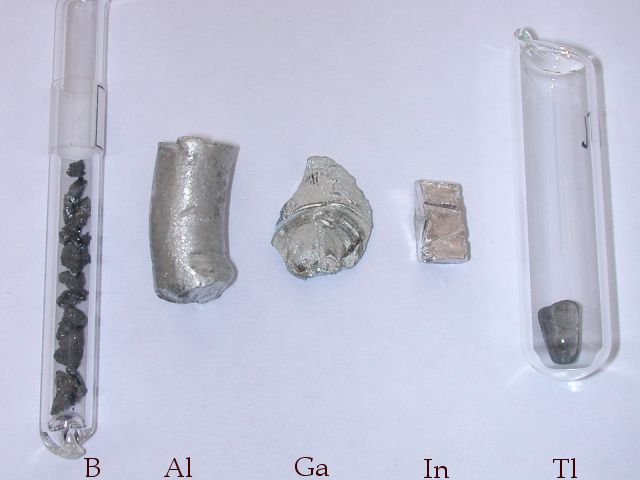
Boron Group
The boron group are the chemical elements in group 13 of the periodic table, comprising boron (B), aluminium (Al), gallium (Ga), indium (In), thallium (Tl), and nihonium (Nh). The elements in the boron group are characterized by having three valence electrons. These elements have also been referred to as the triels. Boron is commonly classified as a (metalloid) while the rest, with the possible exception of nihonium, are considered post-transition metals. Boron occurs sparsely, probably because bombardment by the subatomic particles produced from natural radioactivity disrupts its nuclei. Aluminium occurs widely on earth, and indeed is the third most abundant element in the Earth's crust (8.3%). Gallium is found in the earth with an abundance of 13 ppm. Indium is the 61st most abundant element in the earth's crust, and thallium is found in moderate amounts throughout the planet. Nihonium is not known to occur in nature and therefore is termed a synthetic element. Several group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lester Andrews
William Lester Self Andrews is an American chemist who makes contributions to the ongoing development of quantum chemistry of metallic complexes. He is the Professor Emeritus of Chemistry at the University of Virginia. He won the Earle K. Plyler Prize for Molecular Spectroscopy in 2010 for "vibrational spectroscopy in cryogenic matrices that combined with quantum calculations, has led to the identification and characterization of many molecules, ions, and complexes across the periodic table". He was born in Lincolnton, North Carolina. His first degree was in chemical engineering at Mississippi State University in 1963 and his doctorate was in physical chemistry at Berkeley Berkeley most often refers to: *Berkeley, California, a city in the United States **University of California, Berkeley, a public university in Berkeley, California * George Berkeley (1685–1753), Anglo-Irish philosopher Berkeley may also refer ... in 1966. References External links List of pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Synthesis
As a topic of chemistry, chemical synthesis (or combination) is the artificial execution of chemical reactions to obtain one or several products. This occurs by physical and chemical manipulations usually involving one or more reactions. In modern laboratory uses, the process is reproducible and reliable. A chemical synthesis involves one or more compounds (known as '' reagents'' or ''reactants'') that will experience a transformation when subjected to certain conditions. Various reaction types can be applied to formulate a desired product. This requires mixing the compounds in a reaction vessel, such as a chemical reactor or a simple round-bottom flask. Many reactions require some form of processing (" work-up") or purification procedure to isolate the final product. The amount produced by chemical synthesis is known as the ''reaction yield''. Typically, yields are expressed as a mass in grams (in a laboratory setting) or as a percentage of the total theoretical quantity that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal Hydrides
In chemistry, a hydride is formally the anion of hydrogen( H−). The term is applied loosely. At one extreme, all compounds containing covalently bound H atoms are called hydrides: water (H2O) is a hydride of oxygen, ammonia is a hydride of nitrogen, etc. For inorganic chemists, hydrides refer to compounds and ions in which hydrogen is covalently attached to a less electronegative element. In such cases, the H centre has nucleophilic character, which contrasts with the protic character of acids. The hydride anion is very rarely observed. Almost all of the elements form binary compounds with hydrogen, the exceptions being He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Pm, Os, Ir, Rn, Fr, and Ra. Exotic molecules such as positronium hydride have also been made. Bonds Bonds between hydrogen and the other elements range from highly to somewhat covalent. Some hydrides, e.g. boron hydrides, do not conform to classical electron-counting rules and the bonding is described in terms of multi-centered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thallium(III) Compounds
Thallium is a chemical element with the symbol Tl and atomic number 81. It is a gray post-transition metal that is not found free in nature. When isolated, thallium resembles tin, but discolors when exposed to air. Chemists William Crookes and Claude-Auguste Lamy discovered thallium independently in 1861, in residues of sulfuric acid production. Both used the newly developed method of flame spectroscopy, in which thallium produces a notable green spectral line. Thallium, from Greek , , meaning "green shoot" or "twig", was named by Crookes. It was isolated by both Lamy and Crookes in 1862; Lamy by electrolysis, and Crookes by precipitation and melting of the resultant powder. Crookes exhibited it as a powder precipitated by zinc at the international exhibition, which opened on 1 May that year. Thallium tends to form the +3 and +1 oxidation states. The +3 state resembles that of the other elements in group 13 ( boron, aluminium, gallium, indium). However, the +1 state, which is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |