|
Thagyamin At Shwedagon Pagoda.jpg
Thagyamin ( my, သိကြားမင်း, ; from Sanskrit ''Śakra'') is the highest-ranking nat (deity) in traditional Burmese Buddhist belief. Considered as the king of Heaven, he is the Burmese adaptation of the Hindu deity Indra. Etymology Thagyamin () is derived from the combination of the Sanskrit word " Shakra" (शक्र; a synonym of Indra) and the Burmese word "Min" (; a common title meaning Lord/King). He is also known by his nickname ''U Magha'' () derived from his preexistential name. Description Thagyamin is often portrayed as holding a conch shell in one hand, and a yak-tail fly-whisk in the other, and seated or standing atop a three-headed white elephant ( Airavata). He is described as the ruler of the celestial kingdom Trāyastriṃśa (). He was designated as the supreme deity of the official pantheon of 37 ''ahtet nat'' (အထက်နတ်, upper deities) by King Anawrahta in the 11th century, in an effort to streamline animist and Hin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Śakra (Buddhism)
Śakra (Sanskrit: शक्र Śakra; Pali: सक्क Sakka) is the ruler of the Trāyastriṃśa Heaven according to Buddhist cosmology. He is also referred to by the title "Śakra, Lord of the Devas" (Sanskrit: '; Pali: '). The name Śakra ("powerful") as an epithet of Indra is found in several verses of the Rigveda. In East Asian cultural traditions, Śakra is known as ''Dìshìtiān'' (帝釋天) or ''Shìtí Huányīn'' (釋提桓因) in Chinese, as ''Taishakuten'' (帝釈天) in Japanese, as ''Jeseokcheon'' (제석천) in Korean, and as ''Đế Thích Thiên'' (帝釋天) or ''Thích Đề Hoàn Nhân'' (釋提桓因) in Vietnamese. In Chinese Buddhism, Śakra is sometimes identified with the Taoist Jade Emperor (Yùhuáng Dàdì 玉皇大帝, often simplified to Yùhuáng 玉皇); both share a birthday on the ninth day of the first lunar month of the Chinese calendar (usually in February). The Trāyastriṃśa heaven in which Śakra rules is located on the top of Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sujā
Indrani (Sanskrit: इन्द्राणी, IAST: ''Indrāṇī, lit.'' Indra's queen), also known as Shachi (Sanskrit: शची, IAST: ''Śacī''), is the queen of the devas in Hinduism. Described as tantalisingly beautiful, proud and kind, she is the daughter of the asura Puloman and the consort of the king of the devas, Indra. According to legend, due to her heavenly beauty and sensuality, Indrani was desired by many men, many of whom tried to marry her. When Indra was away performing his penance for the slaying of Vritasura, Nahusha, a mortal king of the Lunar dynasty, was chosen as the ruler of heaven. The latter tried to seduce Shachi and make her his queen, though she cleverly executed a scheme to dethrone him and later reunite with her husband. She is an important goddess in Shaktism, a major sect of Hinduism. Indrani (or Aindri) is one of the Sapta Matrika—the seven divine mothers. She is worshipped in South India as an independent deity, and is most often wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nat (deity)
The nats (; MLCTS: ''nat''; ) are god-like spirits venerated in Myanmar and neighbouring countries in conjunction with Buddhism. They are divided between the 37 ''Great Nats'' who were designated that status by King Anawrahta when he formalized the official list of nats. Most of the 37 ''Great Nats'' were human beings who met violent deaths. There are two types of ''nats'' in Burmese Belief: ''nat sein'' () which are humans that were deified after their deaths and all the other nats which are spirits of nature (spirits of water, trees etc.). Much like sainthood, ''nats'' can be designated for a variety of reasons, including those only known in certain regions in Burma. ''Nat'' worship is less common in urban areas than in rural areas and is practised among ethnic minorities of Myanmar as well as in mainstream Bamar society. However, it is among the Theravada Buddhist Bamar that the most highly developed form of ceremony and ritual is seen. Every Burmese village has a ''nat kun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perun
In Slavic mythology, Perun (Cyrillic: Перýн) is the highest god of the pantheon and the god of sky, thunder, lightning, storms, rain, law, war, fertility and oak trees. His other attributes were fire, mountains, wind, iris, eagle, firmament (in Indo-European languages, this was joined with the notion of the ''sky of stone''), horses and carts, and weapons (hammer, axe (Axe of Perun), and arrow). He was first associated with weapons made of stone and later with those of metal. Sources Of all historic records describing Slavic gods, those mentioning Perun are the most numerous. As early as the 6th century, he was mentioned in '' De Bello Gothico'', a historical source written by the Eastern Roman historian Procopius. A short note describing beliefs of a certain South Slavic tribe states they ''acknowledge that one god, creator of lightning, is the only lord of all: to him do they sacrifice an ox and all sacrificial animals.'' While the name of the god is not mentioned her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
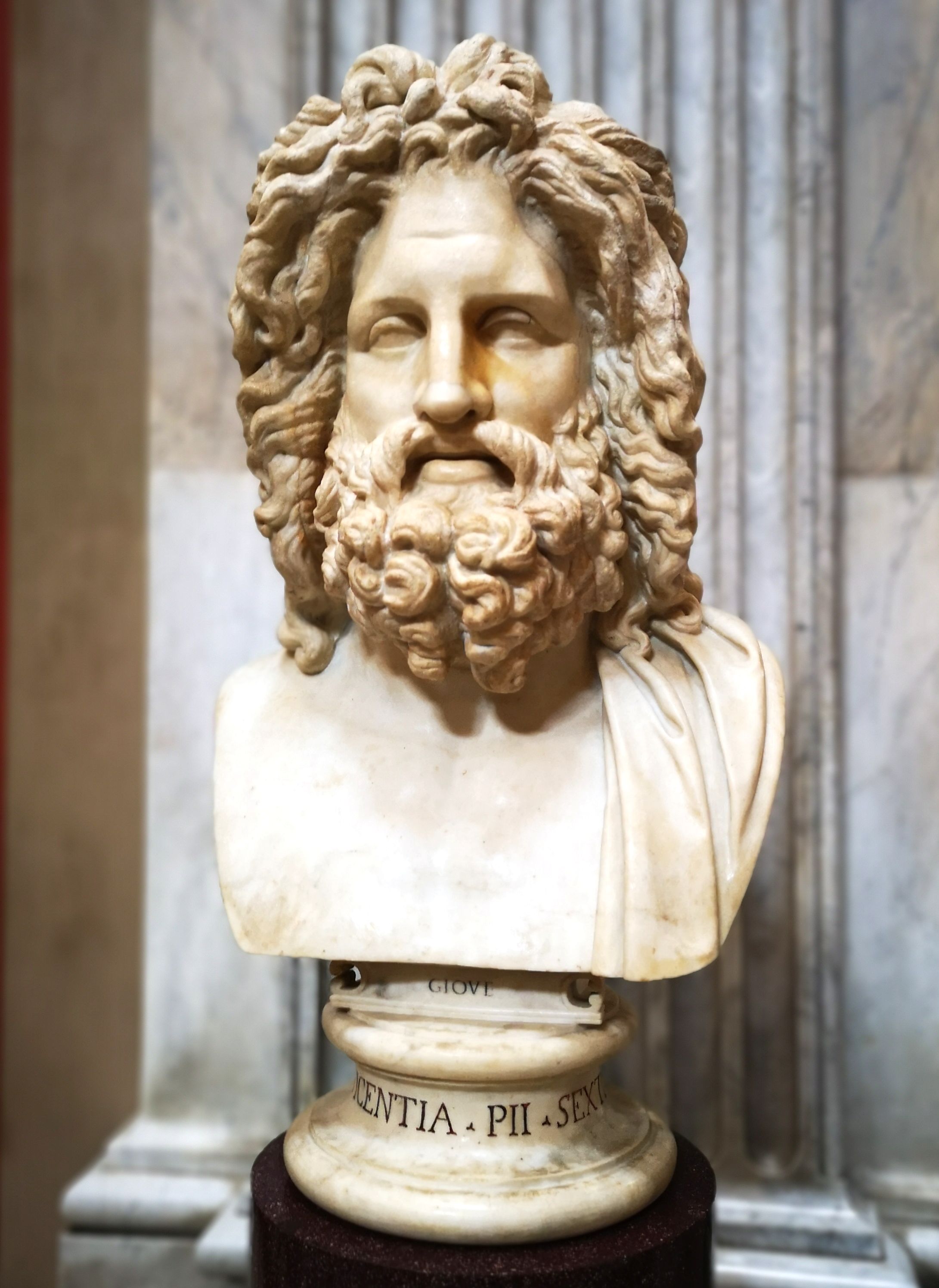
Jupiter (mythology)
Jupiter ( la, Iūpiter or , from Proto-Italic language, Proto-Italic "day, sky" + "father", thus "sky father" Greek: Zeus, Δίας or Zeus, Ζεύς), also known as Jove (genitive case, gen. ''Iovis'' ), is the sky god, god of the sky and god of thunder, thunder, and Pantheon (gods), king of the gods in ancient Roman religion and Roman mythology, mythology. Jupiter was the chief deity of Roman state religion throughout the Roman Republic, Republican and Roman Empire, Imperial eras, until Constantine the Great and Christianity, Christianity became the dominant religion of the Empire. In Roman mythology, he negotiates with Numa Pompilius, the second king of Rome, to establish principles of Roman religion such as offering, or sacrifice. Jupiter is usually thought to have originated as a sky god. His identifying implement is the thunderbolt and his primary sacred animal is the eagle, which held precedence over other birds in the taking of auspices and became one of the most comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thor
Thor (; from non, Þórr ) is a prominent god in Germanic paganism. In Norse mythology, he is a hammer-wielding æsir, god associated with lightning, thunder, storms, sacred trees and groves in Germanic paganism and mythology, sacred groves and trees, Physical strength, strength, the protection of humankind, hallowing, and fertility. Besides Old Norse , the deity occurs in Old English as , in Old Frisian as ', in Old Saxon as ', and in Old High German as , all ultimately stemming from the Proto-Germanic theonym , meaning 'Thunder'. Thor is a prominently mentioned god throughout the recorded history of the Germanic peoples, from the Roman Empire, Roman occupation of regions of , to the Germanic expansions of the Migration Period, to his high popularity during the Viking Age, when, in the face of the process of the Christianization of Scandinavia, emblems of his hammer, , were worn and Norse paganism, Norse pagan personal names containing the name of the god bear witness to his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeus
Zeus or , , ; grc, Δῐός, ''Diós'', label=Genitive case, genitive Aeolic Greek, Boeotian Aeolic and Doric Greek#Laconian, Laconian grc-dor, Δεύς, Deús ; grc, Δέος, ''Déos'', label=Genitive case, genitive el, Δίας, ''Días'' () is the sky father, sky and thunder god in ancient Greek religion, who rules as king of the gods on Mount Olympus. His name is cognate with the first element of his ancient Roman religion, Roman interpretatio graeca, equivalent Jupiter (mythology), Jupiter.''Larousse Desk Reference Encyclopedia'', The Book People, Haydock, 1995, p. 215. His mythology and powers are similar, though not identical, to those of Indo-European deities such as Jupiter, Perkūnas, Perun, Indra, Dyaus, and Zojz (deity), Zojz. Entry: "Dyaus" Zeus is the child of Cronus and Rhea (mythology), Rhea, the youngest of his siblings to be born, though sometimes reckoned the eldest as the others required disgorging from Cronus's stomach. In most traditions, he is m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jataka Tales
The Jātakas (meaning "Birth Story", "related to a birth") are a voluminous body of literature native to India which mainly concern the previous births of Gautama Buddha in both human and animal form. According to Peter Skilling, this genre is "one of the oldest classes of Buddhist literature."Skilling, Peter (2010). ''Buddhism and Buddhist Literature of South-East Asia,'' pp. 161-162. Some of these works are also considered great works of literature in their own right. In these stories, the future Buddha may appear as a king, an outcast, a deva, an animal—but, in whatever form, he exhibits some virtue that the tale thereby inculcates. Often, Jātaka tales include an extensive cast of characters who interact and get into various kinds of trouble - whereupon the Buddha character intervenes to resolve all the problems and bring about a happy ending. The Jātaka genre is based on the idea that the Buddha was able to recollect all his past lives and thus could use these memorie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indra's Net
Indra's net (also called Indra's jewels or Indra's pearls, Sanskrit ''Indrajāla'', Chinese: 因陀羅網) is a metaphor used to illustrate the concepts of Śūnyatā (emptiness), pratītyasamutpāda (dependent origination),. and interpenetration in Buddhist philosophy. The metaphor's earliest known reference is found in the Atharva Veda. It was further developed by the Mahayana school in the 3rd century '' Buddhāvataṃsaka Sūtra'' and later by the Huayan school between the 6th and 8th centuries. In the ''Buddhāvataṃsaka Sūtra'' "Indra's net" is an infinitely large net owned by the Vedic deva Indra, which hangs over his palace on Mount Meru, the axis mundi of Buddhist and Hindu cosmology. In East Asian Buddhism, Indra's net is considered as having a multifaceted jewel at each vertex, with each jewel being reflected in all of the other jewels. In the Huayan school of Chinese Buddhism, which follows the ''Buddhāvataṃsaka Sūtra'', the image of "Indra's net" is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
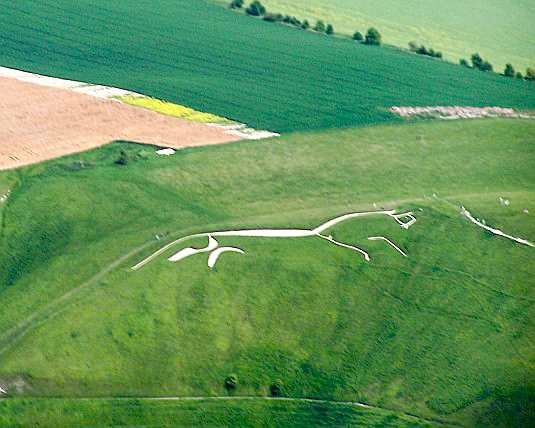
White Horse (mythology)
White horses have a special significance in the mythologies of cultures around the world. They are often associated with the sun chariot,''The Complete Dictionary of Symbols'' by Jack Tresidder, Chronicle Books, 2005, , page 241Google books copy/ref> with warrior-heroes, with fertility (in both mare and stallion manifestations), or with an end-of-time saviour, but other interpretations exist as well. Both truly white horses and the more common grey horses, with completely white hair coats, were identified as "white" by various religious and cultural traditions. Portrayal in myth From earliest times, white horses have been mythologised as possessing exceptional properties, transcending the normal world by having wings (e.g. Pegasus from Greek mythology), or having horns (the unicorn). As part of its legendary dimension, the white horse in myth may be depicted with seven heads ( Uchaishravas) or eight feet (Sleipnir), sometimes in groups or singly. There are also white horse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)